Different Types of Amplifiers and Operational Amplifiers
Learn about amplifiers, electronic devices that increase signal power, and operational amplifiers, including inverting and noninverting circuits. Discover the principles and classifications of amplifiers in this informative guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
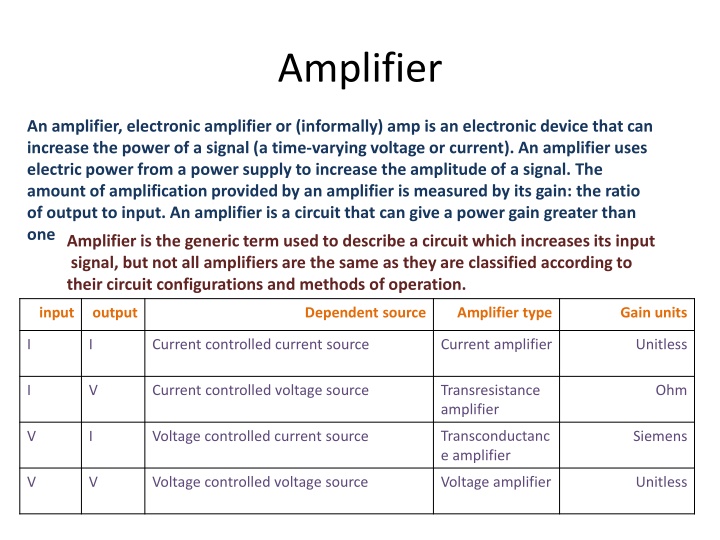
Amplifier An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). An amplifier uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output to input. An amplifier is a circuit that can give a power gain greater than oneAmplifier is the generic term used to describe a circuit which increases its input signal, but not all amplifiers are the same as they are classified according to their circuit configurations and methods of operation. input output Dependent source Amplifier type Gain units I I Current controlled current source Current amplifier Unitless Transresistance amplifier I V Current controlled voltage source Ohm Transconductanc e amplifier V I Voltage controlled current source Siemens V V Voltage controlled voltage source Voltage amplifier Unitless
AMPLIFIER Each type of amplifier in its ideal form has an ideal input and output resistance that is the same as that of the corresponding dependent source Amplifier type Dependent source Input impedance Output impedance Current CCCS 0 Transresistance CCVS 0 0 Transconductance VCCS Voltage VCVS 0 In practice the ideal impedances are not possible to achieve. For any particular circuit, a small-signal analysis is often used to find the actual impedance. A small- signal AC test current Ix is applied to the input or output node, all external sources are set to AC zero, and the corresponding alternating voltage Vx across the test current source determines the impedance seen at that node as R = Vx / Ix
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PARTICAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS CIRCUIT : 1- INVERTING AMPLIFIRE :