Digging into AIG Data: Depths of Knowledge Levels Explained
Unveil the Depths of Knowledge levels from Recall and Reproduction to Extended Thinking in educational settings. Understand the nuances of each level and how they impact student learning and assessment strategies. Discover the essence behind the different cognitive demands placed on students at each level and how educators can effectively integrate them into the classroom environment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
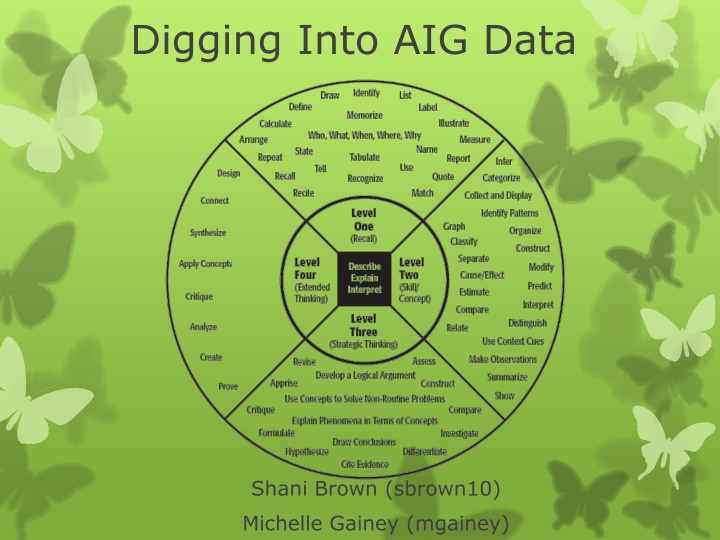
Digging Into AIG Data Shani Brown (sbrown10) Michelle Gainey (mgainey)
Depths of Knowledge DOK Level Title of Level 1 Recall and Reproduction 2 Skills and Concepts 3 Short-term Strategic Thinking 4 Extended Thinking
Level One Basic tasks that require students to recall or reproduce knowledge and/or skills. Working with facts, terms and/or properties of objects. May also involve use of simple procedures and/or formulas. Little transformation or extended processing of the target knowledge required
Level Two Some mental processing beyond recalling or reproducing a response. Generally requires students to contrast or compare; convert information from one form to another; classify into meaningful categories ; describe or explain issues and problems, patterns , cause and effect, significance or impact, relationships, points of view or processes. Working with or applying skills and/or concepts to tasks related to the field of study in a laboratory setting. Transform/process target knowledge before responding.
Level Three Demand a short-term use of higher order thinking processes, such as analysis and evaluation, to solve real-world problems with predictable outcomes. Stating one s reasoning is a key marker of tasks that fall into this particular category. Require coordination of knowledge and skill from multiple subject-matter areas to carry out processes and reach a solution in a project-based setting.
Level Four Extended use of higher order thinking processes such as synthesis, reflection, assessment and adjustment of plans over time. Students are engaged in conducting investigations to solve real-world problems with unpredictable outcomes. Employing and sustaining strategic thinking processes over a longer period of time to solve the problem is a key feature of curricular objectives that are assigned to this level.
Lets Collaborate! At your tables, preview the questions in The River . Discuss what DOK level each of the questions fall under .
How would this look in the classroom?
Questions/Comments www.tinyurl.com/JanPrincipals