Dijkstra's Algorithm and Machine Learning Concepts
Delve into the world of Dijkstra's algorithm, a powerful tool for finding shortest paths in graphs, and explore various aspects of machine learning such as reinforcement learning. Discover the strengths, weaknesses, and applications of these technologies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
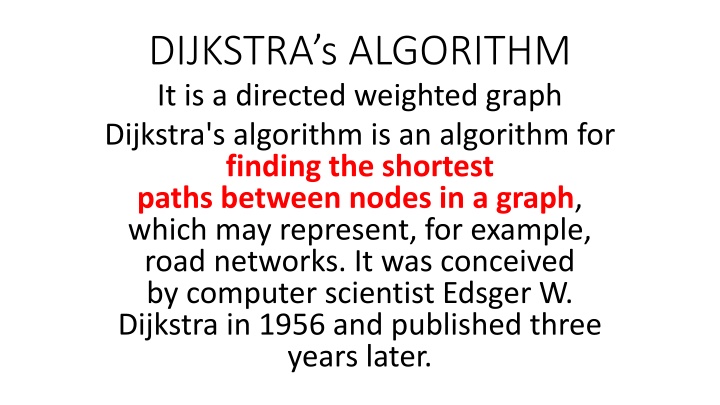
DIJKSTRAs ALGORITHM It is a directed weighted graph Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years later.
The major disadvantage of the algorithm is the fact that it does a blind search. consume a lot of time waste of necessary resources. Another disadvantage is that it cannot handle negative edges. This leads to acyclic graphs and most often cannot obtain the right shortest path.
LEARNING AGENTs [An agent] is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with E.
EXAMPLEs DATA MINING ROOUTE FINDER TIC-TAC-TOE
Types of machine learning How will the system be exposed to its training experience? Direct or indirect access: indirect access: record of past experiences, databases, corpora direct access: situated agents reinforcement learning Source of feedback ( teacher ) ..? supervised learning unsupervised learning mixed: semi- supervised ( transductive ), active learning, ....
What is different about reinforcement learning: Training experience (data) obtained through direct interaction with the environment Influencing the environment Goal-driven learning: Learning of an action policy Trial and error approach to search: Exploration and Exploitation