Elevator Physics and Newton's Laws
Explore the fascinating world of elevator physics and Newton's laws through a series of scenarios such as how you feel during different elevator movements, forces at play during acceleration, determining acceleration from scale readings, calculating apparent weight changes, and analyzing elevator tensions. Discover how forces such as gravity, normal force, and applied force impact our experience in elevators.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
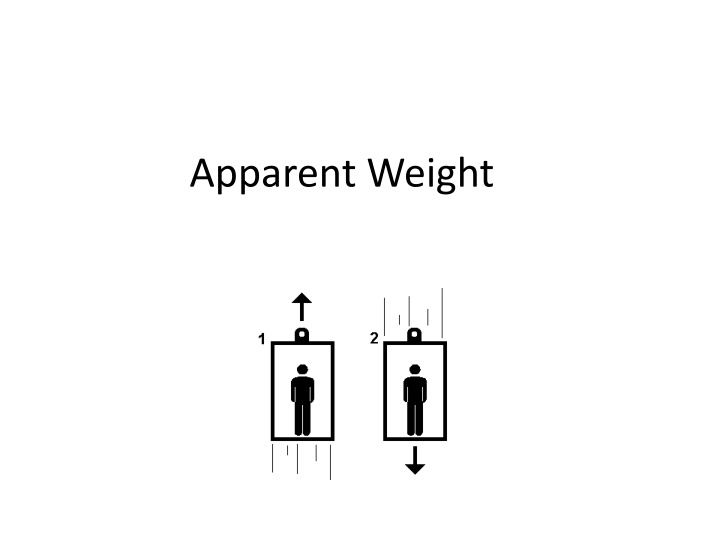
How do you feel when the elevator starts an upward trip? moves upward at a constant velocity? slows at the end of an upward trip? starts a downward trip? moves down at a constant velocity? slows at the end of a downward trip? Why do you feel these ways? What force is changing size?
FBD for riding an elevator: Which force changes when the elevator accelerates? FN Fg
Elevator Lab While stationary a spring scale measures a force of 1.96N when a brass cylinder is hanging on the scale. While riding in an elevator that is starting the trip up (from the first to the third floor) the scale reads 2.01N. Determine the acceleration of the elevator.
1stApplication of the 2ndLaw While riding an elevator, Mr. Slim stands on a scale. Normally, the scale tells him he weighs 655N, but while the elevator is accelerating the scale reads 715N. What is the magnitude and direction of the elevator s acceleration?
How heavy does a 5.00 kg book in your hand feel (how strong an applied force must you exert) while riding in an elevator that is: Accelerating down at 2.00 m/s/s? Moving down at a constant 4.00 m/s? Accelerating up at 2.00 m/s/s? Free Falling?
Ex: Free Body Diagram based 2ndLaw Problems A 300kg elevator is supported by a steel cable. Determine the tension in the cable when the elevator is: a) stationary b) accelerating upward at 0.50m/s/s c) moving upward at a constant 2.0m/s d) slowing down 0.5m/s every second, while still moving upward.
2nd Law Example A 35 kg child rides in an elevator. How heavy does the child feel (what is the normal force acting on the child) when the elevator is: accelerating upward at 3.5 m/s/s? moving upward at a constant 7.0 m/s? accelerating downward at 3.5 m/s/s? sitting still?