Efficiencies of Pump: Types and Operating Points
Learn about the three types of efficiencies of a pump - manometric, mechanical, and volumetric efficiencies - and how to calculate the operating point of a pump system using specific characteristics. Explore a detailed solution example to understand the discharge in a water system, given certain pump characteristics.
Uploaded on | 3 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
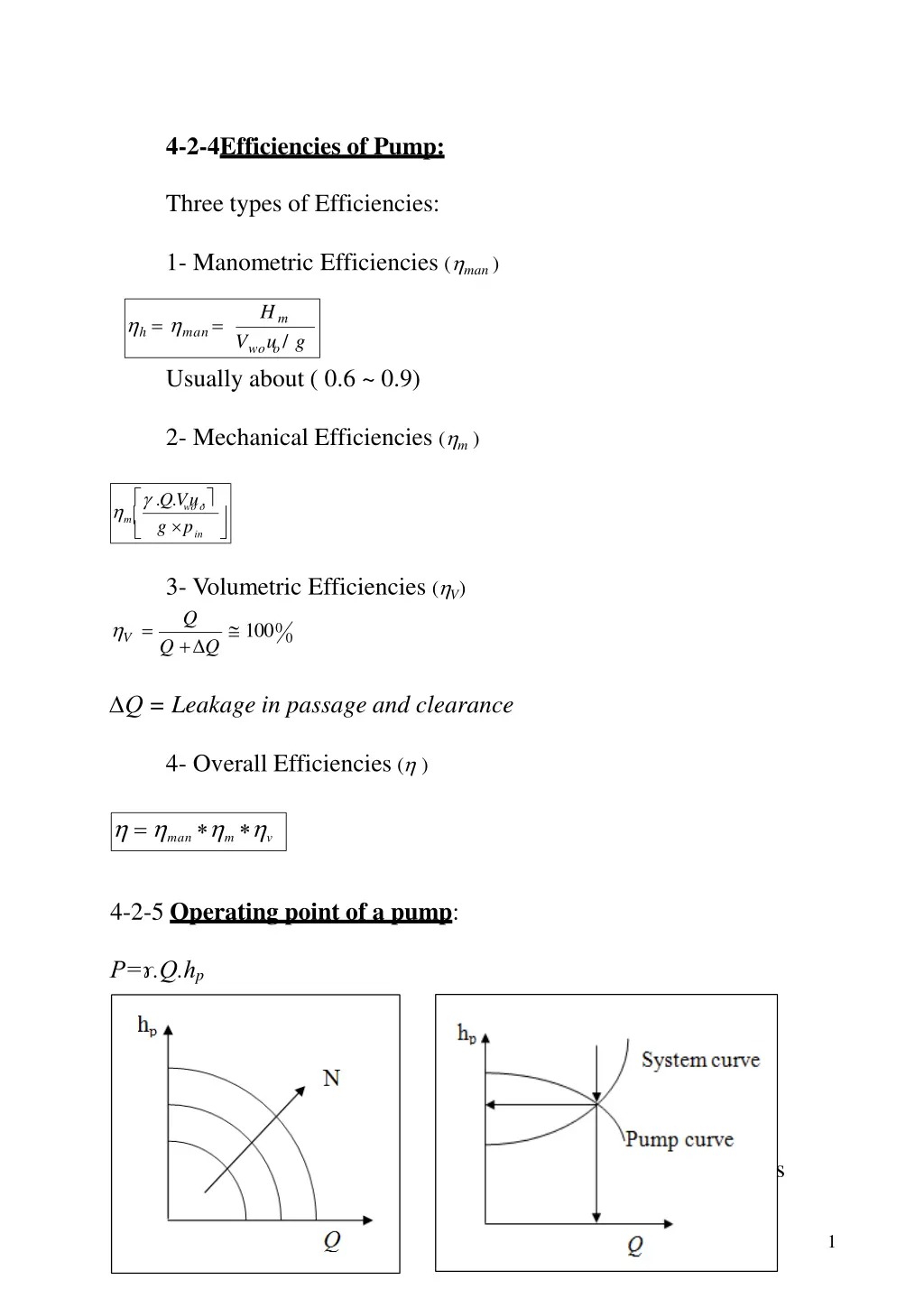
4-2-4Efficiencies of Pump: Three types of Efficiencies: 1- Manometric Efficiencies ( man) Hm u / g h = man= V wo o Usually about ( 0.6 ~ 0.9) 2- Mechanical Efficiencies ( m) .Q.V u. wo o m g p in 3- Volumetric Efficiencies ( V) Q = 1000 V 0 Q + Q Q = Leakage in passage and clearance 4- Overall Efficiencies ( ) = man m v 4-2-5 Operating point of a pump: P= .Q.hp System characteristic s 1
-For the system, use S.F.E.E. 2 2 P V 1 2g =P V 1 2 2 2g + + z1 + hp + + z2+ + hm.l hf .l K(v2/2g) f (L/D)(v2/2g) = (Z2 Z1 ) + (8Q2/ 2gD4)[ k + f (L/D)]for system car.Eq. Example: What will be the discharge in the water system in fig. if the pump has the following characteristics? m3/s Q 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.41 hp 59 57.5 54.5 30 Zero m 2
Solution: S.F.E.E. (1) and (2) V2 1 + z1 + hp = V2 P1 + P2 +2+ z2 + hm.l + h f .l 2g 2g Ds = Dd Vd=Vs , hp= (Z2 Z1 ) + v2/ 2g [ 0.5+ 0.35+1+ 0.015*( 1000/0.4) hp= 30+127Q2 m3/s m Q 0 0 0.1 0.01 0.2 0.04 0.3 0.41 Q2 127Q2 0 1.27 30 31.7 hp 3






















