Dysfluency: Causes, Effects, and Resources
Learn about dysfluency, a complex speech skill that manifests as stuttering or stammering in both children and adults. Discover the causes, effects, when to seek advice, and valuable resources for support. Find guidance on speech and language therapy services, stammering charities, and resources for parents.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
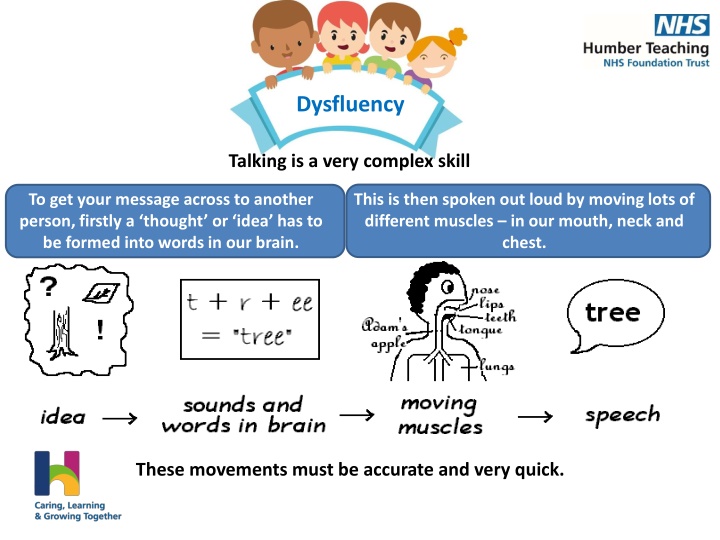
Dysfluency Talking is a very complex skill This is then spoken out loud by moving lots of different muscles in our mouth, neck and chest. To get your message across to another person, firstly a thought or idea has to be formed into words in our brain. These movements must be accurate and very quick.
Some children show hesitant or stumbling speech as they learn this highly complex skill. If children continue to be dysfluent as they get older, we may describe this as stammering. Dysfluency Talking is a very complex skill T-t-t-tree People often call this way of talking stammering or stuttering 8% of children go through a stage of this as part of their speech development. We sometimes call it dysfluent speech at this stage
Dysfluency Up to 3% of adults stammer It may run in families, but there is not always a family history It is not related to a child s ability 75% children will stop stammering, sometimes with help of the Speech and language therapist Dysfluency usually starts between the ages of 2 to 5 years 8% of children go through a stage of being dysfluent as they learn to speak. It affects more boys than girls Cause There is no single cause Cause Effect
Dysfluency When to seek advice about Dysfluency More information: Speech and language therapy department Dysfluency Team: 01482 692929 op 3 The stammer has been present for over 12 months The stammer is constant Your child shows signs of tension when talking You have a family history of stammering Adult stammering If you are an adult who stammers then contact CHCP speech and Language therapy services at Hessle Health Centre 01482 335165 X Your child is over 7 years old Your child loses eye contact or appears self conscious when getting stuck Your child starts showing an awareness of their stammer e.g. avoids talking, hands over mouth.
Dysfluency More Information and Useful Resources Action for stammering children is a charity which was set up to help support children who stammer and their parents . It works closely with the Michael Palin Centre for Stammering Children based in London. www.actionforstammeringchildren.org https://actionforstammeringchildren.org/support British Stammering Association BSA is a national organisation for adults and children who stammer, run by people who stammer. The BSA has an accessible website with information about all aspects of stammering. Website: www.stamma.org Helpline: 0808 8020002 https://stamma.org/get-support/parents https://stamma.org/get-support/in-education
Dysfluency My Stammering Tap and My Stammering Child are films we have made with children and adults who stammer to raise awareness and understanding about stammering. They can be seen on YouTube, by clicking the links or by scanning the QR codes. Help others understand the nature of dysfluency and how they can help My Stammering Child https://youtu.be/czMT- xZ71_4?si=_VcF-4QCwPhLJl7i My Stammering Tap https://youtu.be/OCaTka_dsPQ?si=l WcRMzP3_b5mWjvj
Dysfluency Your Speech and Language Assessment What to Expect Next Steps Therapist will ask you some questions about your child s speech Your child may just be monitored through the triage system or they may get referred to the specialist dysfluencyteam How long has your child been stammering? You may be asked to monitoryour child s speech over a shorttime this will help us make a decision about what the nextstep is. What do they do when they stammer? This may include a parent workshop/individualsession, a teacher s workshop, individual/groupregular or intensive therapy, support group. Are they aware they are stammering? Do other members of your family stammer? Referring to another service. Is the constant or does it come and go? This may be in clinic , by telephone or by video call
Dysfluency There is No Guaranteed Cure for a Stammer however Speech and Language Therapists Can Help Help others understand the nature of dysfluency and how they can help Support parents/carers to know how to help their child/young person Support children and young people. This may include learning strategies to help speech or understand how to become less sensitive and anxious about stammering and become confident communicators.

