Digital Logic Inverter Operations
Explore the classification of circuits, voltage-transfer characteristics, noise margins, power dissipation, and propagation delays in digital logic inverters. Learn about the key parameters and characteristics that define the behavior of inverters in electronic circuits.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Clasificacion de Circuitos y frecuencia maxima Digital Logic Inverter
The Voltage-Transfer Characteristic (VTC) The function of the inverter is to invert the logic value of its input signal The voltage-transfer characteristic is used to evaluate the quality of inverter operation o VTC parameters VOH: output high level VOL: output low level VIH: the minimum value of input interpreted by the inverter as a logic 1 VIL: the maximum value of input interpreted by the inverter as a logic 0 Transition region: input level between VIL and VIH
Noise Margins The VTC is generally non-linear VIH and VIL are defined as the points at which the slope of the VTC is =-1 Robustness (noise margin at a high level): NMH = VOH - VIH Robustness (noise margin at a low level): NML = VIL - VOL Static inverter characteristics for ideal VTC: VOH = VDD VOL = 0 VIH = VIL = VDD/2 NMH = NML = VDD/2
Power Dissipation 2 fCV P = DD 2 D Static power dissipation: power dissipated when the inverter stays in logic 0 or logic 1 Dynamic power dissipation: power dissipated as the output is switching
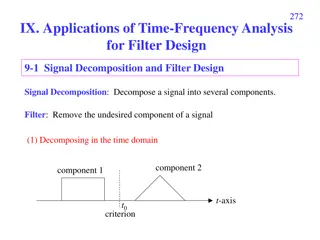
t ( )RC e = ( ) v t V V V Propagation Delay + 0 o tPHL: high-to-low propagation delay tPLH: low-to-high propagation delay tP(propagation delay) = (tPLH + tPHL)/2 Maximum switching frequency fmax= 1/(2tP) The transient of the inverter can be characterized by a RC charge/discharge model