Desalination and Reverse Osmosis: Methods and Applications
Learn about desalination and reverse osmosis, including the processes involved, such as vacuum distillation and reverse osmosis technology. Discover how these methods help in converting saltwater to freshwater, the importance of membrane technology, and the energy-saving benefits of reverse osmosis. Explore the significance of reverse osmosis in water purification for various uses, along with the key differences between normal osmosis and reverse osmosis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Desalination and Reverse Osmosis Koh Huai Ze (10)
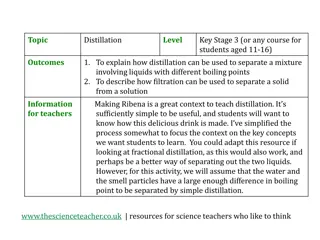
What is Desalination? O The process of removing salt and other minerals from water O Water is desalinated in order to convert salt water to fresh water so that it is suitable for human consumption O Very costly as it requires large amounts of energy and specialised infrastructure
Methods of Desalination Vacuum Distillation Vacuum Distillation O The boiling of water at a much lower temperature than normal, saving energy Reverse Osmosis Reverse Osmosis O Uses membranes to desalinate, applying reverse osmosis technology O Uses semi-permeable membranes and pressure to separate salts from water O Less energy is used compared to thermal distillation O Also used to purify fresh water for medical and industrial uses
Reverse Osmosis In normal osmosis: O Water molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a partially permeable membrane In reverse osmosis: O Water molecules are forced to move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration by applying a huge amount of pressure
Reverse Osmosis Result: O The solute is retained on the pressurised side of the membrane O The pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side Membrane used: O Designed to only allow water molecules to pass through O Does not allow larger molecules such as salt ions to pass through
Process of Process of Reverse Osmosis Reverse Osmosis
Hope you have learnt something from this THANK YOU THANK YOU
An Overview of Desalination Processes produce freshwater from salt water a suitable separation process must be devised. The task can be accomplished in many different ways, all of them based on the principle that water and salts do not separate spontaneously, and thus require some kind of energy source to power the separation process. The first desalination units used for freshwater production were based on the evaporation of pure water via the addition of heat provided by the sun or by combustion processes. In recent years, the development of modern polymer materials has led to the production of membranes which allow the selective passage of water (semi-permeable membranes) or ions (ionic exchange membranes), thus providing the basis for membrane desalination processes. In order to produce freshwater from salt water Dr. Ola Abdelwahab 13
Membrane Processes A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species in a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights
Membrane Processes Membrane Processes Four common types of membranes: Reverse Osmosis Nanofiltration Ultrafiltration Microfiltration
An Overview of Desalination Processes produce freshwater from salt water a suitable separation process must be devised. The task can be accomplished in many different ways, all of them based on the principle that water and salts do not separate spontaneously, and thus require some kind of energy source to power the separation process. The first desalination units used for freshwater production were based on the evaporation of pure water via the addition of heat provided by the sun or by combustion processes. In recent years, the development of modern polymer materials has led to the production of membranes which allow the selective passage of water (semi-permeable membranes) or ions (ionic exchange membranes), thus providing the basis for membrane desalination processes. In order to produce freshwater from salt water Dr. Ola Abdelwahab 18
Membrane Processes A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species in a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights
Membrane Processes Membrane Processes Four common types of membranes: Reverse Osmosis Nanofiltration Ultrafiltration Microfiltration
Treated water will then be transfer to the tank in Lodi where it is distributed to the costumers.