Energy Processes in Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
This content provides an in-depth exploration of the processes involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration, including key terms such as chloroplast, mitochondria, pigment, Calvin Cycle, and more. It explains the functions of various components like chlorophyll, stroma, and thylakoid, and introduces important scientists like Van Helmont, Priestly, and Ingenhousz. The images included visually represent concepts related to energy transfer, ATP production, and the overall mechanisms of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Daneal Rozman, Elizabeth Bird, Mario Caro, Rosario Medina
http://education- portal.com/cimages/videopreview/vid eopreview- small/thumbnail_106361.png http://www.ftexploring.com/enrgypics/m nky60.gif http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~shethrk/ courses/ast06/lectures/lecture2/s1.4_files /photosynrespira.gif http://alternativecancer.us/energy_cell.gif http://science.jrank.org/kids/article_ima ges/food_p05.jpg http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100 /lectf03am/energy.jpg
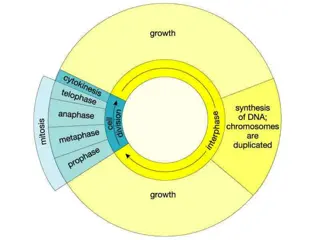
Chloroplast / absorbs sunlight during photosynthesis in plant cells Mitochondria / energy source that occurs during cellular respiration in both animal and plant cells Pigment / gives plants color Calvin Cycle / uses energy from light rnx to produce sugar Photosynthesis / the conversion of light energy into chemical energy stored in organic compounds Cellular Respiration / the process where the chemical energy of food molecules is released and changed to ATP Glycolysis / takes place in the cytoplasm of cells Krebs Cycle / takes place in the mitochondria matrix Electron Transport Chain / takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Aerobic Respiration / produces 38 ATP with oxygen present Anaerobic Respiration / produces 2 ATP without oxygen present Photosynthesis Equation / 6CO2+6H2O -> C6H12O6+6O2 Adenosine Triphosphate / high energy compound (only releases energy) Adenosine Diphosphate / medium compound stores or releases energy) Autotrophs / organisms that get their energy directly from sun Heterotrophs / organisms that eat food to obtain their energy Chlorophyll / main pigment in plants, found in the chloroplast Stroma / where Calvin Cycle occurs Light Dependent reactions / traps the energy from the sunlight. makes ATP and ADP Thylakoid / where light rxn occurs Van Helmont / the scientist that measured the soil, planted a seed and watered the plant until it grew Priestly / the scientist that discovered a candle can burn much longer with a glass lid over it when there is a piece of fresh mint in the container Ingenhousz / the scientist that concluded that Preiestly's plants had to be exposed to light in order for this theory to be true Fermentation / what anaerobic conditions lead to
http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-QfmjgRFkcRk/UXMz0u06PYI/AAAAAAAAGbo/4hpF5NSNn6s/s1600/photosynthesis_diagram.jpghttp://2.bp.blogspot.com/-QfmjgRFkcRk/UXMz0u06PYI/AAAAAAAAGbo/4hpF5NSNn6s/s1600/photosynthesis_diagram.jpg
Without the ability to obtain and use energy, life would not exist. Energy comes in the form of heat, light, and electric. Energy can also be stored in the bonds of chemical compound. Two types of energy in living things are autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophs are organisms that get their energy directly from the sun which are plants or anything that uses photosynthesis. Heterotrophs are organisms that eat food to obtain their energy which are animals and humans, heterotrophs will eat autotrophs. All energy produced begins with the sun. Chemical energy is the main compound cells use to store and release energy (ATP). Adenosine triphosphate is high energy compound that only releases energy. Adenosine diphosphate is medium compound that stores and releases energy. Adenosine monophosphate is a low energy compound which only stores energy. Chloroplast absorbs sunlight during photosynthesis in plant cells. Mitochondria is the energy source that occurs during cellular respiration in both animal and plant cells. Pigment is found in plants and is what gives plants their color. The Calvin Cycle uses energy from light reaction to produce sugar (glucose) which occurs in the stroma. Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy into chemical energy stored in organic compounds. Cellular Respiration is the process where the chemical energy of food molecules is released and changed to ATP. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. Krebs Cycle takes place in the mitochondria matrix and makes CO2 and ATP. Electron Transport Chain takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and makes lots of ATP. Aerobic Respiration produces 38 ATP with oxygen present. Anaerobic Respiration produces 2 ATP without oxygen present which results in fermentation which is what anaerobic conditions lead to. Photosynthesis Equation is 6CO2+6H2O -> C6H12O6+6O2. Chlorophyll is the main pigment in plants, found in the chloroplast. Stroma is where Calvin Cycle occurs. Light Dependent reaction traps the energy from the sunlight and makes ATP and ADP. Thylakoid is where light reaction occurs. Van Helmont is the scientist that measured the soil, planted a seed and watered the plant until it grew. Priestly is the scientist that discovered a candle can burn much longer with a glass lid over it when there is a piece of fresh mint in the container. Ingenhousz is the scientist that concluded that Preiestly's plants had to be exposed to light in order for this theory to be true.