Curriculum Components & Development Overview
Overview of curriculum components, development, and evaluation in education. Explore curriculum foundations, learning objectives, syllabus content, and the role of curriculum in teaching and assessment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Curriculum, components, development and evaluation Dr. Farzana Mahdi Professor Department of Biochemistry farzana.mahdi@gmail.com
Curriculum Learning Objectives After this interaction, learner should be able to- -- Define and explain the concept of curriculum -- Enumerate curriculum foundations and components -- Explain the curriculum in his/her own subject area -- Discuss the importance and need for curriculum evaluation
Definition Curriculum is a plan of action which incorporates the learning outcomes to be attained over a period of time by exposing the learner to various learning experiences
What is a Curriculum? ? A statement of learning objectives ? A statement of learning experiences ? A statement of learning outcomes ? A listing of the subject matter (syllabus)
WHAT IS CURRICULUM? Intended aims & objectives, content, experiences, outcomes and processes of the educational programme Entry Flexibilities requirements Education structure Assessment system Length Programme organisation CURRICULUM Syllabus content: Knowledge, skills, attitudes, expertise to be achieved. Expected methods of learning, teaching, feedback and supervision.
Curriculum Latin word means Race- course What it denotes?
It denotes Path to be followed Frame within which it has to be followed
? Curriculum Provides direction to both teachers as well as students Assists in selection of appropriate learning resource material Helps to adopt appropriate teaching-learning activities Helps in designing appropriate assessment tools Ultimately helps designing relevant and efficient educational programme
Curriculum Student What to learn *Content How to learn *Educational strategy Teaching Learning tools Assessment Educational Enviornment Learning Outcome
Models of curriculum Development The Tyler model The Taba Model The Saylor and Alexander Model The Goodlad Model The Hunkins Model The Miller and Seller Model The Zais Model
Zais Model Needs knowledge of A Curriculum foundations B Curriculum components
Curriculum foundations Answer of four basic questions give desired shape to curriculum Why a subject is being taught? Who is being taught? MBBS/BDS How a subject will be taught? face to face or distance mode What is to be achieved Learning outcome
Why is anatomy being taught? Students understand the Inter- relationship of various structures of human body in better way Students score better in AIPGME/ state PGME/ USMLE Emphasis on basics Emphasis on recent advances
Curricular Components Educational Objectives what will the learner be able to do at the end of instructions. Educational Materials learning resources like books, manuals, models, A - V aids etc. Educational Methods denote the way the materials will be used e. g. lectures, practicals, group discussions, self study, field visits etc. Evaluation to certify the attainment of stipulated proficiency; and to provide a feedback to the learner and the teacher
Which is correct ? A B Objectives Objectives Materials Assessment planning Methods Materials Assessment planning Methods Assessment Assessment
Which is correct ? A B Objectives Objectives Materials Assessment planning Methods Materials Assessment planning Methods Assessment Assessment
Curriculum development Curriculum planning should be flexible (example of communication skill) Same learning objective could be achieved by using different teaching methodology.
Curriculum development Approaches Subject centered Learner centered Problem solving
Subject centered approach Emphasis to complete subject matter Number of lectures / number of topics / number of hours are assigned (Contemporary MBBS curriculum)
DISCIPLINE BASED O & G SURG MED MICR PHYSIO MATH PED CM FM ANAT PATH PHARM BIO CH. COMP BIO PHY CHEM G.K.
Learner centered approach Approach es Learner centered Subject centered Problem solving Emphasis on fulfilling the needs of learner. Students will be active and responsible participants in their own learning. Strengthens student motivation, promotes peer communication, builds student teacher relationships and promotes active learning. (Learner s intent to crack PGME/USMLE/ NEET)
STUDENT DECIDES ON Learning objectives Course contents Methods to be used to achieve objectives Learning resources Sequence and pace of learning. Time of Assessment BE LEARNER ORIENTED
Problem solving approach Approach es Learner centered Subject centered Problem solving Emphasis on ability of learner to solve a given problem Involves subject as well as learner centered approach
None of the approaches are entirely satisfactory
SPICES model of Medical curriculum (Harden et al 1984) Modern System Student-centered Problem-based Integrated Traditional System Teacher-centered Information-gathering Discipline-based - - - Community-based Electives Hospital-based Standard-program - - Systematic Apprenticeship-based - (More the curriculum is on left side, the better it is )
INEGRATION HORIZONTOL VERTICAL SPIRAL
INTEGRATED Anatomy Biochemistry
Advantages of Integration Reduces fragmentation of medical course. Improves education effectiveness of teaching. Promotes staff communication and collaboration. Advantages of subject based Omission of topics is avoided. Content of discipline is not neglected. Less costly. Teacher friendly. Provides a career choice.
Curriculum Designs Teacher oriented Student oriented Problem Based Integrated Community Oriented Elective Systematic Information Gathering Discipline based Hospital based Uniform Apprenticeship/ Opportunistic THE IDEAL MODEL?
Ideal Curriculum NATIONAL HEALTH POLICY
Ideal Curriculum NATIONAL HEALTH POLICY STATE HEALTH POLICY
Ideal Curriculum NATIONAL HEALTH POLICY STATE HEALTH POLICY UNIVERSITY GOALS
Ideal Curriculum NATIONAL HEALTH POLICY STATE HEALTH POLICY UNIVERSITY GOALS Curriculum Goals Department Goals Objectives - Assessments & Teaching Strategies
Ideal Curriculum NATIONAL HEALTH POLICY STATE HEALTH POLICY UNIVERSITY GOALS Curriculum Goals Department Goals Objectives - Assessments & Teaching Strategies D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 Dn Assignments
Present situation of medical education UNIV. GOAL Curriculum Goals Department Goals Objectives - Assessments & Teaching Strategies D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 Dn Assignments
Curricular determinants National health objectives Institutional Objectives Departmental Objectives Subject Content Learning experiences Assessment plan
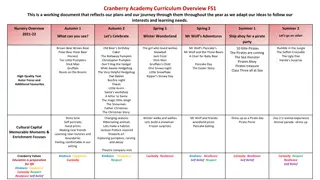
Curriculum Development: A Six Step Approach David E Kern
Contents Step 1 Problem Identification and General Needs Assessment Step 2 Targeted Needs Assessment Step 3 Goals and Objectives Step 4 Educational Strategies Step 5 Implementation Step 6 Evaluation and Feedback
CURRICULUM IS TOO IMPORTANT NOT TO BE EVALUATED
WHAT CAN EVALUATION ADDRESS? intentions vs achievement: curriculum in practice structure outcomes & effects content relevance EVALUATION teaching process learning professional induction cost-benefit qualities of graduates the unexpected But almost never, cause and effect
THE EVALUATION SYSTEM OUTCOME PURPOSE METHOD Decision CONTEXT Communication Curriculum change & development
APPROACH There is no one correct approach Your evaluation MUST be based on your defined objectives. Remember: Evaluation is part of a change management process for curriculum renewal
"Curriculum is in the air. No matter what the problem in medical education, curriculum is looked to as the solution R M Harden