Effective Liquidity and Working Capital Management Measures
Enhance your business's liquidity and working capital management with strategies like internal financing sources, liquidity reserves, working capital optimization, and immediate operational measures to prevent insolvency risks. Explore options such as shareholder support, tax creditor deferral, supplier creditor negotiations, and short-term sales strategies for boosting liquidity and financial stability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Liquidity and working capital management measures
Overcoming a liquidity crisis (cont.) Internal Financing Sources Internal Financing Sources The possibilities of internal financing sources depend strongly on the company and the respective industry. If the company has been successful in the past and has substantial assets or a large number of machines, there are alternatives to debt capital or the injection of equity. Liquidity Reserves Liquidity Reserves Non Operating Assets Non Operating Assets Sale and Lease Back Sale and Lease Back OPTION OPTION 01 01 OPTION OPTION 02 02 OPTION OPTION 03 03 Release of existing Liquidity reserves Sale of non- operating assets (e.g. reserve land or former production, storage and operating facilities) Sale of assets required for operations - Sale and lease back Working Capital Working Capital Cash Management Cash Management OPTION OPTION 04 04 OPTION OPTION 05 05 Working Capital Management (see following slides) Installation of a liquidity management office screening for business health
Overcoming a liquidity crisis (cont.) Overview of measures for prevention of insolvency and liquidity crisis by measure owner Overview of measures for prevention of insolvency and liquidity crisis by measure owner In the event of an acute liquidity crisis and concrete insolvency risk, all relevant options should be used. Provided that a coherent restructuring concept is in place, many parties involved are often prepared to support - otherwise, in case of doubt, they too would face a high risk of loss. Shareholder Shareholder Equity injection Shareholder loan Deposit payout Tax creditor Tax creditor Deferral of tax liability Decree Suspension of execution Supplier creditors Supplier creditors Prolongation of the term of payment Deferral Payment by instalments agreement Interest remission Social insurance agency Social insurance agency Deferral of contributions Suspension of execution Creditors (banks) Creditors (banks) Increase in credit lines Interest concessions ("restructuring interest") Prolongation Waiver of repayment Public sector Public sector Subsidies Guarantees Approval of structural crisis cartels screening for business health
Immediate operational measures Operational Measures Complementary objectives serve to secure equity and liquidity in the short term. In the medium term to make the company competitive on the cost side Result effective Liquidity Effective Optimization of stocks Reduction of material costs Prevention of impending Avoiding the Avoiding the indebtedness indebtedness risk of over- - risk of over Accounts Receivable Management Reduction of personnel expenses illiquidity Accounts Payable Management Reduction of other operating expenses Short-term sales increase/stabilization Disinvestments Reduction/ postponement of investments screening for business health
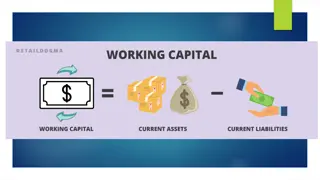
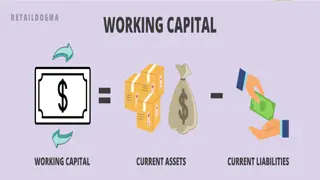
Working Capital Management Structural Measures Structural Measures Operative Measures Operative Measures Special sale of old stocks, return to suppliers bringing forward customer- related production orders Review/reduction of lot sizes (especially in the case of missing customer reference) Check the relationship of setup costs to inventory financing Changes in the supplier relationships Improvement of the planning system/ -accuracy Shortening of processing times Reduction of product variety, complexity and special designs Introduction Modular design Set up consignment warehouses Merging of warehouses Optimization of the stock accounting Working Capital Management or Working Capital Controlling is intended to optimally control the so-called working capital, the capital tied up in a company 01 01 Working Working Capital Capital Measures Measures 02 02 screening for business health
Working Capital Management (cont.) Structure of Accounts Receivable Structure of Accounts Receivable Dunning System Dunning System Is there a ban on dunning? Reasons? When is the 1st reminder sent? How often? What happens after the last dunning level? How are reminders formulated? Exploitation of legal remedies? Who initiates the reminders? Who is involved in process? How is the sales department involved? Cause analysis of overdue receivables? Age Domestic/ foreign Countries (payment history) Divisions Customers / buyers (creditworthiness) Sales responsibilities Dunning is the process of methodically communicating with customers to ensure the collection of accounts receivable. Communications progress from gentle reminders to threatening letters and phone calls and more or less intimidating location visits as accounts become more overdue. 02 01 Accounts Accounts Receivable Receivable Payment Terms Payment Terms Which conditions on which basis? Who determines new conditions? Amount of average payment term? Procedure with down payments? Which means of payment? 03 screening for business health
Working Capital Management (cont.) The payment of invoices at the right time can maintain liquidity in the company and increase interest income The terms of payment are determined by the suppliers when the order is placed and only in a few cases is there room for manoeuvre for the client The following levers can be considered for the derivation of measures: Invoice Receipt Verification Invoice receipt date should be used as the basis for calculating the due date Calculation of cash discount deductions Checking whether it is economically more sensible to take advantage of a discount than to take advantage of a payment term Minimize payment runs Bundling the payment of invoices into only one or two payment runs per week Optimization Optimization of liabilities of liabilities screening for business health
Working Capital Management, 3 levels of action Factoring / Optimization of the dunning process, Shortening the payment periods Risk hedging (creditworthiness, price changes, interest rate and currency risks) cash pooling In particular, three central levels of action are available to optimize working capital: Optimization of the Accounts Receivables Optimization of stocks and supply Optimization of the accounts Payable Accounts Accounts Receivables Receivables Reduction of inventories Special sales Just-in-time production, consignment stock Stocks and Stocks and Supply Supply Accounts Accounts Payable Payable Extension of payment periods screening for business health
Working Capital Management: The Operating Cycle Current assets are needed because sales do not convert into cash instantaneously; there is always an operating cycle cycle involved in the conversion of sales into cash The Operating cycle is divided into three phases: Acquisition of resources such as raw materials, labor and overheads. Manufacturing of products, this includes conversion of raw materials into work in progress and finished goods. Sales of the finished product either for cash or on credit (accounts receivable) The length of the operating cycle of a firm is the sum of the inventory conversion period and debtors conversion period . (Gross Operating Cycles) operating Cash Cash Inventory Inventory Operating Operating Cycle Cycle Accounts Accounts Receivable Receivable screening for business health
Working Capital Management - Inventory Conversion Period ??? ???????? ????????? ??? ???????? ?????????? 365 The inventory conversion period is the total time needed for production and sales. It includes raw material conversion period, work-in progress conversion period and finished goods conversion period. ??? ???????? ?????????? ?????? = ???? 1 ???? ?? ???????? ???? ?? ?????????? 365 ???? ?? ???????? ?????????? ?????? = ???? 1 ????? ?? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ????? ???? 365 ????? ?? ????? ?????????? ?????? = ???? 1 screening for business health
Working Capital Management - Debtors Conversion Period The debtors conversion period is the time required to collect the outstanding debts from customers. However, a company may acquire goods or services on credit thereby positioning payment. The period during which payment is postponed is known as payable deferral period. It is the length of time the firm is able to defer payments on various purchases. The difference between the(gross) operating cycle and payable deferral period is known as net operating cycle or cash conversion cycle. ??????? (???????? ??????????) ?????? ????? 365 ??????? ?????????? ?????? = ???? 1 ????????? (???????? ???????) ?????? ???? ???? 365 ???????? ???????? ?????? = ???? 1 screening for business health
Exemplary financial measures: Sale and Lease Back Lease-back, sale-lease-back and sale-and-rent- back are synonymous terms for a special form of leasing in which an organization sells an asset (property, machinery or vehicle, but also intangible assets such as brands or patents) to a leasing company and simultaneously leases them back for further use. One-off liquidity effect / realization of hidden reserves Long-term liquidity burden from lease payments Much more difficult with used goods than together with acquisition of new goods (manufacturer leasing) Object value consideration instead of company assessment (at least in the starting point "Creditworthiness of the object") Company Receives cash Receives cash payment payment Pays leasing instalments Pays leasing instalments over the contract period over the contract period Sells machinery Sells machinery or property or property Leases machinery Leases machinery or property back or property back Sale and Lease Back Organization screening for business health
Exemplary financial measures: Factoring Factoring is a method of sales financing in which the supplier sells its receivables from the delivery of goods to a financial institution. Sale of receivables with transfer of the credit risk (genuine factoring) Company Company Delivers Delivers Goods / Services Goods / Services Sells Claims Sells Claims Pays out claim Pays out claim or Factoring Factoring Organization Organization Customer Customer without transfer of the credit risk (fake factoring) Checks Creditworthiness Checks Creditworthiness Pays Claim Pays Claim screening for business health
Exemplary financial measures: Shareholder Loan Easy and quick to implement (even informal) A classic problem of founder-operated medium-sized companies: Often the crisis is not recognized or recognized too late or it s considered as a short-term weakness Because next year "for sure" will be better, the owner provides his own capital This capital is later missing as an own contribution to the restructuring In the event of insolvency, shareholder loans are subordinated Company Company Company pays interest and amortization Shareholder Shareholder Shareholder provides a Loan to the company screening for business health
Exemplary financial measures: Equity Injection Inserting equity in the form of capital or cash for the purpose of lowering debt ratios and/or providing capital to stimulate growth. Considerations: Considerations:- - Additional financing by the existing shareholders is easier: "we know each other". It does not change the shareholder structure and relationships (at least as long as everybody tags along) No company valuation required Problems arise when only some of the existing shareholders participate or external investors join: Who bears the risk? What does the investor get (what he does not already have)? screening for business health
Exemplary financial measures: Equity Injection HOWEVER HOWEVER Many owners are hasty in injecting equity in the crisis. It is important to first develop a restructuring plan and determine the overall capital requirements. If this exceeds the possibilities of the owners, further sources of financing must be found. These usually require significant contributions from the owners. If the money is then already tied up in the company, banks in particular often refuse to support them. screening for business health