Effective List Management in Python Programming
Learn how to efficiently store and manipulate multiple pieces of data using lists in Python. Explore techniques such as adding to a list, editing list contents, and removing items by index or value. Discover the power of lists for handling large sets of data effortlessly.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lists CMSC 201
Motivation If we want to average three numbers, we can easily do the following: num1 = input( Please enter a number: ) num2 = input( Please enter a number: ) num3 = input( Please enter a number: ) print((num1 + num2 + num3) / 3) What if we want to average a 100 different numbers? Do we make a 100 different variables?
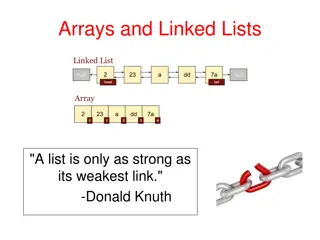
Lists Lists are a way of storing multiple pieces of information in the same place! They work like this: myList = [9, 10, 11] Creates three variables, one that has the value 9, one with the value 10, and one with the value 11. These are stored in order! print(myList[0]) Prints 9, since it is the first thing in the list. myList[1] will be 10, and myList[2] will be 11.
Lists Why is this better? This means that we can refer to items in the list by their number (or index index). The index can be a variable or an actual number. a = 10 print(myList[a]) Also, the lists can get as big as we want!
Adding to a List If you want to add something to the end of a list, simply call append. myList = [ 3, 4, 5] myList.append(6) print(myList) (3, 4, 5, 6)
Editing List Contents If you want to change something in a list, just use the assignment operator! myList = [1, 2, 3] myList[1] = 100 print(myList) (1, 100, 3)
Remove By Index If you want to delete something at a certain index, just call pop(index). myList = [10, 12, 14] myList.pop(1) print(myList) (10, 14)
Remove By Value If you want to delete a certain value from a list, use remove(value) myList = [10, 12, 14] myList.remove(14) print(myList) (10, 12)
List Contents Lists can hold any combination of types! This is fine: myList = [ hi , True, 10] We can even put lists inside lists! myList = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
2D Lists myList = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]] When thinking of 2D lists, think of it as a grid! 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 If you want to get out the thing at row 1, col 2 you write: myList[1][2]