DC Circuit Elements and Network Classification
Explore the concepts of DC circuits, network classification, and energy sources in this informative content from Amit Kasar of the Engineering Science Department at the International Institute of Information Technology, IIT. Learn about active and passive networks, unilateral and bilateral networks, linear and nonlinear networks, lumped and distributed networks, as well as energy sources such as voltage and current sources. Enhance your understanding of circuit analysis with this comprehensive resource.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DC CIRCUIT Amit Kasar Engineering Science Department International Institute of Information Technology, I IT www.isquareit.edu.in
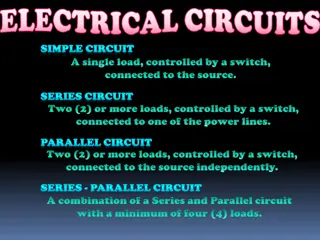
Network- A combination of circuit element (Resistance, Inductance, Capacitance) with energy sources is called as Network. Classification of Network Active & Passive Unilateral & Bilateral Network Network Classification Linear & Nonlinear Network Lumped & Distrubuted Network International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Active Network- A network which contain at least one source of Energy. (Fig. A) Passive Network- A network without any Energy source. (Fig. B) Fig. A Fig. B Unilateral Network- A network whose operation is depend upon direction of current flowing through it called as unilateral network. Best example is Diode. Bilateral Network- A network whose operation is independent upon direction of current flowing through it called as unilateral network. Best example is Resistor. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Continue Linear Network- A network whose parameters like Resistance, Inductance & Capacitance are always constant irrespective of change in voltage, time & temperature called as linear network. Ohms law can apply for such network. Nonlinear Network- A network whose parameters like Resistance, Inductance & Capacitance are always constant with change in voltage, time & temperature called as nonlinear network. Ohms law cannot apply for such network. Lumped Network- A network in which all circuit elements can physically separable for the analysis purpose called lumped network. Distributed Network- A network in which all circuit elements cannot be physically separable for the analysis purpose called distrubuted network. Example is transmission line. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Energy Sources Energy Sources Voltage Source Current Source Practical Current Source Practical Voltage Source Ideal Voltage Source Ideal Current Source International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Voltage Source Ideal Voltage Source- A voltage source is a device which provides a constant voltage to load at any instance of time and is independent of the current drawn from it. Practically, the ideal voltage source cannot be made. It has zero internal resistance International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Voltage Source Practical Voltage Source- Practically voltage source have some internal resistance. Due to this internal resistance there is some voltage drop occurs & remaining voltage appear across the load. A practical voltage source is thus denoted by resistance in series which represents the internal resistance of source. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Current Source Ideal Current Source- A current source is a device which provides a constant current to load at any instance of time and is independent of the voltage supplied to circuit. Practically, the ideal current source not available. It has infinite resistance. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Current Source Practical Current Source- Practically current sources do not have infinite resistance across there but they have a finite internal resistance connected in parallel. So the current delivered by the practical current source is not constant and it is also dependent somewhat on the voltage across it. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Ohms Law As the physical state ( temperature)of the conductor remains constant , the current flowing through conductor is directly proportional to potential difference applied across it. But ohms law can not be applied to nonlinear resistance like diode & nonmetallic conductor like silicon carbide. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Kirchoffs law Kirchoff s Current law- The algebraic sum of currents meeting at a point or junction or nodeis equal to zero. In other words we can say that incoming currents is equal to outgoing currents. The currents are entering the node & currents are leaving the node. International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
Kirchoffs law Kirchoff s Voltage law- In any closed loop network, the algebraic sum of product of current & resistance equal to the sum of all the voltage drops within the same loop which is also equal to zero. In other words the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero. V = 0 International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in
References [1] https://www.codrey.com/dc-circuits/voltage-source-and-current-source [2] https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/dccircuits/dcp_2.html [3] https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/dccircuits/dcp_4.html International Institute of Information Technology, I IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057 Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in