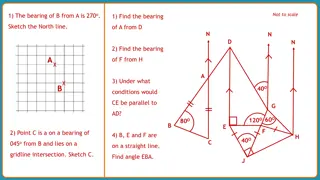
Coterminal & Reference Angles
In mathematics, coterminal and reference angles play crucial roles in trigonometry. Coterminal angles have the same terminal side, while reference angles help simplify calculations. Discover formulas, examples, and practical applications in this comprehensive guide.
Uploaded on Apr 16, 2025 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Reference and Coterminal Angles
What are coterminal angles? These are two or more angles in standard position with the same terminal side. Standard position is where the vertex is at the origin and the initial side along the positive x-axis. These angles are found by taking the measure of the angle, and adding multiples of 360 degrees or 2 . Every angle has infinite coterminal angles.
Coterminal angles example Image source: Coterminal Angles
What is a reference angle? This is the acute angle formed by the terminal side of the given angle and the X-axis. This is only if the angle is not one of the four quadrantal angles (90 , 180 , 270 , 360 ). If the angle is greater than 360 , or less than 0 , the reference angle can be found by using a coterminal angle.
Reference angle example Image source: Reference Angles
Reference Angle Formulas Quadrant 1 = Actual Quadrant 2 = 180 Angle in radians = Angle Quadrant 3 = Angle 180 in radians = Angle Quadrant 4 = 360 angle in radians = 2 angle
Example 1 Q: If the angle measure is 50 in standard position, find one coterminal angle. A: 50 + 360 = 410
Example 2 Q: If the angle measure is 110 in standard position, find the reference angle. A: 180 110 = 70
Example 3 Q: If the angle measure is 120 , find the one coterminal angle and reference. A: 120 + 360 = 240 (coterminal) 240 180 = 60 (reference)
Example 4 Q: If the angle measure is 279 , find two coterminal angles and the reference angle. A: 279 + 360 = 639 (coterminal) 279 + (360(2)) = 999 (coterminal) 360 279 = 81 (reference)
Extra Examples: Determine a positive and negative coterminal angle. 1. 500 500 360 = 140 360 = 140 220
Extra Examples: 2. 7? 5 7? 5 + 2? = 7? 5 + 10? 17? 5 5 = 7? 5 2? = 3? 7? 5 10? 5 5 =
Extra Examples: Find the reference angle. 3. 60 60 4. 400 400 360 = 40 5. 160 Quadrant: II 180 160 = 20