Economic Systems & Circular Flow: Production Possibilities Frontier
Concept of the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) as it illustrates trade-offs within an economy producing two goods. Learn about economic growth, opportunity cost, and various factors influencing the PPF through engaging visual aids and practice scenarios. Enhance your understanding of economic systems and the circular flow in Chapter 2.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PPC Review, Economic Systems & Circular Flow Chapter 2
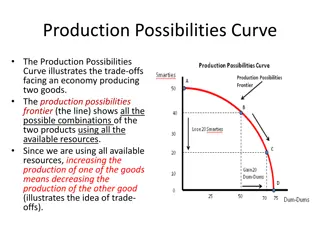
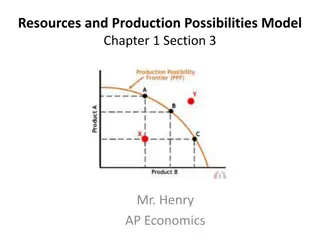
I. The Production Possibilities Frontier (curve) The PPC is an illustration of the trade-offs facing an economy that produces only two goods. It shows the maximum quantity of one good that can be produced for any given production of the other.
Economic Growth Economic growth results in an outward shift of the PPF because production possibilities are expanded. and 30 coconuts). The economy can now produce more of everything. (20 fish and 25 coconuts), it can move to point E (25 fish Production is initially at point A
PPC Practice Draw a PPC showing changes for each of the following: Pizza and Robots 1. New robot making technology 2. Decrease in the demand for pizza 3. Mad cow disease kills 85% of cows Consumer goods and Capital Goods 4. BP oil spill in the Gulf 5. Faster computer hardware 6. Many workers unemployed 7. Significant increases in education
Question #1 New robot making technology Q A shift only for Robots Robots Q Pizzas
Question #2 Decrease in the demand for pizza Q The curve doesn t shift! A change in demand doesn t shift the curve Robots Q Pizzas
Question #3 Mad cow disease kills 85% of cows Q A shift inward only for Pizza Robots Q Pizzas
Question #4 BP Oil Spill in the Gulf Q Capital Goods (Guns) Decrease in resources decrease production possibilities for both Q Consumer Goods (Butter)
Question #5 Faster computer hardware Q Quality of a resource improves shifting the curve outward Capital Goods (Guns) Q Consumer Goods (Butter)
Question #6 Many workers unemployed Q Capital Goods (Guns) The curve doesn t shift! Unemployment is just a point inside the curve Q Consumer Goods (Butter)
Question #7 Significant increases in education Q Capital Goods (Guns) The quality of labor is improved. Curve shifts outward. Q Consumer Goods (Butter)
II. Economic Systems The two general types of economic systems seek to address the economic problem in differing ways. In the market system, individual choice (desires of suppliers and demanders) is key to addressing the economic problem. In the command system, government direction (through central planning entities) is key to addressing the economic problem.
III. The Circular-Flow Diagram This is a model that represents the transactions in an economy by flows around a circle. It demonstrates the interdependence between households and businesses in a market economy. Some basic concepts: a) Household: A person or group of people that share their income. b) Business: Organization that produces goods and services for sale. Sometimes displayed as firm on this diagram. c) Firms sell goods and services in the product market. d) Firms buy resources they need to produce in the factor (or resource) market.