Covalent Bonds and Lewis Dot Structures
Learn about the concept of covalent bonds where electrons are shared between nonmetal atoms, as well as Lewis Dot structures illustrating electron sharing. Explore examples like H2O, CO2, and C6H12O6, and understand how to create Lewis Dot structures for different molecules.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
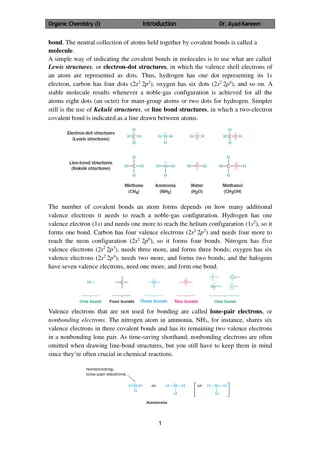
Electrons are shared between 2 or more nonmetal atoms. Can also be between a nonmetal and a metalloid. Ex: H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 All nonmetal atoms! EN value less than 1.5
Can be solid, liquid, or gas at room temp. Low melting and boiling points Cannot conduct electricity Insoluble in water Polar Covalent bonds electrons shared unequally (EN difference 0.5 1.5) Nonpolar Covalent bonds electrons shared equally (EN difference 0 0.5) Compounds are called molecules Creates partial + and ends
Lewis Dot Structures Octet Rule: All atoms will form bonds in order to have full (8) valence electrons. Except Hydrogen (2) 1. Arrange element symbols so that first atom is in the middle. 2. Draw Lewis dot structures for each element. 3. Circle electrons that will be shared between atoms. 4. Re-draw atoms with lines as shared electrons. Cl Cl Ex: CCl4 Cl C Cl C Cl Cl Cl Cl
Covalent Bonds between 2 elements can vary! 1 pair of valence electrons shared = SINGLE bond 2 pairs shared = DOUBLE bond 3 pairs shared = TRIPLE bond
Add in these examples under doc camera. H2O N2 NH3 HF CO2
1. List the prefix and name of 1st element. Don t use mono on 1st element! 2. Prefix and name of 2nd element + -ide ending. Prefixes 1 = mono 2 = di 3 = tri 4 = tetra 5 = penta Examples CO2 S2O3 N4F CO Carbon monoxide 6 = hexa 7 = hepta 8 = octa 9 = nona 10 = deca Carbon dioxide Disulfur trioxide Tetranitrogen monofluoride
1. Write the symbol of the first element and subscript to match the prefix. 2. Repeat for 2nd element. DO NOT SIMPLIFY SUBSCRIPTS! Diatomic elements: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 Ex: Triphosphorus pentachloride P3Cl5 Ex: Tricarbon hexasulfide C3S6 Ex: Antimony tetrabromide SbBr4
Lewis Dot Sharing Draw the Lewis Dot structures and show the SHARING of unpaired electrons by circling. Then show the structural formula. 1. C2H4 2. CH4 3. N2 4. HCl 7. S2 5. CO2 6. CCl4 8. F2
Recap of Covalent Bonding!
Example: C2H4 Dicarbon tetrahydride
Example: C2O4 Dicarbon tetroxide
Example: Cl2O2 Dichlorine dioxide