Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common symptom resulting from digestive issues and abnormal water-electrolyte transport. It can be classified based on duration, severity, and causes such as infections or malabsorption. Acute diarrhea lasts less than two weeks, while chronic diarrhea persists for more than two weeks. Severity ranges from mild with low-grade fever to severe with signs of dehydration. Infants may develop lactose intolerance leading to worsened symptoms. Proper understanding of diarrhea helps in effective management and treatment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diarrhea Diarrhea is a symptom that results from disorders involving digestive, absorptive, and secretory functions. Diarrhea is caused by abnormal intestinal water and electrolyte transport
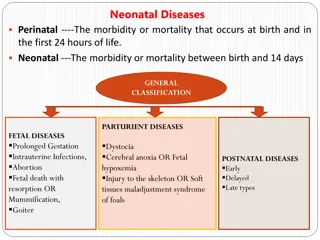
classification of diarrhea diarrhea classified according to duration into acute diarrhea and chronic diarrhea Acute diarrhea, less than two weeks. Chronic diarrhea, more than two weeks.
Acute diarrhea is defined as a sudden increase in frequency and a change in consistency of stools, often caused by an infectious agent in the GI tract Chronic diarrhea is an increase in stool frequency and increased water content with duration of more than 14 days chronic diarrhea is more likely related to a malabsorption or inflammatory cause
Diarrhea classified according to severity, into 1-Mild diarrhea. 2-moderate diarrhea. 3-sever diarrhea.
Mild diarrhea -Low grade fever -The episodes of diarrhea consist of 2 to 5 loose, watery bowel movements per day. -The mucous membrane of the mouth appears dry -The pulse will be rapid. -Decrease skin elasticity -Urine output is usually normal.
Moderate diarrhea -Low grade fever -The episodes of diarrhea consist of 6 to 10 loose, watery bowel movements per day. -The mucous membrane of the mouth appears dry. -The pulse will be rapid . Decrease urine output.
Sever diarrhea Assessment. Severe diarrhea may result from progressive mild diarrhea. Infants with severe diarrhea are obviously ill. fever(39.5 to 40.0 C). Both pulse and respirations are weak and rapid. The skin is pale and cool. Infants may appear apprehensive and lethargic. dehydration
Sever diarrhea Infants may develop a lactase leads to lactose intolerance. With lactose intolerance, a child cannot take formula or breast milk or new diarrhea will begin.
Sever diarrhea The episodes of diarrhea usually consist of a bowel movement every few minutes. The stool is liquid green, perhaps mixed with mucus and blood, and it may be passed with explosive force. Urine output will be scanty and concentrated
Assessment of diarrhea For each stool passed, record its Frequent Color Consistency Odor size and the presence of any blood or mucus.
Vomiting Vomiting is the forceful ejection of gastric contents through the mouth.
Types of vomiting 1- regurgitation 2- projectile ( disease ) 3- rumination ( induced vomiting ) psychological disorder
Dehydration Dehydration is a common body fluid disturbance encountered in the nursing care of infants and young children; it occurs whenever the total output of fluid exceeds the total intake, regardless of the underlying cause.
Type of dehydration Isotonic dehydration: occurs in conditions in which electrolyte and water deficits are present in approximately balanced proportions. hypotonic dehydration: occurs when the electrolyte deficit exceeds the water deficit. Hypertonic dehydration: results from water loss in excess of electrolyte loss and is usually caused by a proportionately larger loss of water or a larger intake of electrolytes. This sometimes occurs in infants with diarrhea who are given fluids by mouth that contain large amounts of solute.
Classification of dehydration Mild-dehydration: The child loses 5% or less from total his body weight. Moderate dehydration: The child loses 5% - 10% from total his body weight. Sever dehydration: The child loses more than 10% from total his body weight.
calculating of body weight loss to determine the ratio of missing body weight , use the following formula. ??????? ???? ???? ? 100% ????? ???? ???? ?
Determine the type of dehydration, The child weight before disease 12 kg While after case become 10 kg 2X100 = 200 / 12 = 16%
Management of dehydration If a child can drink, the most effective way to replace fluid is by offering oral rehydration therapy (ORS). For a child who will not drink, an IV solution such as normal saline or 5% glucose in normal saline is begun.
Lecturer Assistant Kareem Al-khafajy