Custom Rate Laws for Reactive Modeling
Explore how to set up custom rate laws for reactive modeling, defining kinetic mineral reactions, symbolic interpretation of rate laws, BASIC scripting, C++ functions, and utilizing internal parameters and syntax guides for advanced customization in reaction modeling.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
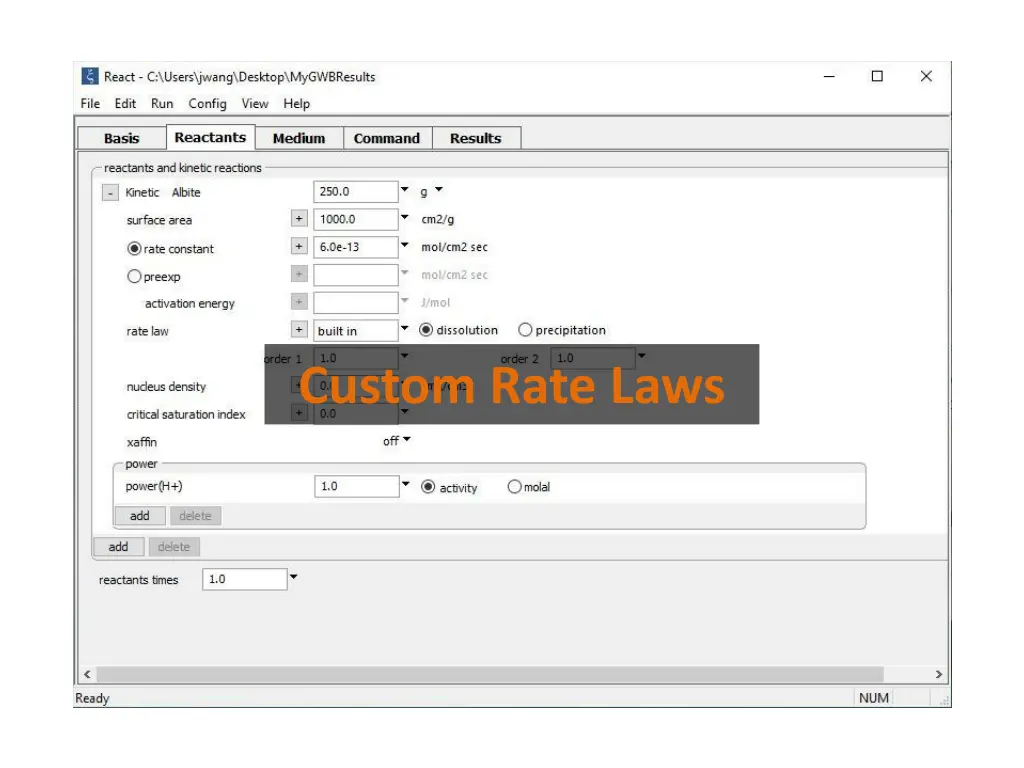
Set Kinetic Rate Laws from the Reactants pane. Set the mineral s initial mass and specific surface area Set either a rate constant, or a pre-exponential factor and an activation energy You can set options for the nucleation, nonlinearity, and cross-affinity Use the built-in rate law, or click + to select other options. Hydrogen ions promote the reaction with a power of one First, add a Kinetic mineral
React, Phase2, X1t, and X2t contain a symbolic interpreter that can evaluate any rate law Simply type out the form of the rate law The equation mimics the rate law set in the previous slide using the built-in rate law
You can type the BASIC script into an editor Click Edit The mineral s dissolution rate is calculated from its rate constant, surface area, and saturation. If saturated, however, its precipitation rate is zero.
or save the BASIC script as a .bas file. Click Browse The same rate law written in the BASIC language and saved as an external .bas file.
Write and compile a C++ function for maximum flexibility Library and function
Your custom rate laws can utilize internal parameters, helper functions , and syntax listed in the Reaction Modeling Guide (RMG) and the Reactive Transport Modeling Guide (RTMG). Method for setting Custom Rate Law Internal parameters (RMG Table 5.1) Helper functions (RMG Table 5.2) BASIC language syntax (RMG Table 5.3) Internal parameters (RTMG Table A.1) Equation Script Script File Compiled function For details, see Custom Rate Laws in the GWB Reaction Modeling Guide.
