Economic Concepts: Scarcity, Incentives, Opportunity Costs, and Externalities
Explore the key economic concepts of scarcity, incentives, opportunity costs, and externalities through insightful examples and scenarios. Learn how these principles shape decision-making and resource allocation in different contexts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
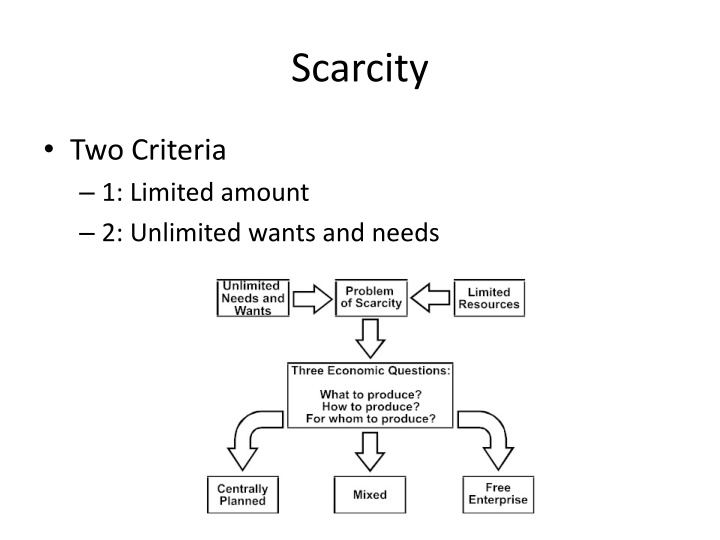
Scarcity Two Criteria 1: Limited amount 2: Unlimited wants and needs
Incentives (perverse or otherwise) Scenario 1 Professor Judy Thornton of the University of Washington reports that when she was a student in Moscow, the small, blue metal lamp on my dormitory desk was so heavy it took two people to lift it. The lamp base had been filled with lead The problem of grossly heavy products was not limited to the lamp industry, however. Professor Thornton tells of a cartoon that appeared in Krokodil, a popular weekly magazine, in which the entire staff of a plant is shown carrying a single giant nail out of the factory. Given this information: Finish the caption on the nail cartoon: Well, comrade, I see that our quota is measured in _________ this month. Professor Thornton explains that the quota based incentives encouraged factories to consciously sacrifice or trade off the unmeasured dimensions of product quality in order to maximize on measured dimensions.
Opportunity Costs/Benefits (choosing is refusing) College A College B Every choice involves opportunities gained and lost. Where are you planning to go to school after school? What chances will you get or lose out on?
Externalities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1FQyKM xv4mA