Disaster Management Types of Plans by Kavita Nagpal
Management By Objective (MBO) is a key approach in disaster management, emphasizing participative goal setting. SWOT Analysis and Hazard/Vulnerability Analysis play essential roles in assessing risks, vulnerabilities, and developing action plans. Recognizing crisis situations and implementing timely responses are crucial in minimizing losses for communities and stakeholders.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Disaster Management TYPES OF PLANS Ar. Kavita Nagpal
Types Of Plans: Management By Objective MBO was first presented by Peter Drucker in his book, The Practice of Management in 1954. The core of MBO is participative goal setting, course of action selection and decision-making. It is observed that in participative goal setting, an individual is more motivated and committed towards achieving the goals. Benefits of MBO 1. Clarity of goals. 2. Effective synergy between overall objectives and individual s objectives. 3. Timeliness. 4. Committed actions from stakeholders make it immensely helpful in disaster management 1. SWOT Analysis evaluates Strengths, Weakness, Opportunities and Threats concerned with disasters. SWOT Analysis can be carried out form micro to macro level; three levels- Community Level Regional Level National Level
Types Of Plans: Management By Objective 2. Hazard and Vulnerability Analysis: Hazard recognition helps in ascertaining the areas that are affected by disasters. Vulnerability is a community s defenselessness to a given hazard, which is ascertained by the extent to which they can foresee, handle, respond to and recover from its impact. Various dimensions of Vulnerability Economic dimension Physical dimension Social dimension Aims of Hazard and Vulnerability Analysis To assess the risks and hazards the communities face and capacity of population to respond to such situations. To determine the facilities at risk and the degree to which they might be affected. To analyze each probable event from start to end. To involve communities, government authorities and organizations in the identification of hazard and assessment of vulnerability. To make action plans to prepare for and respond to the identified risks. To identify activities to avert or reduce the effects of expected hazards, risks and vulnerabilities.
Types Of Plans: Management By Objective Steps of Hazard and Vulnerability Analysis 1. Recognition of hazards and vulnerabilities. 2. Estimation of the probability of occurrence of an event. 3. An analysis of the probable human impact of each disaster terms of loss of lives and quantum of physical injury. 4. An assessment of the probable damage to the property. This includes analysis of replacement cost, setting-up cost and cost of repair. 5. An assessment of capacity, highlighting the capability and availability of resources with the community to reduce disaster risks and to organize effective response.
Identifying Crisis Situations: A Framework Crisis is an unwanted situation that takes people by surprise and pose a threat to the community at large. The time to take a decision for responding to this type of situation is usually very short, because of which the situation gets out of control and results in huge losses of both humans and property. A crisis has the potential to cause harm if no handled timely or properly. If identification of crisis can be done before, the losses can be diluted to a great extent. Crisis management is a process by which a community deals with a disaster which adversely affects the community and its stake holders. It is study that deals with recognizing, measuring, comprehending and coping with an emergency situation from the moment it appears to the point where rescue and recovery starts.
Identifying Crisis Situations: A Framework Three phases of Crisis Management are: 1. Pre-Crisis phase Identification, prevention and preparation. 2. Crisis Response Phase respond to crisis 3. Post- Crisis Phase review and ascertain the reasons of occurrence of crisis. Crisis identification steps: 1. An Analysis of the current situation based on information of past crises that the place might have had. 2. A study of regional vulnerability. 3. Identification of the ideal situation in which the crisis could be easily handled. 4. Identification of gap-based analysis 5. Formulation of detailed strategies 6. Communication of the plans to all stakeholders. 7. Monitoring of the situation closely to help in identifying the crisis.
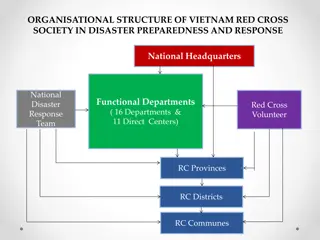
Organisational Structure and Design A blueprint of an Organisational structure should be made to determine the responsibility and accountability of each stakeholder. It is a formal division of the authorities and roles for ease of decision-making and serves as an integrating and controlling mechanism. The organisational structure for disaster management has four distinct departments based on the functionalities: 1. Disaster Mitigation division. 2. Disaster Preparedness division. 3. Disaster Response division. 4. Disaster Recovery division.
Authority, Delegation and Decentralization Authority - The authorities are the people who have the power to make decisions and to make sure that laws are obeyed. Delegation - is the assignment of any responsibility or authority to another person (normally from a manager to a subordinate) to carry out specific activities. Decentralization is the process of reallocation of duties and the decision making power to individuals away from a core authority. Roles, Skills and Competencies Leaders: leads initiatives and influence people to work for achievement of goals. Informational Role: Collection & dissemination of accurate information to handle disasters. Resource Allocator: During disastrous events judicious allocation of the resources by ascertaining the needs of the affected population is taken care by RAs. Taking on these roles requires certain skills:- 1. Leadership Skills. 2. Conceptual Skills. 3. Human Relation Skills. 4. Managerial Skills. Certain required Competencies: 1. Knowledge, which acquire through learning. 2. Experience. 3. Behaviour.
Importance of Control Process in Disaster Management Control Is a check mechanism that ensures all the activities in the organization take place according to the plan, and if there is any deviation, timely action is taken to bring back activities on the planning path. Benefits of Control Process: 1. Helps in achieving goals. 2. Makes efficient use of resources by ensuring that each activity is performed according to predetermined standard. 3. Improves employee motivation. 4. Ensures order and discipline. 5. Facilitates coordination in action. 6. Helps in minimizing errors. Types of Control: 1. Feed Forward Control pre - judgement on the bases of situation and control is triggered. 2. Concurrent Control - when action do not lead to the expected response, in such cases, action should stop immediately and the situation is brought under control. 3. Feedback Control An analysis of the action of the past gives insights and learning about what went wrong.
Group Dynamics It is a classification of behaviours and processes taking place within and between social groups. A noted social psychologist Kurt Lewin coined the term group dynamics in the early 1940s. An understanding of the intricacies relating to group behaviour helps in decision-making. Study involves sensitive information like social class divisions, regionalism and other forms of social prejudice. Nature and attitude of persons involved in group tasks. These information will help in establish in autonomous work groups The inter and intra group relationship of individuals should be good so that the achievement of goals is facilitated. Instead of being competitive, the individuals have to be adaptive and cooperative. Members of group follow the code of conduct of the group, and the responsibilities and obligations of each member are dictated by group norms. If a group is highly cohesive, the member may settle a conflict and can clear misunderstanding easily. The important aspect of an autonomous work group is that members trust one another and collaborate towards achieving goals. The attitude of collaborative decision making is warranted so that the group can take quick decisions at times of crises.
Understanding the Importance of Team Building in Disaster Management Team work foster better and open communication between individuals. It will help in : 1. A team has shared values and a common goal. 2. No individual identity of member. 3. A team has individuals who can be trained as member rather than as high performers . 4. A team shares values, integrity and commitment. 5. An effective team takes risks.
Capability Assessment Capability assessment helps in getting a realistic view of the quality and quantity of available resources for mitigating disaster and responding to it. Capacity assessment is a very important part of emergency management plans. It includes: 1. Personnel 2. Equipment and Material Capacity assessment rating are: 1. Satisfactory 2. Needs improvements 3. Deficient Capability Enhancement plans are documents based on the capability assessment data. Capability assessment must be done at regular intervals