Disaster Management: Types, Definitions, and Examples
Explore the world of disaster management with insights into types of disasters, definitions, and examples of man-made and natural disasters. From earthquakes to chemical spills, learn about the different categories and impacts of various calamities. Understand the Disaster Management Act of 2005 and how communities can cope with catastrophic events beyond their capacity.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DISASTER MANAGEMENT DISASTER MANAGEMENT DR. SIDHI PRABHUDESAI ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPT OF SWASTHAVRITTA
DEFINITION DEFINITION The Disaster Management Act 2005 states: Disaster means a catastrophe, mishap, calamity or grave occurrence in any area, arising from natural or man-made causes, or by accident or negligence which results in substantial loss of life or human suffering or damage to, and destruction of property, or damage to, or degradation of, environment, and is of such a nature or magnitude as to be beyond the coping capacity of the community of the affected area.
TYPES OF DISASTERS TYPES OF DISASTERS Human Induced/ Man-made Natural Sudden Insidious Wars & Civil conflicts Geophysical Hydrological Meteorological Climatological Biological
MAN MAN- -MADE DISASTERS MADE DISASTERS 1. Bhopal Gas Tragedy-India- 3rdDec 1984 at Union Carbide Pesticide Plant - Released - methyl isocynate 2. Chernobyl nuclear power station in Soviet Union- 26thApril 1986 - Released - Iodine 131, Cesium 134 & 137, Strontium 90
MAN MAN- -MADE DISASTERS MADE DISASTERS 3. Insidious radiation exposure, chemical plants releasing toxic products in rivers, global warming (heat trapping gases in atmosphere released by burning of fossil fuels & depletion of ozone layer due to chlorofluorohydrocarbons) 4. Attack on Twin buildings of World Trade Centre in New York
NATURAL DISASTERS NATURAL DISASTERS Geophysical Hydrological Meteorological Climatological Biological a)Earthquake a) Flood a) Cyclone, storm, tornado, a) Draught a) Epidemics b)Volcano b) Landslides b) Cold wave, derecho c)Tsunami c) Wave action c) Extreme temp, fog frost, b) Extreme hot/cold b) Insect conditions infestations freeze, hail c) Forest wildfire d) Lightening, heavy rain d) Glacial lake outburst e) Sand-storm, dust-storm e) Subsidence f) Snow, ice, winter-storm
DISASTER MANAGEMENT DISASTER MANAGEMENT 3 fundamental aspects: 1. Disaster response 2. Disaster preparedness 3. Disaster mitigation
DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE Search, rescue & first-aid- uninjured survivors give immediate help Field care- Health service directed towards proper care to casualties - Maximisation of bed availability & surgical services - Provision for food & shelter - Establishment of centres for inquiry - Victim identification should be given priority
DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE Triage- Rapidly classifying the injured on the basis of severity of their injuries & likelihood of their survival with prompt medical intervention 4 colour code system High priority treatment or transfer Medium priority Ambulatory patients Dead/ moribund patients
DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE Tagging- name, age, place of origin, triage category, diagnosis & initial treatment Identification of dead- 1) Removal of dead from disaster scene 2) Shifting to the mortuary 3) Identification 4) Reception of bereaved relatives Health hazard from cadaver- Gastroenteritis, food poisoning
DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE RELIEF PHASE - This phase begins when assistance from outside starts to reach the disaster area - Food, blanket, clothing, shelter, sanitary engineering equipment & construction material are the needed supplies after the initial emergency phase VACCINATION- recommended for health workers
DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE DISASTER IMPACT & RESPONSE NUTRITION- assessing food supply after disaster - gauging nutritional needs - Calculating daily food rations - monitoring nutritional status
REHABILITATION REHABILITATION Restoration of pre-disaster conditions 1. Water supply- chlorination to disinfect water (increase residual chlorine to 0.2-0.5 mg/litre) - Protection measures to be followed: i) Restrict access to people & animals ii) Ensure adequate excreta disposal away from source iii) Prohibit bathing, washing & animal husbandry
REHABILITATION REHABILITATION 2. Food safety- kitchen sanitation maintained in feeding programmes 3. Basic sanitation & personal hygiene- emergency latrines constructed for excreta disposal 4. Vector control- Mosquitoes (dengue fever, malaria) - Rats (leptospirosis, rate bite fever) - Fleas (plague)
DISASTER MITIGATION DISASTER MITIGATION Measures designed either to prevent hazards from causing emergency or to lessen the likely effects of emergencies Measures include: a) Flood mitigation works b) Land-use planning c) Improved building codes d) Protection of vulnerable population & structures
DISASTER PREPAREDNESS DISASTER PREPAREDNESS Programme of long-term development activities whose goals are to strengthen the overall capacity & capability of a country to manage all types of emergency Measures: 1) Evaluate risks of regions to disaster 2) Adopt standards & regulations 3) Organize communication, information & warning systems 4) Ensure coordination & response mechanisms 5) Ensure availability of financial & other resources 6) Develop public education programmes 7) Coordinate information with news, media etc 8) Organize disaster stimulation exercises to test response mechanism
GENERAL MEASURES GENERAL MEASURES Do not use telephone Listen to the messages broadcast by radio Carry out instructions given by radio or loudspeaker Keep family emergency kit ready
FLOODS FLOODS Time factor Activity Before - - - Identify risks in the area. Eg. Downstream dam habitants Watching water levels after heavy rains Listening to weather forecast During - - - - Turn off electricity (reduces risk of electrocution) Protect people & property (upper floor, raised shelters) Beware of water contamination Evacuate danger zones After - - - - Wait until the water is declared safe before drinking Clean & disinfect rooms that were flooded Sterilize or wash utensils with boiling water Get rid of food that has been in or near water
STORMS, HURRICANES, TORNADOES STORMS, HURRICANES, TORNADOES Time factor Activity Before - - - - - Listening to weather forecast Choose a shelter in advance- cellars, basement etc Minimize effects of storm- eg. Check state of roofs, trees Take measures against flooding Prepare a family emergency kit During - - - - - - Listen to the information Do not go out in a car or a boat once storm is announced Evacuate houses- if told by authorities Tie down any object liable to be blown away- nail planks etc If caught outside- take refuge/ lie down flat in a ditch Keep away from electrical conductors - If out in a boat, get back to the shore If caught outside - Look for shelter in building (never under a tree) After - - - Stay indoors & do not go to stricken areas Give first aid to injured Check exteriors of dwellings & call for assistance - Keep away from fences & electric cables - Kneel down rather than standing
EARTHQUAKES EARTHQUAKES Time factor Activity Before - - - - Build in accordance with urban planning regulations Ensure all electrical & gas appliances are firmly fixed Avoid storing heavy objects in high positions Hold family evacuation drills During - - - - Keep calm, do not panic Indoors- move to central part of building Keep away from stairs Outdoors- keep away from buildings & electric cables After - - - Do not go in damaged buildings as tremors might start again Give first aid to injured Wait until the water is declared safe before drinking
CLOUDS OF TOXIC FUMES CLOUDS OF TOXIC FUMES Time factor Activity Before - - - Find out evacuation plans Familiarize themselves with alarm signals Equip doors & windows with tight fastenings During - - - - Close doors & windows Stop up air intakes Seal cracks or gaps with adhesive tape Turn off ventilators & air conditioners After - - Comply with authorities instructions Do not go out until declared safe
DISASTERS IN INDIA DISASTERS IN INDIA Northern mountains- snow storms, landslides, earthquakes Eastern coastal areas- floods, cyclones Western desert areas- draughts Eg.- Tsunami in Indian Ocean (2004) - Uttarakhand Flash Floods (2013) - Kashmir Floods (2014)
LEGISLATURE LEGISLATURE National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)- MoHA agency responsible for preparation of Disaster Management Disaster Management Act 2005- sets up NDMA at National level - sets up SDMA at State level Emergency Medical Relief Wing- DGHS under Ministry of Health & Family Welfare- coordinates activities related to health World Disaster Reduction Day- 2ndWednesday of October
METEOROLOGY METEOROLOGY Indian Meteorological Department (IMD)- 5 centres- Kolkata, Bhubaneshwar, Vishakhapatnam, Chennai & Mumbai- detects cyclone storms Satellite imagery facilities & cyclone warning radars provided to Cyclone Warning Centres Insat Disaster Warning System (DWS)- coastal areas of Tamil Nadu & AP Snow & Avalanche Study Establishments (SASE)- Manali- issues warning about avalanches 24-48 hours in advance
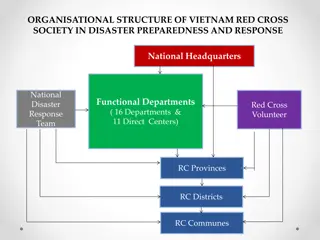
INTERNATIONAL AGENCIES INTERNATIONAL AGENCIES- - HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE ASSISTANCE OCHA- UNs Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs WHO UNICEF FAO International Committee of Red Cross etc. HUMANITARIAN
THANK YOU THANK YOU