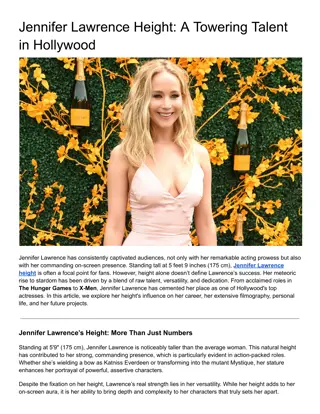
Effective Student-Supervisor Relationship Expectations and Best Practices
Explore the importance of student-supervisor relationships in academic success, focusing on expectations from both parties. Learn about common pitfalls, shared experiences, and practical guidelines for successful supervision processes. Discover insights from research and literature on fostering positive relationships and enhancing doctoral student engagement.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Student Supervision Basic Module Training of Trainers (ToT) EFFECTIVE SUPERVISION PROCESS PART 2 Raja Maznah Raja Hussain Rohana Othman Nurahimah Yusoff Jennifer Chan Kim Lian Mansor Ahmad Zainab Noor 11-12 August 2015
DAY 2 8.30-9.00am Expectations of Supervisors and Supervisees 9.00-10.00am Contractual Plan of Studies - Common Issues and Pitfalls in Supervision and Sharing of Experience 10.00-10.30am Activity 3&4; and submit assignment 10.30am - Tea Break 11:00am-1:00pm- Review of research process - read the two cases and write your case
The Other Perspective and Expectations
Insights from Research and Literature A positive student-supervisor relationship is an important factor in student success. One of the strongest predictors of postgraduate completion is having expectations met within the student/supervisor relationship. Sadly, mutual expectations are rarely discussed explicitly, thus leading to unmet, unclear and unarticulated expectations.
STUDENTS EXPECTATIONS FROM SUPERVISOR (PHILIP AND PUG, 2000) Friendly, open and supportive Read work well in advance Availability of supervisor, interest in research Friendly, open and supportive Constructively critical Good knowledge of the research area Meetings for exchange of ideas Sufficient interest in their research to guide the students Role model Academic role development
Expectations from supervisor on the students (Philip and Pug, 2000) 1. Students to be independent 2. Produce drafts 3. Regular meeting with students 4. Honest in report their progress 5. Follow the advice given 6. Student excited about their work , to surprise them and fun to work with
Cont Barnes (2010) studies supervisor expectations and found five broad expectations of student engagement: 1. Be committed to the doctoral process; 2. Have integrity; 3. Work hard; 4. Make progress; and 5. Be good citizens of the department.
Clarifying Expectations Mismatched Expectations Realistic Expectations Adjusting Expectations Mutual Expectations
Supervisors Expectations From a supervisor s perspective, the student s role is to: Attend regular meetings with the supervisor; Submit written work to the supervisor regularly; Take notice of the supervisor s comments and feedback; Produce a research proposal within an appropriate timescale.
Supervisees Expectations However, the supervisee may have a different set of expectations that might include: Supervisors to be available; Supervisors to structure meetings usefully; Supervisors to read the students work in advance of meetings; Supervisors to be constructively critical;
Cont Supervisors to be friendly, open and supportive; Supervisors to have good knowledge of the research area; Supervisors to show a keen interest in the research; Supervisors to display an interest in the career prospects of students.
Clarifying Expectations and Establishing Good Communications Research Direction How much direction do you expect from your supervisor? How much direction does your supervisor expect to exert over your research?
Cont Knowledge and Skills: Would you rather find things out on your own, or would you prefer to be taught by your supervisor? How do your preferences line up with your supervisor s? What skills do you have and which skills does your supervisor expect to have?
Cont Time Management and Meetings How often do you expect to meet with you supervisor? How much does he/she expect from you?
Cont Feedback and Constructive Criticism: How often do you expect input or feedback from your supervisor? What are your supervisor s expectations?
Cont Turnaround Times How quickly do you expect your supervisor to provide feedback on work that you have submitted for review? How quickly does your supervisor anticipate being able to provide feedback?
Cont Communication between Meetings Does your supervisor prefer to communicate by telephone or e-mail? How quickly do you expect a response to an email or phone message?
Cont Expectations for Written Work: Does your supervisor expect to receive your work all at once, or in smaller chunks? Does s/he expect drafts to be works in progress or fairly polished pieces almost ready for publication? At what intervals does your supervisor expect you to submit work? Would your supervisor prefer to receive documents in hardcopy, or electronically? Adapted from McGill University
Contractual Plan of Studies Supervision is deemed as a complex process and deals with people, research project, time and financial aspects. A Mutual Agreement Developing a memorandum of understanding. Different for each student and can be revised annually.
Contractual plan of studies 1. research work to progress well within the stipulated time of studies 2. supervisor and student must work out an agreeable or acceptable contractual plan of studies at the beginning of supervision process 3. realistic and feasible 4. useful guide to monitor the progress of research work.
Supervision contract with doctoral students Learning contract: learning goals, tasks, method of assessment, duration Code of practices Practicalities : timetable, study plan, assessment and evaluation Communications procedures and methods - face to face, emails, Record : log book Roles and responsibilities
ACTIVITY 2: CONTRACTUAL PLAN OF STUDIES GANTT CHART, MILESTONES (30 MINUTES) ( SUBMIT ASSIGNMENT-10% ) 1. Working as a group; based on your experience as a supervisor, develop contractual plan of study 2. Present the contractual plan and highlight the key issues and the importance in relation to the completion of research work in student supervision.
Sample Agreement for Supervision: Student and supervisor Sample of contractual agreement MOU Template (Otago) Sample supervision/mentorship agreement (Western Ontario) Supervisor Agreement (Saskatchewan) Letter of Understanding (Canadian Association for Graduate Studies, CAGS).
Common Issues and Pitfalls Common supervision problems include: supervisor lacking necessary expertise to provide support supervisor s absent due to study leave or sickness supervisor providing unclear guidance and advice supervisor being slow in providing feedback on written work supervisor leaving during student s PhD student feeling undermined or bullied by a supervisor.
Activity 3 Key expectations of supervisors and supervisees (15 minutes) Working in a group, list the key expectations of supervisors and supervisees. Derive scenarios of experiences among participants and discuss responses to the situations. Share your list with the class. Make a note of the similarities and differences in the key expectations of supervisors and supervisees
Activity 4 Feedback Practice - 15 Minutes Reflect on your feedback practice and share with your group members. During the session you will have an opportunity to present to the colleagues and facilitator for review.
ACTIVITY 2: CONTRACTUAL PLAN OF STUDIES GANTT CHART, MILESTONES (30 MINUTES) ( SUBMIT ASSIGNMENT-10% ) 1. Working as a group; based on your experience as a supervisor, develop contractual plan of study 2. Present the contractual plan and highlight the key issues and the importance in relation to the completion of research work in student supervision.
CONCLUSION Thank You.