Danish Intelligent Energy Alliance: For Future Energy System Development
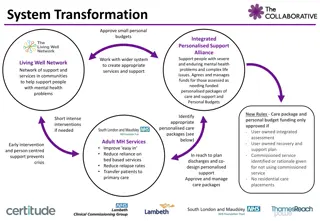
The Danish Energy Association established the Danish Intelligent Energy Alliance in 2012 to bring together a diverse range of contributors for the development of the future energy system. This alliance includes energy companies, utilities, municipalities, and suppliers, aiming to create an integrated and flexible energy system that maximizes the value of intermittent energy production. With a focus on technology, suppliers, investors, and various stakeholders, the alliance emphasizes cooperation and innovation in the energy sector. Members of the alliance encompass technology suppliers, energy companies, utilities, municipalities, investors, consultancies, and universities, among others.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemistry Chemistry 1 1st stclass class Water Resources department Water Resources department By: Israa Murtadha Hameed Israa Murtadha Hameed
Chemistry of environmental Chemistry of environmental pollution pollution 11th lecture By: Israa Murtadha Hameed Israa Murtadha Hameed
What is Environment What is Environment Environment: is a complex of many variables, which surrounds mankind as well as the living organisms. Environment includes water, air and land and the interrelation ships which exist among and between water, air and land and human beings and other living creatures such as plants, animals and micro organisms. Israa Murtadha Hameed
What are What are Characteristics of the Characteristics of the ecosystem? ecosystem? Each ecosystem consists of the following: They are the basic inorganic and organic substances in the environment. Non-living beings: living creatures : Human , plant, animals and micro organisms. Israa Murtadha Hameed
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements that have a high atomic weight and a density at least 5 times greater than that of water. Their multiple industrial, domestic, agricultural, medical and technological applications have led to their wide distribution in the environment; raising concerns over their potential effects on human health and the environment. Their toxicity depends on several factors including the dose, route of exposure, and chemical species, as well as the age, gender, genetics, and nutritional status of exposed individuals. Israa Murtadha Hameed
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements that have a high atomic weight and a density at least 5 times greater than that of water. Their multiple industrial, domestic, agricultural, medical and technological applications have led to their wide distribution in the environment; raising concerns over their potential effects on human health and the environment. Their toxicity depends on several factors including the dose, route of exposure, and chemical species, as well as the age, gender, genetics, and nutritional status of exposed individuals. Israa Murtadha Hameed
BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) This test is based on the amount of oxygen needed by microorganisms to biodegrade organic compounds. Organics that are not biodegradable will report the BOD value as "zero." COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) is the most popular alternative test to BOD for establishing the concentration of organic matter in wastewater samples. It can test wastewater that is too toxic for the BOD test. Israa Murtadha Hameed
The BOD test is also known as "BOD5" since it is based on the accurate measure of DO (dissolved oxygen) at the beginning and end of a five-day period in which the sample is held in dark, incubated conditions (i.e., 20 C or 68 F). The change in DO concentration over five days represents the "oxygen demand" for respiration by the aerobic biological microorganisms in the sample. Israa Murtadha Hameed
There are 5 major unit processes in water treatment plante including: chemical coagulation Flocculation Sedimentation Filtration Disinfection There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes. Israa Murtadha Hameed
1- Chemical Coagulation The first chemical added is chlorine dioxide and it is an oxidant used to break down naturally occurring organic matter such as decaying leaves and other plant material. A chemical coagulant known as aluminum sulfate is used as the primary coagulant. A polymer, a long chain of synthetic organic compounds, is also added to the water as a coagulant aid to help in strengthening the primary coagulant s bonding chains. The coagulants are added at the rapid mix unit; this is a unit that creates turbulent mixing energies to help thoroughly disperse the chemical coagulants into the raw water and to begin the coagulation process. The coagulants that cause very fine particles to clump together into larger particles that can then be removed later in the treatment process by settling, skimming, draining or filtering. Israa Murtadha Hameed
2- Flocculation The coagulated water then flows to the next major unit process, the flocculation process. Flocculation is a slow stirring process that causes the small coagulated particles to form floc. The flocculation process promotes contact between the floc particles and the particulates (sediment) in the water. Generally, these contacts or collisions between particles result from gentle stirring created by a mechanical or hydraulic means of mixing. There are two sets of flocculation basins that contain mechanical mixing paddles that the water passes through to gently stir the coagulated water. The floc formed creates a surface in which the particulates in the water adsorb (adhere) to the surface of the floc thus forming larger settleable particles for ease of removal by sedimentation and filtration. Israa Murtadha Hameed
3- Sedimentation The flocculated water then flows to the next major unit process, the sedimentation process. The purpose of the sedimentation process is to remove suspended solids (particles) that are denser (heavier) than water and to reduce the particulate load on the filters. Sedimentation is accomplished by decreasing the velocity of the water being treated below the point where it can transport settleable suspended material, thus allowing gravitational forces to remove particles held in suspension. When water is almost still in sedimentation basins, settleable solids will move toward the bottom of the basin. This process of sedimentation removes almost ninety percent of the solids in the water. The clearer water on the surface is collected in the launder tubes that direct the water to the filter gallery to remove the remaining ten percent of solids. Israa Murtadha Hameed
4- Disinfection The settled water then flows from the Pre-Sedimentation Building to the Filtration Facility. Before arriving at the Filtration Facility chlorine is added to the water at the pre- chlorination point to begin the disinfection process. The disinfection process is designed to kill or inactivate most microorganisms in water, including essentially all pathogenic organisms whether they are from bacteria, viruses or intestinal parasites. Pathogenic organisms are the microscopic bugs in the water that can cause waterborne diseases such as gastroenteritis, typhoid, dysentery, cholera, and giardiasis. Israa Murtadha Hameed
5- Filtration The chlorinated settled water then flows into the Filtration Facility and onto the filters for the last of the major unit processes used to treat the drinking water. Filtration is the process of passing water through material such as a bed of coal, sand, or other granular substance to remove particulate impurities that were not removed during the sedimentation process. The water treatment plant uses rapid rate multi- media gravity filter beds. The filters are comprised of a top layer of anthracite, a middle layer of filter sand and then a bottom layer of garnet sand and one an underdrain system that collects the filtered water. The water enters on top of the filter media and passes down through the filter beds by gravity. Israa Murtadha Hameed
The different materials work like a giant strainer and trap remaining particulates. When the filters start to get packed full with particles, the operators clean them using a procedure called backwashing . Potable water is run backwards through the filters releasing the entrapped particulates that are collected in drain troughs. The backwash water is sent to the Backwash Recovery Pond and, after a settling process, the backwash water is returned to the raw water settling pond for re-use. The water that is collected from the bottom of the filters is then considered potable. Israa Murtadha Hameed
quality of industrial waste water Most Industrial effluents are derived from industrial factories may be so loaded with organic and inorganic substances. The effluents and the treatment of the waste waters of some industries are of greater concern than the domestic sewage of the same area; the industrial effluents if possible should be kept away and treated separately from municipal sewage treatment. Purification of industrial wastes by natural processes in streams is not recommended. Total industrial of reclaimed waste water remains very limited because of high cost and non- rigid environment metal laws. Israa Murtadha Hameed
Any Questions? Israa Murtadha Hameed