Effective Research Methodologies for Data Collection and Analysis
Discover various research designs such as analytical research, experimental research, and descriptive research along with methodologies like systematic reviews and surveys. Explore different contexts, settings, and interventions in research settings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
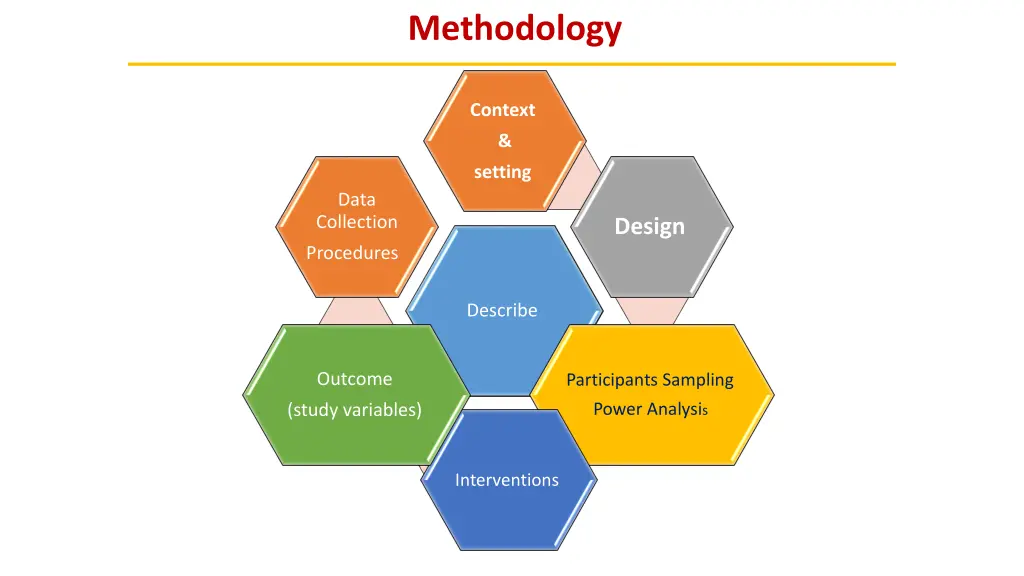
Methodology Context & setting Data Collection Design Procedures Describe Outcome Participants Sampling Power Analysis (study variables) Interventions
Methods Few words can usually do the job. Place and time; where & when the participants were selected. Study design and Setting Who was studied, & how many were studied? Describe important eligibility criteria Refusal to participate, dropouts, & missing information Randomization, Sampling & Power analysis Participants
Research Design Analytical Research Experimental Research Pre-designs Descriptive Research Reviews Quasi-designs Case Study Survey True-designs Cross-Sectional Meta-Analyses Longitudinal Statistical- designs Correlational
Analytical Research Reviews (with/without) meta-analysis A systematic review is defined as a review of the evidence on a clearly formulated question that uses systematic and explicit methods to identify, select and critically appraise relevant primary research, and to extract and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. Statistical methods (meta-analysis) may or may not be used to analyze and summarize the results of the included studies
Descriptive Research Case Study A detailed information from a single subject Often uses a narrative format May be non-experimental or experimental Develops a profile of the subject using: Visual observation Interviews/surveys/questionnaires Objective data May provide generalizations about other subjects with similar conditions
Descriptive Research Survey Cross-sectional: Status of a various group (s) at a given point in time. Observational studies in which all the measurements are performed on a single occasion (no follow-up period) Longitudinal (Cohort): Status of a given group at various points in time Prospective vs. Retrospective Correlational: Relationships between variables
Experimental Research Experimental research involves a direct assessment of how one variable influences another This allows the establishment of causality Independent variables Dependent variables Control (confounding) variables Experimental research design Pre-Experimental Quasi-Experimental True-Experimental
Pre-Experimental Research Design One-shot studies T One-group pretest-posttest Static group comparison (one shot w/2 groups) T X O1 O2
Quasi Quasi- -Experimental Designs Experimental Designs Quasi-experimental designs: Experiments that have treatments, outcome measures, and experimental conditions but that do not use random selection and assignment to treatment conditions. Non-equivalent control group design Time series Single subject designs (Case study) O3 O4 O5 O1 O2 O6 T
True Experimental Designs True Experimental Designs Characteristics of true experimental designs Manipulation (treatment) Randomization (sampling of subject& assignment of subject) Control group One independent variable Types Posttest control group design Pretest-posttest control group design
Pre-testing The measurement of a dependent variable along subjects before they have been exposed to an independent variable. Post-testing The measurement of a dependent variable among subjects after they have been exposed to an independent variable. Experimental Group A group of subjects to whom an experimental stimulus is administered. Control Group A group of subjects to whom no experimental stimulus is administered and who should resemble the experimental group in all other respects.
Post-test Only Control Group Design One group is administered a treatment. NO experimental treatment or procedures is administered to second group. Pretest are not taken on each group. Posttest measurements are taken on each group. T X O2 P O2 Statistical test Independent t test (parametric) Wilcoxon signed rank test (non-Parametric)
Pre-test-post-test control group design One group is administered a treatment. NO experimental treatment or procedures is administered to second group. Pretest and Posttest measurements are taken on each group. R O1 X O2 R O1 O2 Statistical test Paired t test (parametric) Wilcoxon signed rank test (non-Parametric)
Solomon Four-Group Design This design involves four groups. Two of the groups experimental and two control. Two groups include no pre-test (so that the effects of the pretest can be evaluated). All group include Posttest. Statistical test Covariance analysis
Participants Participants Exclusion criteria Sampling Inclusion criteria Consent form Participants
Sampling Target Pop. (N) Sample (n) Effective Sampling produces a n which is representative of N Note: n is only ever representative of the N it was drawn from, i.e. not necessarily the general population.
17 SAMPLING BREAKDOWN
Types of Samples Probability (Random) Samples Simple random sample Systematic random sample Stratified random sample Cluster sample Non-Probability Samples: Convenience sample 3 factors that influence sample representativeness Sampling procedure Sample size Participation (response) 18
Methods Intervention(s) or Main exposure(s). include interventions that were controlled by the investigators or exposures that the investigators measured but did not manipulate, Intervention Describe new methods in enough detail that another researcher can reproduce your experiment. Describe established methods briefly, and simply cite a reference where readers can find more detail. Report reliability and validity and moreover, if you test it Outcome measures Describe new methods in enough detail that another researcher can reproduce your experiment. Describe established methods briefly, and simply cite a reference where readers can find more detail Data collection procedures Statistical analysis State all statistical tests and parameters Ordinary ones without comments, Advanced or unusual ones require citation
Methodology It is first section of the paper in which subheadings should be used . Cut and-past from previous work of the author(s), not somebody else s. Enough information must be given so that the models/experiments can be reproduced. If new measures, methods describe in detail. If the method has been previously published in a scientific journal, only the reference should be given with some identification. Don t mix some of the results in this section. Write in the Future (Past) tense Avoid use of trades names (usually generic or chemical name)






















