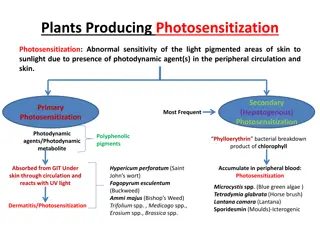
Endophytes and Plants: A Hidden Love Affair Revealed
Dive into the intriguing relationship between endophytes and plants, where microorganisms live inside plant tissue, offering benefits such as growth promotion, biofertilization, nitrogen fixation, and phosphate solubilization. Explore the fascinating world of endophytic bacteria and their role in enhancing plant health and productivity. Uncover the secrets of plant growth promotion properties, biocontrol against phytopathogens, and the synthesis of key compounds crucial for plant development. Discover the hidden romance between plants and their unseen microbial partners, shaping a harmonious ecosystem within the plant kingdom.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ENDOPHYTES AND PLANTS A hidden love affair
Endophytes Endophytes = microorganisms living inside the plant tissue Relationships: Neutral Mutualistic Commensal
A.Colonization through damaged areas of the epidermis B. + C. Colonization through epidermal cracks D. Colonization facilitated by fungal root penetration Andreolli M., Lampis S., Vallini G. (2017) Diversity, Distribution and Functional Role of Bacterial Endophytes in Vitis vinifera. In: Maheshwari D. (eds) Endophytes: Biology and Biotechnology. Sustainable Development and Biodiversity, vol 15. Springer, Cham
Plant growth promoting properties Enhancing the availability and assimilation of nutrients Synthesis of specific compounds required by plants Plant protection against phytopathogens
Biofertilization Biofertilization = increasing the availability of nutrients that support plant growth Biological fixation of nitrogen, dissolution of bound phosphorus
Biological fixation of nitrogen Diazotrophy = conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase Diazotrophic endophytic bacteria rise in the total nitrogen content of the plant
Phosphate solubilization Phosphorus in soil in insoluble forms: inorganic minerals - apatite organic forms - inositol phosphate, phosphomonoes and phosphotriesters
Phosphate solubilization Organic acid-producing bacteria (gluconic, lactic, oxalic, citric): chelation of phosphorus-bound metal cations soil pH decrease release of phosphate ions
Phytostimulation Phytostimulation = growth support by phytohormones production: auxins cytokinins Giberellins abscisic acid
Biocontrol Biocontrol = support for growth through protection against phytopathogens: Production of antimicrobial substances Production of lytic enzymes Competition for nutrients
Bacterial siderophores Siderophores = low molecular weight molecules capable of binding Fe3+ Competition for iron with phytopatogens Possible supply of iron for plants
What do we do? Isolation of endophytes from grapevine (Vitis vinifera) Test their plant growth promoting properties Determine differences between bio/conventional vineyards Determine differences between seasons