Coronary Circulation: Heart's Blood Supply & Flow
Coronary circulation is vital for supplying the heart muscle with oxygenated blood. This system comprises arteries, veins, and factors that regulate blood flow. The two main coronary arteries, the right and left coronary arteries, branch out to provide oxygen-rich blood to different parts of the heart muscle. Venous drainage ensures the removal of deoxygenated blood. Phasic changes in coronary blood flow are influenced by the cardiac cycle, with blood flow fluctuations between systole and diastole. Factors like oxygen demand, metabolic factors, and coronary perfusion pressure play crucial roles in regulating coronary blood flow. Understanding these aspects is essential for grasping the complex network that sustains heart health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CORONARY CIRCULATION - By Fuldona Pandit
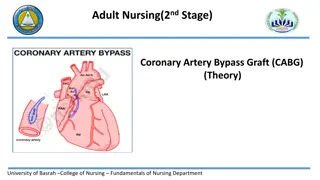
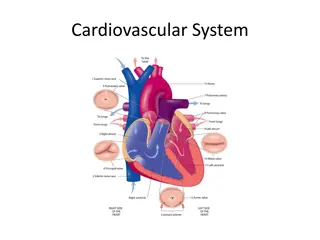
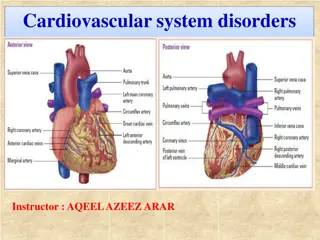
CORONARY CIRCULATION Heart muscle is supplied by two coronary arteries. Right coronary artery supplies whole of the right ventricle and posterior portion of left ventricle. Left coronary artery supplies mainly the anterior and lateral parts of left ventricle. Coronary arteries divide and subdivide into smaller branches, which run all along the surface of the heart. Smaller branches are called epicardiac arteries and give rise to further smaller branches known as final arteries or intramural vessels.
Venous drainage from heart muscle is by three types of vessels. 1. Coronary Sinus drains blood from left side of the heart and opens into right atrium near tricuspid valve. 2. Anterior Coronary Veins drain blood from right side of the heart and open directly into right atrium. 3. Thebesian Veins drain deoxygenated blood from myocardium, directly into the concerned chamber of the heart.
PHASIC CHANGES IN CORONARY BLOOD FLOW Blood flow through coronary arteries is not constant. It decreases during systole and increases during diastole. In left ventricle, during the onset of isometric contraction, blood flow declines sharply due to two reasons, namely increase in myocardial tissue pressure and decrease in aortic pressure. A small amount of blood flows into right ventricle during systole. It is because the force of contraction is not as severe as in the case of left ventricle.
FACTORS REGULATING CORONARY BLOOD FLOW Like any other organ, heart also has the capacity to regulate its own blood flow by autoregulation. Coronary blood flow is regulated mainly by local vascular response to the needs of cardiac muscle. Factors regulating coronary blood flow: 1. Need for oxygen : Amount of blood passing through coronary circulation is directly proportional to the consumption of oxygen by cardiac muscle. 2. Metabolic factors : Coronary vasodilatation during hypoxic conditions occurs because of some metabolic products, which increase the coronary blood flow by vasodilatation.
3. Coronary Perfusion Pressure : coronary perfusion pressure is the balance between mean arterial pressure in aorta and the right atrial pressure. Since right aterial pressure is low, the mean arterial pressure becomes the major factor that maintains the coronary blood flow. 4. Nervous Factors : Coronary blood vessels are innervated both by para-sympathetic and sympathetic divisions of autonomic nervous system. these nerves influence the coronary blood flow indirectly by acting on the musculature of heart.
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the heart disease that is caused by inadequate blood supply to cardiac muscle due to occlusion of coronary artery. It is also called coronary heart disease. Coronary occlusion Myocardial ischemia & Necrosis Myocardial infarction Cardiac pain - Angina pectoris