Electric Circuits
In 'Electric Circuits Unit 131,' immerse yourself in the world of electrical circuits with detailed explanations and practical examples. Gain a comprehensive understanding of fundamental concepts and explore advanced topics to enhance your knowledge. This unit provides a solid foundation for beginners and serves as a valuable resource for those seeking to deepen their expertise in circuit analysis and design. Dive into the complexities of electric circuits and unlock the potential for innovation and problem-solving in this dynamic field.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electric Circuits Unit 13 1
Series and Parallel Circuits Leaning Objectives 1. Explain what series and parallel circuits are 2. Calculate the value of I, V and total resistance in series and parallel circuits 2
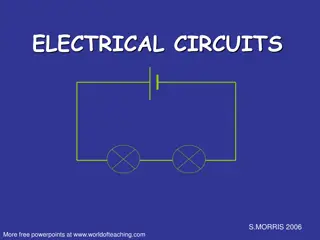
Series circuit Series Circuit 3
Series Circuits 1. Current in each component is the same V 2. Potential difference (EMF) across the power-supply in a series circuit is sum of p.d across each of the components V V 3. Total resistance is equal to the sum of all the resistances (R=R1+R2+..) EMF=18V 4
Question1 Q1. The lamp and the variable resistor are in parallel or series? Answer: Series The current in the circuit is 2 A. Q2. What is the value of A1? Answer: 2 A Q3. What is the value of A2? Answer: 2 A 5
Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Parallel Circuit 6 Video
Parallel Circuits V 1. Total current in the main circuit is the sum of the currents in the branches Potential difference across each of the component is the same Total resistance R : 2. 3. V EMF=18V Note: Current in lower value resistor is more then the current in the higher value resistor 7
Question 2 Q1. The two lamps L1 and L2 are in series or parallel? o Parallel Q2. If A2 is 1 A & A3 is 2A, what is A1? o 3 A Q3. Complete the missing items 8
Summary: Series and Parallel Current PD Resistance ??? Series Same Distributed R=R1+R2+R3 Parallel Distributed Same 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 +... Total resistance is always smaller than the smallest resistance 9
Question 3 Q1. The lamp and the variable resistor are in parallel or series? Answer: Series The current in the circuit is 5 A. Q2. What is the value of current in lamp? Answer: 5 A Q3. What is the value of current in variable resistor Answer: 5 A Q4. V1= 1 Volt, calculate V2 Answer: 0.5 Volt Q5. Lamp has a resistance of 2 and Variable resistor has a resistance of 3 . What is the total resistance? Answer: R = R1+R2 = 2 +3 = 5 10
Question 4 Parallel or Series? What is the total resistance? What is the potential difference across 3 ? What is the potential difference across 6 ? What is the current in 3 ? What is the current in 6 ? What is the total current in the circuit? 11
Question 5 12
Question 6 13
Summary: Series and Parallel Current PD Resistance ??? Series Same Distributed R=R1+R2+R3 Parallel Distributed Same 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 +... Total resistance is always smaller than the smallest resistance 16