Earthquake Dynamics and Plate Tectonics
Earthquake epicenter vs. focus, plate tectonics processes, types of plate boundaries, global quake distribution, depth records, mantle-core transition, earthquake terms, elastic rebound theory.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Questions of the Day 2/28/2017 What is the difference between the epicenter of an earthquake and the focus of an earthquake?
List processes involved in plate tectonics Convection currents in the mantle (temperature and density differences) Different densities of crustal plates oceanic and continental Composition and chemical properties of types of rocks magnetic, formation differences, % elements/ type Time- how fast the plates move: different plates rate of speed, and different times rate of speed Magnetic fields inside and outside of the earth structure
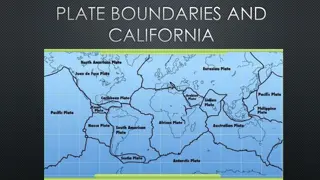
Types of plate boundaries Plate tectonics is currently the Plate tectonics is currently the most unifying geophysical theory of the planet dynamics, theory of the planet dynamics, based on the interactions between the earth s interior and its outer shell. between the earth s interior and its outer shell. Lithosphere plates move, break up, collide, slide past one another to form Lithosphere plates move, break up, collide, slide past one another to form new continents and oceans. new continents and oceans. Plate movement is a direct result of convection currents in the mantle Plate movement is a direct result of convection currents in the mantle Plates interact in one of three ways: divergence, convergence, and lateral Plates interact in one of three ways: divergence, convergence, and lateral sliding sliding Materials from plates are recycled at subduction zones/ mid ocean ridges most unifying geophysical based on the interactions
Global Distribution of Earthquakes why here?
Earthquakes and plate movement What is the deepest recorded earthquake on the border of SA? Explain how we know where the mantle ends and the core begins? How do we know the elemental make up in each layer?
Earthquake terms: Earthquake - movement of the ground caused by the release of energy from a sudden shift of rocks in Earth's crust. Fault - a break in Earth's crust where movement of rock (and quakes) occur
Elastic rebound theory: Earthquakes are produced by the rapid release of energy stored in rock that has been subjected to great forces. When the strength of the rock is exceeded, it suddenly breaks, releasing energy as seismic waves.
More quake terms: Focus - the point below Earth's surface where movement of rock produces an earthquake; where an earthquake starts Epicenter - the point on Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
Earthquake energy: When tectonic plates move they sometimes generate energy at their boundaries and that shock wave is known as a seismic wave. Seismometers (a.k.a. seismographs) are used to measure seismic waves, but those waves are not always detectable.
Seismogram = ? The graph output by a seismograph. It is a record of the ground motion at a measuring station as a function of time.
Body Seismic wave types: P waves: primary (first) waves which are push- pull in nature (compressional) S waves: secondary waves which shake particles at right angles to their direction of travel (transverse)
Two types of waves are measured How do each of the waves travel differently? Explain why some stations do not receive S waves.
What are S and P waves? Seismographs record movement and waves Surface waves travel along the outer layers of the earth Body waves travel through the earth s interior P waves ( push pull waves) ( like a spring): can move through solid rock or fluids. Fastest seismic wave. P-wave Animation S waves travel at right angles ( like a rope): can only move through solid rock. Slower than p-wave. S-wave Animation Earthquakes were 1st studied by the Chinese over 2000 yrs ago, Hmm why would they be interested?
Surface seismic waves: Travel along Earth s outer layer, causing ground movement similar to how ocean waves toss a ship. x How do scientists locate earthquakes? By measuring the arrival time of P and S waves (whose velocities are known) earthquakes can be triangulated.
Reading a Seismograph Which are the P waves and which are the S waves? Which type of wave would arrive at a location 1st? What causes them to arrive at different times?
Which station did was closer to the Epicenter? Which was farthest away? How do you know? (use evidence to explain)
Seismographs ---- record S and P wave arrival at a specific station - how is this information useful to determine the origin of the earthquake?? Consider the seismicity maps and the data we reviewed - if each station has it s own set of data, that means we could do what?
Rate of wave travel -Why do S and P waves travel at different rates? - How did the the ability to measure S and P waves help us understand what is in the center of the earth? One of the other ways to report and measure Earthquake information is the Mercalli scale.
Two different scales to measure Mercalli scale - perception based - 1884 became modified and again later - quantifies effects of the earthquake and damage caused using roman numerals - Numbering from 1 - 12 - Human perspective/ reports of damage
Hogwallow to Rattlesburg Use the reports from residents to identify the strength of earthquake waves at each location. Where does the epicenter seem to be? What was the highest rating reported? What is your overall impression of use of this scale? (pros and cons)