Coronary Blood Flow Regulation Mechanisms
Explore the intricate control of coronary blood flow through autoregulation, metabolic theory, myogenic theory, pressure gradients, and neural factors. Discover the role of local chemical and neural factors in maintaining optimal blood flow in the coronary vessels.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
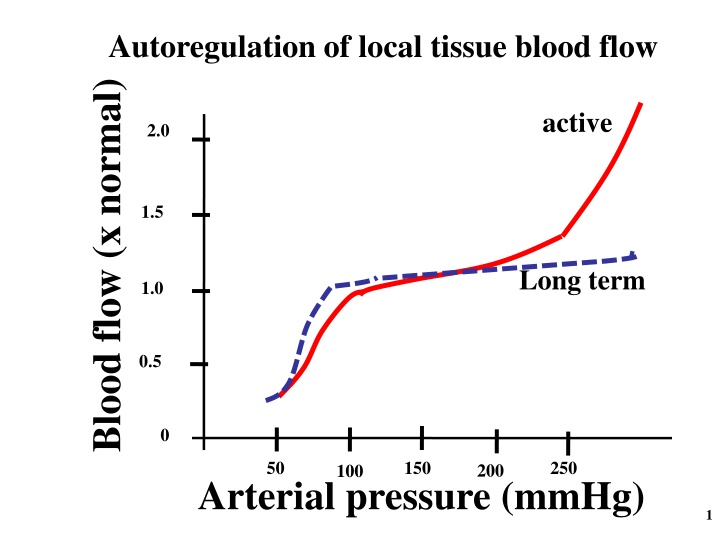
Autoregulation of local tissue blood flow Blood flow (x normal) active 2.0 1.5 Long term 1.0 0.5 0 50 150 250 200 100 Arterial pressure (mmHg) 1
1. The metabolic theory. blood flow vasodilator substances vasodilatation blood flow Wash off vasodilator substances vasoconstriction 2
2. The myogenic theory Smooth muscle Lumen
Coronary circulation Aorta Lt coronary A. Circumflex A. Rt coronary A. Lt ant. Descending A. 225 ml/min 4 -5 % of CO
Pressure gradients & flow in the coronary vessels Pressure (mmHg) Pressure difference During systole During diastole Left vent right vent Left vent right vent aorta 120 120 80 0 121 25 120 121 25 1 - 95 systole Left ventricle Right ventricle Both ventricles 0 80 0 80 80 diastole
Control of Coronary Blood Flow Local chemical factors Neural factors Adenosine potassium ions hydrogen ions carbon dioxide bradykinin SNS PNS
Neural factors Parasympathetic Sympathetic direct effects indirect effects direct effects indirect effects
sympathetic direct effects indirect effects HR Vasoconstriction contractility metabolic rate Vasodilatation
Parasympathetic direct effects indirect effects HR Vasodilatation slightly contractility metabolic rate Vasoconstriction
