Delving Into Earth's Layers and Earthquakes
Explore the fascinating world beneath our feet with a comprehensive overview of Earth's layers, including the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. Discover the science behind earthquakes, from the release of stored energy to the different types of seismic waves. Uncover the role of faults in Earth's dynamic processes and how instruments like seismographs help us study and understand these natural phenomena.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
INSIDE EARTH By Brooke E.
Introduction Earthquakes are movements or vibrations in the Earth. They are caused the release of stored energy in earth's outer layer. There is also an instrument that detects, measures, and records the energy of an earthquake.This is called a seismograph, and it produces seismograms. Pressure within the earth can cause rocks in its outer layer to break. These breaks are called faults. When an earthquake begins, pressure deep within Earth causes rocks along faults to move and break. As they move, energy is released as vibrations. These vibrations are called seismic waves. As seismic waves move through Earth and along its surface, they are felt as shakings and vibrations.
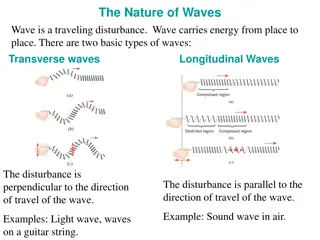
Primary Waves Called P waves Fastest waves First to arrive at a distant point Travels through solids, liquids, and gases
Secondary Waves Called S waves Slower that P waves Arrives later at a distant point Travels through solids only
Surface Waves Called L waves Slowest waves of all Felt at the surface Causes the most damage
Introducing... The layers of the Earth!
Crust Thinnest layer Grass, dirt, and sand Contains oxygen Deeper under continents than oceans Earth's most outer layer We live on it Solid rock The thin yellow layer is the crust
Mantle Thickest layer Layer of rock lying below the crust Allows tectonic plates to slowly move Rocks move or flow due to pressure and high temperatures
Outer core Made of melted iron Totally liquid Inner core floats in this layer
Inner core Solid sphere Center of the earth Spins at a different rate than the rest of the planet
The yellow section Crust
The red layer Mantle
Outer core The yellow layer is the...
Inner core The layer that is the center of the earth