Effective Communication in Total Quality Systems
Learn about the importance of effective communication in total quality systems. Explore the fundamentals of communication, levels of communication, and its role in total quality. Discover how communication impacts customer focus, leadership, and teamwork in achieving organizational goals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Effective Communication in Total Quality System Rohit Ravva Sumanth Gadde AJ Schubert
Defining Communication Communication: the transfer of a message (idea, emotion, feeling, or something else) that is both received & understood. Only when message is received and understood is there communication
Communication vs. Effective Communication Effective Communication: Message is received, understood, and acted upon in desired manner Ex. Boss tells all employees to stay 15 minutes after hours for a week Employees understand message 3 employees choose to not stay after hours
Effective Communication May require: persuasion, motivation, leadership by the managers, and monitoring
Communication Levels One-on-one: two people (face-to-face, telephone, even a simple gesture or facial expression) Team or unit: peer group (solve problems or set team goals) Company-level: communication among groups (meeting with various departments - acount, sales, market) Community-level: groups inside and outside company (company s sales force communicating with clients)
Role in Total Quality If total quality is the engine, communication is the oil that keeps it running. Total quality key elements: customer focus, total employee involvement, leadership, teamwork, decision making, problem prevention, problem solving, and conflict resolution. ALL need effective communication
Customer Focus Determining customer needs requires Listening Asking Observing Probing
Effective Leadership Effective leaders need effective communication to: Inspire others Communicate goals Motivate employees to commit to company s goals
Teamwork Team members must continually communicate among themselves, with managers, and other teams. Communication needed for decision making, problem prevention, problem solving, and conflict resolution.
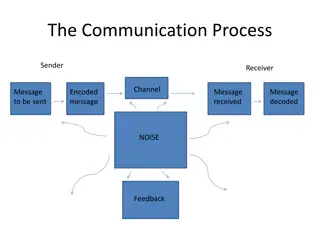
UNDERSTANDING COMMUNICATION AS A PROCESS Communication is a process with several components. These components are Sender-originator or source of the message Receiver-person or the group for whom the message is intended Message-the information, idea, feeling that is to be conveyed Medium-it is the vehicle used to convey the message
The Four basic categories of media are Verbal- Face to face conversations, telephone conversations, speeches etc. Non verbal-This category includes gestures, facial expressions and body language. Written-This category includes letters, memorandums, manuals etc. Electronic-This category includes the transmission of digital data.
RECOGNIZING INHIBITORS OF COMMUNICATION Managers should be familiar with the various factors that can inhibit effective communication. some of the most common inhibitors of the effective communication are Differences in the meaning Lack of trust Information over load Interference Condescending Poor listening skills
Premature judgments Inaccurate assumptions
ESTABLISHING A CONDUCTIVE COMMUNICATION CLIMATE Corwin p.king describes good communication as one that gives people the information they need to do their jobs well and also builds morale and encourages activity He also describes the bad communication as creates doubt and confusion, demotivating people and leading to cynicism
Some of the steps that manager should take care that does not happen Communicating with peers and employees as little as possible Being vague and obscure Communicating with only a select few individuals Limiting employee access Communicating only when it is personally advantageous to do so Ignoring the good ideas of the employees These are the possible ways that manager should take care that should not happen.
Communication by listenng Listening is one of the most important skill It is one of the skill that people are least likely to have
What is listening and hearing? Hearing is a natural process, but listening is not. Hearing is decoding of sound waves but listening involves perception. A person with highly sensitive hearing abilities can be a poor listener, but a person with impaired hearing can be a excellent listener Effective listening means receiving the message, correctly decoding it, and accurately perceiving .
INHIBITORS OF EFFECTIVE LISTENING Effective listening occurs when receiver accurately perceives the message. Several inhibitors can prevent this from happening, and some of them are due to Lack of concentration Interruptions Preconceived ideas Thinking ahead Interference Tuning out
LISTENING EMPATHICALLY Empathic listening is the highest level of listening . Empathic listening means listening with the intent to understand .It does not mean agreeing with what being said. Rather it means attempting to fully understand. Pretending means acting as if you are listening but tuning out. Using non verbal curves such as eye contacts, facial expressions etc. Selective listening means tuning in to only parts of the message. It involves on focusing intently on the speakers words.
LISTENING RESPONSIVELY Responsive listening involves seeking to receive and affirm the messenger as well as the message. Responsive listening can pay substantial dividends for managers in a total quality setting. Personal benefits to the managers include these Barriers are broken down Valuable insights are gained Communication is encouraged Misconceptions are cleared up Learning takes place
Some pointers that managers can use to become more responsive listeners and to help employees Allocate your listening time Concentrate fully Grant a fair hearing Make it easy for the person to talk Understand completely Clarify expectations.
IMPROVING LISTENING SKILLS Most people have room for improvement in their listening skills Listening skills can be enhanced when there is awareness of the need to improve Upgrade your desire to listen Ask the right questions Judge what is really being said Eliminate listening errors.
Understanding Nonverbal Communication Factors Much of the communication is nonverbal. Postures, gestures, voice tone and proximity factors are the components of non verbal communication. Body Factors Voice Factors Proximity Factors
Body Factors :- Postures, body poses, facial expressions, gestures and dress can convey a message. One of the keys to understanding nonverbal cues lies in the concept of congruence.
Voice factors:- It is an important part of nonverbal communication. The factors such as volume, tone, pitch of voice and rate of speech indicates anger, fear, impatience, unsureness, interest, confidence and variety of other messages.
Proximity factors:- It involves factors ranging from where you position yourself when talking to an employee, to how your office is arranged, to the color of the walls and decorations.
Communicating Verbally Show interest Be friendly Be flexible Be tactful Be courteous
Show interest :- when speaking with an employee show an interest in the topic, show that you are sincerely interested in communicating message also in receivers message. Be friendly:-A positive, friendly attitude will enhance verbal communication. A superior or disinterested attitude will shut off your communication.
Be flexible:- Flexibility can enhance verbal communication. If a manager calls his team members to explain new company policy but find they are focused on a problem that is disrupting their work schedule, he must be flexible enough to put his message aside for the moment and deal with the problem. Be tactful:-
Asking Questions effectively Drop your defenses State your purpose Acknowledge emotions Phrase questions carefully
Drop your defenses:- People have their public and private faces; what is said is not what is felt. They build walls and put up defenses, in order to communicate effectively it is necessary to break through defenses and open up. State your purpose:- It allow the receiver to focus on your question rather than worrying about why you are asking it.
Acknowledge emotions:- Avoid ignoring the emotions of people. Use open ended questions:- You will learn more when listening than talking. Phrase your questions carefully. Avoid questions with yes / no answers.
Communicating in writing Plan before you write Be brief Be direct Be accurate Practice self-Editing
Be brief:- Explain your purpose and state your points in as few words as possible. Be direct:- You don t want recipients wasting time rather than getting to the point. (Time is Money) Be accurate:- Take time to identify specifics such as dates, numbers, quantities and so on.
Practice self editing:- Never send your first draft. First draft is what you are saying and second draft is how you say it.
Writing Better Reports Define the problem Develop a work plan Gather relevant data Process findings Develop conclusions Make recommendations
Communicating Corrective Feedback Be positive Be prepared Be realistic Don t be completely negative
The two approaches of giving corrective feedback :- Tell-ask-listen Listen-ask-tell
Whos on First? baseball_diamond.gif 0007E9E4Macintosh HD 7C261D7F:
Whos on First? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sShMA 85pv8M
Improving Communication Keep up-to-date; can t communicate what you don t know Prioritize information; don t overload employees with info. Decide who to inform; employees have enough on their mind Determine how to communicate Follow up; make sure employees understand
Written vs. Verbal Written General info (company policies) Info that requires action (turn in ethics form by Friday) Verbal Reprimanding/commending employee Resolving conflict
Electronic Communication Pros Instant Mass copies Printable Cons No body language, voice tone, facial expression, or eye contact Easy to overuse; unecessary messages