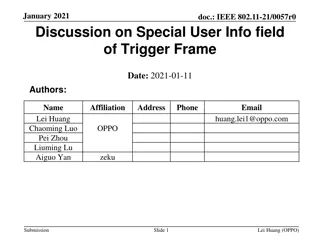
Different Types of Dictionaries and Their Features
Explore the world of dictionaries, from the various types available to their essential elements and functions. Learn about monolingual, bilingual, and trilingual dictionaries, as well as how dictionary size impacts coverage. Discover the significance of dictionaries in language learning and communication.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dictionaries Types and Usage 2
Introduction What is a dictionary? What are the different types of dictionaries? What are the elements of a dictionary? What are the different kinds of information dictionaries provide?
Whats a dictionary ? A dictionary (also called a wordstock, word reference, wordbook, lexicon, or vocabulary) is a collection of words in one or more specific languages, often listed alphabetically, with usage information, definitions, phonetics, pronunciations, and other information; or a book of words in one language with their equivalents in another, also known as a lexicon. According to Nielsen (2008) a dictionary may be regarded as a lexicographical product that is characterized by three significant features: (1) It has been prepared for one or more functions. (2) It contains data that have been selected for the purpose of fulfilling those functions. (3) Its lexicographic structures link and establish relationships between the data so that they can meet the needs of users and fulfill the functions of the dictionary. 4
Types of dictionaries: Dictionaries vary in coverage, size, and scope. They can be classified on the basis of different criteria. Knowing the types of dictionaries available is very important to decide which ones to buy or use. The following criteria are used to classify dictionaries:
Number of languages: Monolingual dictionaries are written in one language only. Each word is followed by its meaning or various meanings and probably other information related to pronunciation, grammar, or word history. Bilingual dictionaries are written in two languages. Each word is followed by its equivalent or possible equivalents in another language. Bilingual dictionaries could be uni- or mono-directional; that is, they go in one direction only, from English to Arabic or vise versa. Trilingual dictionaries are written in three languages. Multilingual language are written in more than two languages.
Size of the dictionary: This has to do with how fully a dictionary covers the lexicon of a particular language. The number of words is a measure of its relative size compared with other dictionaries in the same language. According to this criteria, dictionaries can be classified into the following.
1. Unabridged dictionaries Unabridged dictionaries which are believed to include all the words of the English language (400,000 to 600,000 words). Examples: Webster's Third New International Dictionary (NID3), and Oxford English dictionary (OED) which has 20 volumes. Semi- unabridged dictionaries are those which include about 315,000 words such as the Random House Dictionary. 2. Pocket size dictionaries Pocket size dictionaries, which include from 40,000 to 60,000 words; e.g. Pocket Oxford Dictionary.
3. College dictionaries College dictionaries include from 150,000 to 170,000 words (almost 200,000 words). Examples: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, The Random House College Dictionary, Webster's New World Dictionary of American English. They are called college dictionaries because they are often used by college students.
4. Desk dictionaries Desk dictionaries include from 60,000 to 100,000 words. Examples: The American heritage dictionary, Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary. They are called desk dictionaries because they are often kept on desks for frequent reference. College and desk dictionaries are often abridged versions of larger dictionaries. e.g. Concise Oxford Dictionary, Longman Concise English Dictionary.
Mode of Presentation: Monolingual Dictionaries: They may also vary as to the mode of presentation, e.g. English monolingual dictionaries present words alphabetically, whereas most Arabic ones present words in accordance with their tri-consonantal and Quadri-consonantal roots. Some monolingual dictionaries are dedicated to special areas in the vocabulary of a language, e.g. there are dictionaries of English idioms, proverbs, scientific usage, etc. Bilingual Dictionaries: Arabic equivalents appear against each English word. If the dictionary is English-Arabic, the English words are presented alphabetically, but if the dictionary is Arabic-English, the Arabic words are listed according to their roots. , many bilingual dictionaries on the market deal with specialized vocabularies by presenting SL terminologies and their TL equivalents in areas such as political, medical, and legal discourses. 11
Scope of coverage by subject: Subject-field dictionaries are confined to a special subject, such as law or medicine. Special-purpose dictionaries are limited to one aspect of language: collocations, slang, pronunciation, etymology, synonyms, usage, offensive and taboo words, spelling, dialect, etc.
Information in Monolingual Dictionaries Monolingual dictionaries provide users with various kinds of information about lexical items. For example, the average English monolingual desk dictionary like The Random House College Dictionary or The Webster s Collegiate Dictionary usually furnishes the user with phonological, syntactic, semantic, and etymological information about English words, among their other things. First: (Phonological Information) It consists of phonemic transcription that indicates the pronunciation of the word, its syllable structure, and its stress pattern including both primary and secondary stress assignment in multi- syllabic words. For example : Narcotism ( n r k t m ). Second: ( Syntactic Information ) It indicates the part of speech of the word, that is, whether it is a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb, and also shows whether a verb is transitive or intransitive. For example: Excite ( transitive verb) Excitement (noun) 13
Thirdly: ( Semantic information ) It forms the core of what dictionary-makers do, as it revolves around the meanings of words in a language. So, the dictionary lists the various senses of words, occasionally giving some pictures of objects in the real world and some example sentences to illustrate rather abstract senses. It may refer to synonyms and antonyms of a given word in the course of explaining what word means. For example, The Random House College Dictionary lists the senses of the word excess and also mentions its synonyms and antonyms. Fourthly: Etymological information It is the study of the history of words, their origins (Latin, French, .etc.), and how their form and meaning have changed over time. By extension, the term "the etymology (of a word)" means the origin of the particular word. When talking about place names, there is a specific term, toponymy. The following English words have been acquired either directly from Arabic or else indirectly by passing from Arabic into other languages and then into English. For example: Some words used in English in talking about Arabic music: Baladi, Mawal, Mizmar, Oud, Qanun, etc. Arabic cuisine words part of the vocabulary of Middle Eastern cuisine is from Turkish, not Arabic. The following words are from Arabic, although some of them have entered Western European languages via Turkish, like Baba ghanoush, Falafel, Hummus, Kibbeh, Kabab, etc. 14
Each Translator Has Skills That Are Needed In His Job: 1. The translator must fully understand the sense or meaning of the original matter. 2. The translator should pose a perfect knowledge of both the source and target language. 3. The translator should avoid what is referred to as word-for-word renderings. 4. The translator is advised to use such forms of speech that are in common use on the part of the receivers of the translated text. 5. The translator should choose and use his words in an appropriate way so as to produce the correct tune. 6. The most obvious skill that translators need is the ability to read and write, and understand a second language. 7. Translators must be able to receive ideas in one language and express them in another. 8. In addition to knowing a second language, translators need to know as much as possible about many things as possible. 9.Translators also need a thorough knowledge of the tools of the trade ( dictionaries, encyclopedias, reference books, catalogs, bibliographies, etc. ) where to find them and when to use them. 15