Diode Applications in Engineering: A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the wide range of diode applications in engineering, including load line analysis, series configurations, Zener diodes, voltage multiplier circuits, and more. Learn about the critical role of diodes in high-speed switching applications and important considerations for various diode types such as Schottky, Zener, LED, and photo diodes. Gain insights into the practical uses of diodes in different circuit configurations and power supply designs. Delve into the concept of reverse recovery time and its significance in diode performance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
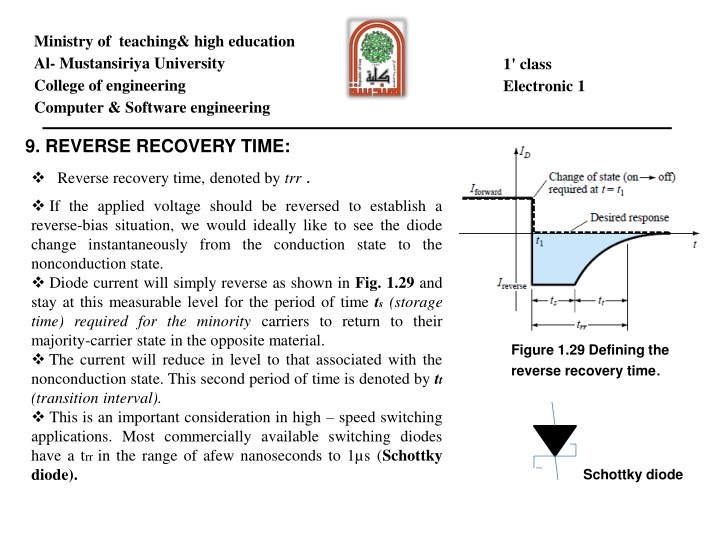
Ministry of teaching& high education Al- Mustansiriya University College of engineering Computer & Software engineering 1' class Electronic 1 9. REVERSE RECOVERY TIME: Reverse recovery time, denoted by trr . If the applied voltage should be reversed to establish a reverse-bias situation, we would ideally like to see the diode change instantaneously from the conduction state to the nonconduction state. Diode current will simply reverse as shown in Fig. 1.29 and stay at this measurable level for the period of time ts (storage time) required for the minority carriers to return to their majority-carrier state in the opposite material. The current will reduce in level to that associated with the nonconduction state. This second period of time is denoted by tt (transition interval). This is an important consideration in high speed switching applications. Most commercially available switching diodes have a trr in the range of afew nanoseconds to 1 s (Schottky diode). Figure 1.29 Defining the reverse recovery time. Schottky diode
10. ZENER DIODES Zener diodes are available having Zener potentials of 1.8 to 200 V with power ratings from to 50 W. There is a slight slope to thegharacteristics requiring the piecewise equivalent model appearing in Fig.(1-20) for zener region, while it is assumed as ideal with a straght vertical line at the zener potential. Fig. 1.20 Zener- diode test Characteristics with the equivalent model for each region 11. LED & OTHER TYPES OF DIODES Figure 1.54 (a) Process of electroluminescence in the LED; (b) graphic symbol
+ + LED Photo Diode - - Photo Diode LED Optical Isolator
CHAPTER TWO Diode Applications 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Load Line Analysis. 2.3 Series Diode Configurations. 2.4 Parallel & Series Parallel Configurations. 2.5 AND / OR Gates. 2.6 Sinusoidal Input: Half Wave Rectifier. 2.7 Full Wave Rectification. 2.8 Clippers. 2.9 Clampers. 2.10 Zener Diodes. 2.11 Voltage Multiplier Circuits. 2.12 Power Supply. 2,12.1 Introduction. 2.12.2 General Filter Considerations. 2.12.3 Capacitor Filter. 2.12.4 RC Filter.






















