Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, acidosis, and ketosis. Learn about its background, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment goals in pediatric patients. Early recognition and management are essential to prevent complications such as severe cerebral edema. Explore clinical pathways and guidelines for managing DKA in children.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diabetic ketoacidosis Carl Eriksson October 2019 0
DKA background Diagnosis Hyperglycemia (glucose > 200) Acidosis (venous pH < 7.3) Ketosis (urine or serum ketones) Risk factors Not previously diagnosed with diabetes 1/3 of children with type 1 diabetes first present with DKA Younger patients, delayed diagnosis are high-risk Previously diagnosed Missed insulin, acute illness 1
DKA presentation History Polyuria, polydipsia, nocturia, enuresis Weight loss Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain Yeast infections Altered mental status Physical Hyperventilation Tachycardia, poor perfusion, decreased skin turgor Altered mental status 2
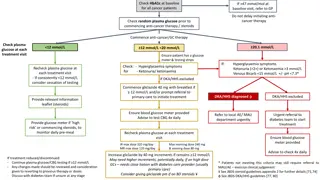
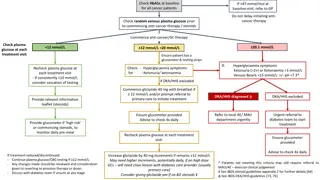
DKA diagnosis and treatment Goals Diagnose DKA Rule out hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state Gently correct acidosis, ketosis, and dehydration Avoid severe cerebral edema (and severe electrolyte disturbances) 3
DKA diagnosis and treatment DCH clinical pathway 4
Questions eriksson@ohsu.edu 6