Endocrine Module Study Guide for Second Year MBBS Students
"The Endocrine Module Study Guide for Second Year MBBS students at Avicenna Medical College provides a comprehensive overview of the curriculum, learning methodologies, assessment methods, and faculty details. It covers the importance of endocrine studies and offers valuable resources for students' academic success."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
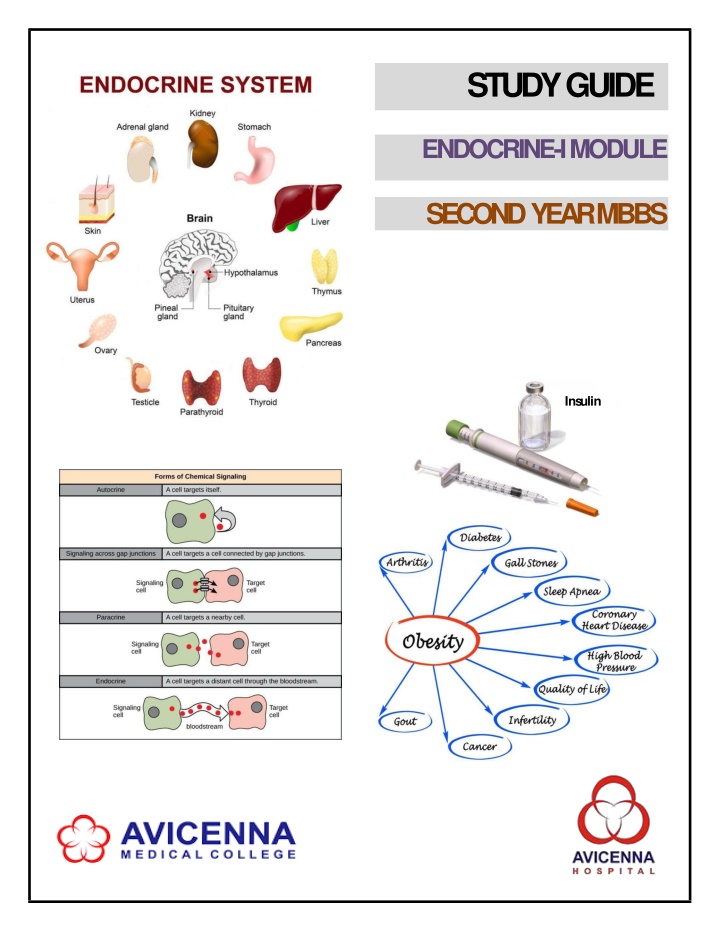
STUDYGUIDE ENDOCRINE-IMODULE SECOND YEARMBBS Insulin
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR ENDOCRINEMODULE Page No 3 4 5 7 7 8 17 19 21 22 S.No CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 4.1 4.2 5 6 7 8 Overview Introduction to StudyGuide LearningMethodologies Module 3:Endocrine Importance of Endocrine Objectives andstrategies LearningResources AssessmentMethods Modular Examination Rules And Regulations(AVMC) Schedule Page | 2
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Year:One Duration: 4 weeks Timetable hours: Lectures, Case-Based Learning (CBL), Team based Learning (TBL), Self-Study, Practical, Skills, Demonstrations, Field Visits, Visit to Wards& Laboratory MODULE INTEGRA TEDCOMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: CO-COORDINATORS: Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad(Biochemistry) Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez (Pathology) Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid(Anatomy) DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITA TINGLEARNING BASIC HEALTHSCIENCES CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS FAMILYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Muhammad Luqman ANATOMY Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid BIOCHEMISTRY Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad MEDICALEDUCATION Professor Dr. Waheed Ahmad COMMUNITYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Rana Muhammad Akhtar Khan INTERNALMEDICINE Dr. Muhammad Usman Amir PATHOLOGY Endocrinology Prof. Dr. Waheed Ahmed Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez PHYSIOLOGY Professor Dr. Binyamin Ahmad PHARMACOLOGY Professor Dr. Rana Tariq Mehmood AVMCMANAGEMENT Professor Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, PrincipalAVMC Brig.Dr. Gul e Rana , Director AVMC Dr. Sadia Awan Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Department of Health CareEducation Page | 3
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the semester-wise module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthemodule Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule. Thiswill helpthestudentto contactthe rightpersonin caseof anydifficulty. Definestheobjectiveswhich areexpectedto beachieved at theendof themodule. Identifies the learning strategies such as lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and casebasedlearning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives. Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links,journals,forstudentsto consultin orderto maximize their learning. Highlights information on the contribution of continuous and semester examinations on the student s overallperformance. Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives. Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations. CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Students will experience integrated curriculum in 3rd and 4th semesters at LNMC in accordance withthe JSMU guidelines and most recent developments that have an impact on individualhealth. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises of system-based modules such as Head and Neck, Neurosciences and Endocrinology which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have better understandingof basicscienceswhentheyrepeatedlylearn in relation to clinicalexamples. Case-based discussions, computer-based assignments, early exposure to clinics, wards, and skills acquisition in skills lab and physiotherapy department are characteristics of integrated teachingprogram. Page | 4
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES Thefollowing teaching/ learningmethodsareusedto promotebetterunderstanding: InteractiveLectures Hospital / Clinic visits Small Group Discussion Case-BasedLearning Practicals Skillssession SelfStudy INTERACTIVELECTURES Inlargegroup,the lecturer introduces atopic or commonclinical conditions andexplains the underlying phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients interviews, exercises, etc. Students are actively involved in the learningprocess. HOSPITAL VISITS: In small groups, students observe patients with signs and symptoms in hospital or clinical settings. This helps students to relate knowledge of basic and clinical sciences of the relevant module. Page | 5
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SMALLGROUPDISCUSSION (SMALLGROUP DISCUSSIONS):Thisformat helps students to clarify concepts acquire skills or attitudes. Sessions are structured with the help of specific exercises such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Students exchange opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures, tutorials andselfstudy.Thefacilitatorrole isto askprobing questions,summarize,or rephrase to help clarifyconcepts. CASE- BASED LEARNING: A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questions based on a clinical scenario. Students discuss and answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gainedin clinical andbasichealth sciencesduring themodule. PRACTICAL: Basic science practicals related to anatomy, biochemistry, pathology, pharmacology and physiologyarescheduledfor studentlearning. SKILLSSESSION:Skills relevant to respective module are observed and practiced where applicable in skills laboratory or DepartmentofPhysiotherapy. SELFSTUDY: Students assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within andoutside the college.Studentscanutilize the time within the college scheduled hours ofself-study. Apart from attending daily scheduled sessions, students too should engage in self-study to ensure that all the objectives arecovered. Page | 6
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SEMESTER 3 MODULE 3 : ENDOCRINE INTRODUCTION The Endocrine system relays information and maintains a constant internal environment of the body called homeostasis.It actsthroughchemicalmessengerscalled hormonesthatinfluencegrowth, development,and metabolic activities. Theaction of theendocrinesystemismeasuredin minutes,hours,or weeksandismore generalizedthantheaction of thenervoussystem. This M.B.B.S second year module will help you develop knowledge and understanding ofthe: Basic concepts of molecular endocrinology that underpin hormone actions, how dysfunction relatesto primary pathogenesis, and how this knowledge informs improvement in diagnosis and the potential for noveltherapies Hypothalamic-pituitaryaxesand theirrole in health anddisease,including thereproductive,adrenal, and thyroidaxes Neuro-endocrine control offood intake, energy expenditure and obesity Theoriesof theetiology andpathogenesis of type2 diabetesmellitus Similarly,thismoduleof endocrinesystemwill enable youto recognize theclinical presentationsof common endocrinological and metabolic disorders and relate clinical manifestations to basic sciences. This Endocrine modulewill berevisited inthe following years. Thestudyguidewill helpyouprioritizetheimportant topicsforlearningin relationto themoduleobjectives through lectures, demonstrations, tutorials, practicals and skills labsessions. Page | 7
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE COURSE TOPICS, OBJECTIVES AND TEACHINGSTRA TEGIES At theendof themodulethestudentswill beableto: LEARNING STRATEGY OUTCOMES &OBJECTIVES FACULTY Overview of the endocrine glands in the body Define and classify theglands Discuss functions of endocrineglands Describe thelocationof allendocrine glands in the body Anatomy Explain the structure and functions ofall endocrine organs in thebody Define the terms endocrine, paracrineand autocrine Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Describe the concept ofhormone receptors and second messenger in hormoneaction Physiology Describe the synthesis, functions and regulationsof thehormones Describe the regulation ofhormone secretion by positive and negativefeedback Classify the different hormones and describe their chemical structure Biochemistry Describe the biochemical function ofhormones Hypothalamic-pituitary end organaxis Describe the development and congenitalanomalies of Pituitarygland Anatomy Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion List the hormones secreted by the pituitarygland Pathology Describe the structuraland functional relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitarygland Pathology Describe the hormones secreted bythe anterior pituitary gland and describe their hypothalamic control Physiology Page | 8
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Discuss the anterior pituitary secretions and related disorders 2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE Physiology Briefly describe posterior pituitarysyndromes Pathology Describe the Microscopic features of pituitary gland Anatomy Practical Describe the gross anatomy , neurovascularsupply and clinical importance of Pituitarygland Anatomy Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Describe the structure, secretion, mode of actionand functions of hypothalamichormones Biochemistry Biochemical functions of growth hormonesand metabolic effects of growthhormones Describe physiological function of growth hormone and relateddisorders Physiology Describe the structure, biosynthesis, actionsand regulation of growthhormone Interactive Lectures/Case- BasedDiscussion Biochemistry Describetheeffectof growth hormoneon carbohydrates, proteins andlipids Biochemistry Molecular structure, biochemical function of anterior pituitaryhormones Discuss pituitary hormones other than growth hormone with clinical complications anddiseases Describe the molecular structure ofanterior pituitary hormones Biochemistry Discuss the biochemical function of anteriorpituitary hormones Interactive Lectures/Case- BasedDiscussion Discuss the clinical manifestations of anterior pituitary disease Discuss the classification of pituitaryadenomas Pathology Discuss the hypothalamic and ant -pituitaryhormones and itsdisorders Explain pharmacokinetics, dynamics & toxicity ofthe drugs used to treat theirdisorders Pharmacology Page | 9
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Hormones of posterior pituitary, their biochemical functions and related disorders List the hormones secreted by posterior pituitarygland and describe theireffects Biochemistry Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Describe posterior pituitary secretions anddisorders Physiology Describe the biochemical functions ofoxytocin and ADH and their relateddisorders Biochemistry List the Post-pituitaryhormones Describe their basic and clinicalpharmacology Explain pharmacokinetics, dynamics & toxicity of the drugs used to treat different disorders of post- pituitary Pharmacology InteractiveLecture Difference between hypo and hyper secretion of hypothalamus and pituitary hormones Differentiate between hypo and hyper secretionof hypothalamus and pituitaryhormones Biochemistry Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Biochemistry Discuss acromegaly anddwarfism Identify pituitary abnormalities, dwarfism,gigantism andacromegaly Physiology Thyroidgland Describe the development and congenitalanomalies of thyroidgland Anatomy InteractiveLecture Describe the microscopic features of thyroid gland Anatomy Practical Describe the gross anatomy , neurovascularsupply and clinical importance of thyroidgland Anatomy Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Explain the formation and secretion of T3 andT4 Discusstheimportance of iodine metabolismand iodine pump Describe actions of thyroidhormone on development and metabolism and associateddisorders Describe theroleof TSHonregulationof thyroid hormones Physiology Page | 10
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Describe the structure, synthesis, mode of actionand metabolic functions of thyroidgland Biochemistry InteractiveLectures Describe thehypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid homeostasis DefineHypothyroidism List the major causes ofhypothyroidism List the main clinical features ofhypothyroidism Differentiate between cretinism and myxedema with regards to etiology, pathogenesis, clinical featuresand labdiagnosis Define Hashimoto sthyroiditis Discuss the pathogenesis of Hashimoto sthyroiditis and its clinicalmanifestations Definehyperthyroidism List the causes of hyperthyroidism List the main clinical features ofhyperthyroidism Discuss Grave s disease, hyperthyroidism thyrotoxicosis and Goiter including pathogenesis and clinical features Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Pathology Differences between hypo andhyperthyroidism Interpret thyroid function tests (T3, T4, TSH, I2 and LATS) Biochemistry Practicals Describe the diagnostic modalities availableto diagnose thyroid pathology Interpret thyroid functiontests Pathology Identify the signs and presentation, causes and investigation ofhypothyroidsm/hyperthyroidism Endocrinology InteractiveLectures Review the pathogenesis of Hashimoto sthyroiditis and Grave sDisease Pathology Identifytheslidesrelatedto benignlesionof thyroid gland Practical Hypothyroidism Describe how drugs influence the steps in synthesis and release of thyroidhormones Describe the clinical presentation and treatment of hypothyroidism Describe clinical presentation and treatment of endemicgoiter SmallGroup Discussion Pharmacology Page | 11
AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE Describe the clinical presentation and pharmacology of drugs used inhyperthyroidism Describe the treatment of and myxedemacoma Describe the causes and effects of iodinedeficiency onbrain andcontrolof thisproblem thyroid storm Community Medicine Small Group Discussion Parathyroid Gland Describe the development and congenital anomalies of parathyroidglands Anatomy Describe the microscopic features ofparathyroid glands Describe the gross anatomy ,neurovascular supply and clinical importance ofparathyroid glands Anatomy SmallGroup Discussion Anatomy Explain the synthesis and function ofparathyroid hormone (calciummetabolism) Biochemistry InteracticveLecture Discuss secretion, action and functions of parathyroidhormones Physiology Definehyperparathyroidism Discuss the causes of hyperparathyroidism and clinical manifestations Definehypoparathyroidism Discuss causes and clinical manifestations of hypoparathyroidism andpseudohypoparathyroidism Pathology Discuss calcitonin hormone and role of vitamin D List the disorders associated with calciumhomeostasis which include tetany, Chovstek ssign Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Physiology Discuss the role of parathyroid hormone, calcitonin and Vitamin D in Calciumhomeostasis Name the causes of hypercalcemia, including drug inducedhypercalcemia Describe the signs, symptoms and complications of hypercalcemia Discuss the treatment ofhypercalcemia Explain the etiology ofhypocalcemia Describe signs symptoms and lab evaluation of hypocalcemia Discuss treatment ofhypocalcemia Pharmacology Page | 12
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Pancreatichormones Describe the development and congenitalanomalies of endocrine portions ofPancreas Anatomy InteractiveLecture Describe the microscopic features ofendocrine portions ofPancreas InteractiveLecture/ Practical Anatomy Describe the gross anatomy , neurovascularsupply and clinical importance of endocrine portions of Pancreas Anatomy Discuss the molecular structure, mode ofaction and biochemical functions ofinsulin Biochemistry Describe hormones of pancreas andinsulin Explaintherole of insulin in maintaining blood glucose concentration Differentiate between neurogenic and nephrogenic diabetesinsipidus Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion Physiology Discuss the molecular structure andbiochemical function of glucagon andsomatastatin Biochemistry Describe glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic Polypeptides Physiology Regulation of blood glucose with referred level andtheir completion Explain the regulation of blood glucose level,hyper and hypoglycemia and complications of diabetes mellitus Biochemistry Define diabetesmellitus Describe the diagnostic criteria and guidelinesfor diagnosis ofdiabetes Discuss the classification of diabetesmellitus List the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetesmellitus InteractiveLecture Pathology Explain the pathogenesis of type-I and type IIdiabetes, beta cell dysfunction, genetic susceptibility and diabetes inpregnancy Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion Pathology Interpret laboratory diagnosis of diabetesmellitus Discussthemorphology& clinical featuresof typeI& II Diabetes including classic triad & chronic manifestations Page | 13
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Discuss acute metabolic complications &Ketoacidosis Explain the morphology and clinical featuresof chronic complications of DiabetesMellitus Demonstrate the estimation of blood glucose level by Kit method & laboratory interpretations for diagnosis of diabetesmellitus Formulate graph of Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) on the basis of givendata Biochemistry Practical Classify oral hypoglycemicdrugs Describe the pharmacology of oralhypoglycemic agents, adverse effects and importantdrug interactions Pharmacology Explain different types of diabetes itscauses, clinical features andinvestigation Endocrinology Interactive Lecture/Case- Based Discussion List the different insulin preparations (Classification, onset, peak and duration ofaction) Describe conventional and intensive insulin therapy and their advantages anddisadvantages Describe the adverse effects ofinsulin Describe injectable hypoglycemic drugs other than insulin (pramlintide andexenetide) Pharmacology Describe Diabetes Enumerate Risk Factors of Diabetes Mellitus(DM) Explain Complications ofDiabetes Discuss Preventive measures of DiabetesMellitus Communit y Medicine InteractiveLecture Discuss the complication ofdiabetes which includes o DiabeticFoot o Diabetic Ketoacidosis/HyperosmolarComa SmallGroup Discussion Multidisciplinary Demonstrate S/C insulin injection technique usingan insulin syringe Skills lab Hands-On Skills Obesity and the body massindex Community Medicine Explain thevariouslevelsofobesityonthebasis of body mass index, hazards andprevention InteractiveLecture Page | 14
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE Adrenal glands Describe the development and congenitalanomalies of adrenalgland Describe the microscopic features ofadrenal gland Anatomy Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion Anatomy Describe the gross anatomy , neurovascularsupply and clinical importance of adrenalgland Anatomy Describe the chemistry, synthesis and metabolic functions of glucocorticoids andmineralocorticoids along with theirabnormalities Biochemistry Explain the synthesis of glucocorticoidhormones Identify the actions of glucocorticoids onmetabolism and targetcells Discuss the mechanism for regulation ofglucocorticoid secretion. Describe the disorders associated withglucocorticoid hormones including Addison s disease, Cushing syndrome Interactive Lecture/Small GroupDiscussion Define Aldosterone escape, Primary Aldosteronism and AndrogenitalSyndrome Explain themechanismof action of mineralocorticoids Discussthemechanismof actionsof aldosteroneand itsregulation Physiology Explain the mechanism of secretion and actionsof medullary hormones List the types of adrenergic receptorsand their functions on targetorgans Enumerate consequences of over and undersecretion of medullary hormones(pheochromocytoma) Describe the chemistry of adrenalmedullary hormones andpheochromocytoma Biochemistry Classification of corticosteroids and their functions analysis, kinetics, dynamics and theirinhibition Explain the systemic effects ofcorticosteroids and to relate these to the adverse effects, precautions and contraindications of steroidtherapy Classify the commonly used corticosteroid preparations List the uses of corticosteroidpreparations Explain corticosteroid withdrawal effect andits prevention Pharmacology InteractiveLecture Page | 15
2ND YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 3 ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Concept of health management system, issues and challenges, solutions and improvement of Health managementsystem Discuss the health management informationof Pakistan in general and specific to thedistrict Identify the sources ofHMIS Discuss the importance ofHMIS Communit y Medicine Describe the various stages of healtheducation and its principles Describe various models of behaviorchange Discuss the principles for HealthEducation Describe the various methods of healtheducation program ofPakistan InteractiveLectures Research Developing aQuestionnaire Define research, its types and itsimportance Discuss researchquestions List characteristics of a good researchquestion Phrase a research questioncorrectly Performing a literature search Describe the importance of LiteratureReview Identify different sources ofliterature Use databases to searchliterature Referencing Discuss referencing of different sources of literature Discuss the different styles forreferencing Epidemiological studyDesigns Classify epidemiological studydesigns Discuss various observational studydesigns Explain and discuss advantages and disadvantages of observational studydesigns Discuss application of observational studydesigns Writing background and Rationale of study Identify different sources ofliterature Conduct literature search by using different databases Discuss referencing of different sources of literature Develop background and build rationale fora researchquestion Interactive Lectures/Small GroupDiscussion Communit y Medicine Page | 16
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES SUBJECT RESOURCES A. GROSSANATOMY 1. K.L. Moore, Clinically OrientedAnatomy 2. Neuro Anatomy by RichardSnell B. HISTOLOGY 1. B. Young J. W. Health Wheather s FunctionalHistology C. EMBRYOLOGY 1. Keith L. Moore. The DevelopingHuman 2. Langman s Medical Embryology ANATOMY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Harper s IllustratedBiochemistry 2. Lehninger Principle ofBiochemistry 3. Biochemistry byDevlin BIOCHEMISTRY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Community Medicine byParikh 2. Community Medicine by MIllyas 3. Basic Statistics for the Health Sciences by Jan WKuzma COMMUNITYMEDICINE A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9thedition. 2. Rapid Review Pathology, 4th edition by Edward F. GoljanMD PATHOLOGY/MICROBIOLOGY 1. http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/webpath.html 2. http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/ A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Lippincot IllustratedPharmacology 2. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology by Katzung PHARMACOLOGY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Textbook Of Medical Physiology by Guyton AndHall 2. Ganong S Review of MedicalPhysiology 3. Human Physiology by LauraleeSherwood 4. Berne & LevyPhysiology 5. Best & Taylor Physiological Basis of MedicalPractice B. REFERENCEBOOKS 1. Guyton & Hall PhysiologicalReview 2. Essentials Of Medical Physiology byJaypee 3. Textbook Of Medical Physiology byInduKhurana 4. Short Textbook Of Physiology byMrthur 5. NMSPhysiology PHYSIOLOGY Page | 17
2ND YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 3 ENDOCRINEMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE OTHER LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the endocrinemoduleto enhancethe learning. Utilize thelabto relatetheknowledge to the specimensandmodels Labs available. A skills lab provides the simulated learning experience to learn thebasic skills and procedures. This helps build the confidence toapproach the SkillsLab patients. Video familiarize the student with the proceduresandprotocols to assist Videos patients. To increase the knowledge students should utilize the available internet resources and CDs/DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase Computer Lab/CDs/DVDs/Internet learning. Resources: Self Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases,read through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the SelfLearning faculty to clarify theconcepts. Page | 18
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory: o Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to assess objectives covered in eachmodule. A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswer). Students after reading the statement/scenario select ONE, the most appropriate response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is no negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponsesonspecifiedcomputer-based/OMRsheetdesignedforAVMC OSPE/OSCE: Objective Structured Practical/ClinicalExamination: Eachstudentwill beassessedonthe samecontentandhavesametimeto completethe task. Comprise of 12-25stations. Each station may assess a variety of clinical tasks, these tasks may include history taking, physical examination, skills and application of skills andknowledge Stations are observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and interactive stations will be assessed by internal orexternal examiners. Unobserved will be static stations in which there may be an X-ray, Labs reports, pictures, clinical scenarioswith relatedquestionsforstudentstoanswer. Rest station is a station where there is no task given and in this time student can organize his/her thoughts. InternalEvaluation Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthefollowing: Module Examination: will be scheduled on completion of each module. The method of o examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective StructuredPractical Examination). Graded Assessment of students by Individual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, small o group activities such as CBL, TBL, TOL, online assessment, ward activities, examination, and log book. Marksof bothmodular examinationandgradedassessmentwill constitute20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by UHS o SemesterExamination. Page | 19
2ND YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 3 ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Example : Number of Marks allocated for Semester Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Class test +Assignments + Modular Exam) 20% Semester Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Semester 80% 100% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75% attendance is needed to sit for the modular and semester examinations Page | 20
2ND YEAR MBBS, ENDOCRINEMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATIONSAVMC Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmust sitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoffor on)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, AVMCCollege ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. AVMCGradingSystem It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 4.0 A+ 75-79 4.0 A 70-74 3.7 A- 67-69 3.3 B+ 63-66 3.0 B 60-62 2.7 B- 56-59 2.3 C+ 50-55 2.0 C <50 Un-grade-able 0 U A candidate obtaining GPA less than 2.00 (50%) is declared un-graded(fail). Cumulativetranscriptisissuedat the endof clearance of all modules. Page | 21