Engineering of Organisms and Mastery of the Human Genome
In this chapter, the focus is on the engineering of organisms and the mastery of the human genome. Topics covered include CRISPR technology, gene-editing milestones, historical genetics breakthroughs, research ethics, top-down versus bottom-up engineering, GMO controversies, chimeras research, sequencing in personalized medicine, and discussions on reproduction, stem cells, and designer babies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
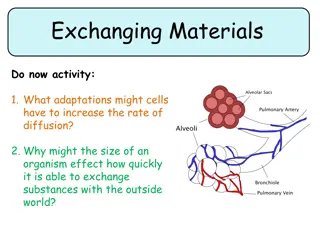
CHAPTER 6: ENGINEERING OF ORGANISMS CHAPTER 7: MASTERY OF THE HUMAN GENOME
THE ODIN AND THE BIOHACKERS A Case Study
TIMELINE TIMELINE Genetics/Genomics Genetics/Genomics 2018: 2018: CRISPR CRISPR- - baby baby He Jiankui used the CRISPR 1866: Mendel 1866: Mendel gene-editing system to edit 1977: 1977: Sanger Sanger Medel s pea plant DNA in human embryos to experiments led to the make them less susceptible Develops rapid DNA discovery of dominant and to HIV. sequencing techniques recessive traits. 1953: 1953: Watson & Watson & Crick Crick AND AND Rosalind Rosalind Franklin Franklin Described the structure of 1859: 1859: Darwi Darwi n n 1990: The 1990: The Humane Humane Genome Project Genome Project Darwin writes On the Origin The project's goals included of Species and in doing so Note: The first use mapping the human popularized the idea of DNA (the source code for of the term genome which succeeded evolution. Built around: life) - changes in individual eugenics was in 2003 heredity, variation, and base pairs serve as a simple around 1183 natural selection vehicle for genetic mutations.
RESEARCH ETHICS FUNDAMENTALS The horrific history of human subjects research eventually led to the development of formal regulations Things to consider in research ethics: Respect for Persons (consent) Paternalism vs. Beneficence Justice (fairness)
TOP-DOWN AND BOTTOM-UP ENGINEERING KEY REGULATION THREE CRUCIAL QUESTIONS
GMOS GOLDEN RICE Are GMOs too harmful to be produced? Have we passed the inflection point? Reflections on the Golden Rice case study?
CHIMERAS: OR HUMAN/ANIMAL HYBRIDS Is this sort of research rightly prohibited? Or are there good enough benefits to pursue this research?
RAPID INCREASE OF SEQUENCING PERSONALIZED MEDICINE GOALS CONCERNS: Privacy (GINA) Harms to small groups and harms of research
REPRODUCTION, STEM CELLS, AND DESIGNER/ TEST-TUBE BABIES Frist test-tube baby was born in 1978 Debates on personhood status of embryos Debate over stem cell research Debate over PGD and eugenics Dolly and cloning
CRISPR/CAS9 BABIES Other variations that would be more acceptable? Or is the moratorium on this research warranted?
THE INFLECTION POINT Is the next inflection point going to be in cloning a human as Wallach suggests? Have we reached any inflection points in widespread use of genomic/ genetic technology? If so, what are they? Has your initial opinion of The ODIN and at home biohacking changed at all?