Dive into Ecosystems and Climate Change
Explore the intricate elements of ecosystems and their vulnerability to climate change. Understand how living and nonliving components interact, the impacts of climate change, and the greenhouse effect. Learn about potential biome shifts, sugar farming locations, and the role of carbon in the environment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biology for a Changing World, 2e Clicker Questions Chapter 23
Which description best describes all of the elements of an ecosystem? A. the predators and prey in an area B. all the species living in an area and the physical and chemical environments C. all the plants and animals in an area D. all the living species that live and interact in the same area
How are ecosystems being affected by climate change? A. Climate change affects the living components by causing differences in the presence and interactions among species. B. Climate change affects the nonliving components of the environment by changing temperature, precipitation, etc. C. Both A and B.
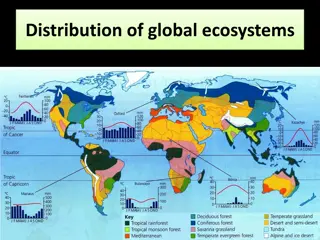
How would a taiga biome ( ) change if average temperatures increased 5 C? A. Taiga would become tundra. Taiga would become temperate deciduous forest. Taiga would become tropical grassland. B. C.
You are starting a new sugar farm to produce maple syrup. Where would be probably the most productive location over the next 100 years? A Canada B North C South D USA
Which of these contribute to the greenhouse effect? A. carbon dioxide B. water vapor C. methane D. All of these contribute to the greenhouse effect.
TRUE or FALSE? The greenhouse effect is an unnatural effect caused only by human actions. A. TRUE B. FALSE
How does the greenhouse effect warm temperatures on Earth? A. Energy from the Sun enters Earth s atmosphere and heats the surface. B. Some of the energy is reflected off the surface and leaves Earth s atmosphere. C. Gases absorb some of the energy and keep it in the atmosphere. D. All of the above.
Which of these does NOT contain carbon? A. pure water B. humans C. air D. plants
How quickly does carbon move through the carbon cycle? A. very quickly B. at a moderate speed C. very slowly D. it depends
If all greenhouse gas emissions stopped today, what would happen to Earth s climate? A. B. Temperatures would immediately stabilize. Temperatures would continue to increase for decades. Temperatures would immediately decrease. Temperatures would continue to decrease over time. C. D.
What is a major difference between how molecules of nitrogen and phosphorus cycle? A. Phosphorus can only cycle very slowly, while nitrogen always cycles very quickly. B. Nitrogen cycles through organisms while phosphorous does not. C. Most phosphorous does not cycle through the air, whereas nitrogen does.
Why would scientists want to collect data on atmospheric carbon dioxide levels? A. Long-term data can show how CO2 levels change over time. B. Short-term measurements do not give perspective on long-term changes. C. Identifying how CO2 levels change over time can help pinpoint the causes. D. All of the above.
Where do scientists get data on the levels of atmospheric CO2? A. They set up several long-term monitoring stations to directly sample the CO2 in the atmosphere. B. They drill soil cores to sample air bubbles to determine past CO2 levels. C. They sample levels of carbon in deposits such as fossil fuels.
Why is it useful to understand climate change? A. A better understanding of past climate changes and their effects on ecosystems can help us predict what will happen this time. B. It could help us find ways to slow, stop, or adapt to climate change before catastrophic change happens. C. Both A and B.