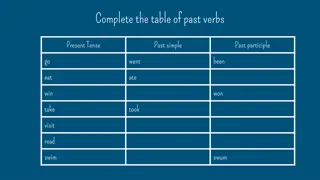
English Language Past Tense Studies
Learn about the past simple and past continuous tenses in English, including affirmative forms, common mistakes, differences between past simple and present perfect, ten irregular verbs with examples, and common irregular verbs in detail. Enhance your understanding of past tense usage through examples and comparisons.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Intelligent Medical Systems Department Intelligent Medical Systems Department Subject: English Language Subject: English Language Class: Class: Third Lecturer: MSC. Lecturer: MSC. Sakina Sakina Hussain Third Hussain Alsuwaydi Alsuwaydi Lecture: ( Lecture: ( 3 3 ) ) Past simple and Past simple and Past continuous Past continuous Study Year: 2024-2025
Past simple Past simple Past simple Past simple The past simple, is a tense in English used to describe completed actions or events that occurred at a specific point in the past.
Affirmative Form Affirmative Form:: For regular verbs, add "-ed" to the base form of the verb (e.g., play played). Subject + regular verb ( Subject + regular verb (ed ed) + object + comp. I played tennis yesterday. ) + object + comp. For most irregular verbs, use the past tense form (e.g., go went, buy bought). Examples: Subject + irregular verb + object + comp. Subject + irregular verb + object + comp. She bought a car last week. She went to the store last night.
Common Mistakes in Past Simple Tense Incorrect: He didn t went to school yesterday. (Correct) Correct: He didn t go to school yesterday. Incorrect: Did she played basketball? Correct: Did she play basketball?
Past Simple vs. Present Perfect Brief comparison: Past Simple: Completed actions at a specific time. I visited the museum yesterday. Present Perfect: Actions with no specific time or still relevant. I have visited the museum. (at the door)
Here are ten irregular verbs in English: 1. Be was/were been 2. Go went gone 3. Eat ate eaten 4. Take took taken 5. Write wrote written 6. See saw seen 7. Break broke broken 8. Do did done 9. Speak spoke spoken 10. Know knew known
Common Irregular Verbs in Detail Begin Began Begun: He began the project last year. Choose Chose Chosen: She chose a red dress for the event. Drive Drove Driven: They drove to the countryside last Sunday.
He played piano yesterday. (Make question) Did + S + Base verb + comp ? Did + S + Base verb + comp ? A/ Did he play piano yesterday? He played piano yesterday. (Use Did not ) S + Did not + base verb+ comp. S + Did not + base verb+ comp. A/ He did not play piano yesterday. He play piano yesterday. (Correct and Use Did not ) He did not play piano yesterday.
Which sentence is correct: He buy a car yesterday. Or He bought a car yesterday. Did he bought a car yesterday? Or Did he buy a car yesterday? She traveled to Turkey yesterday. Or She travels to Turkey yesterdays.
Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Complete the sentences with the correct past tense verb: - She ______ (visit) her grandmother last weekend. - They ______ (go) to the park yesterday. A/ 1- visited 2- went Correct the Mistake: Find and fix the errors in these sentences: - He didn't went to school last Monday. A/Go - Did she played basketball yesterday? A/Play
A Day in London Last Saturday, Tom went to London. He woke up early and had a quick breakfast. Then, he took the bus to the museum. He saw many interesting paintings. After that, he walked to the park and sat on a bench. He talked to a friend and enjoyed a little rest. Later, Tom went to the market and bought some fruit. He ate a sandwich and drank a lot of water. In the evening, he returned home. It was a wonderful day!
Introduction to Past Continuous The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. Example: I was watching TV at 9 PM.
Structure of the Past Continuous Tense Affirmative Sentences Structure: Subject + was/were + verb Subject + was/were + verb- -ing ing (Was) is used with he/she/it (singular subjects) and were is used with I/you/we/they (plural subjects). Example: She was reading a book. They were playing football in the park.
Negative Sentences Structure: Subject + was/were + not + verb Subject + was/were + not + verb- -ing ing In negative sentences, we use was not (wasn t) or were not (weren t). Example: I wasn t sleeping when you called. We weren t listening to music at that time.
Questions Structure: Was/Were + subject + verb Was/Were + subject + verb- -ing ing? ? In questions, was or were comes first, followed by the subject, then the verb in the ing-form. Example: Was she reading a book? Were they watching a movie last night?
Important Rules and Tips 1. Use Was and Were Correctly: Was is used for singular subjects (I, he, she, it) in the past continuous. Example: He was studying late last night. Were is used for plural subjects (you, we, they) and also with you in the singular. Example: We were playing soccer when it started raining.
2. The Verb in the -ing Form: In the past continuous, the main verb always ends in -ing. This shows that the action was ongoing. Example: She was walking to school. -For regular verbs, just add -ing (play playing, walk walking). -For irregular verbs, follow the usual rules: -If a verb ends in -e, drop the -e and add -ing (make making). -Double the final consonant if the verb is short and ends with a vowel + consonant (run running).
Time Expressions Commonly Used with Past Continuous: - -At + specific time (e.g., At At + specific time (e.g., At 8 8 PM, At midnight, At that moment) PM, At midnight, At that moment) Example: At 7 PM, I was cooking dinner. - -While + past continuous (used for two actions happening at the same time) While + past continuous (used for two actions happening at the same time) Example: While I was watching TV, my brother was playing video games. - -When + past simple (used to show an interruption) When + past simple (used to show an interruption) Example: I was reading when she called. - -For/During/All day (used to show the duration of the action) For/During/All day (used to show the duration of the action) Example: He was sleeping all day yesterday.
Interrupted Actions: The past continuous is often used for actions that were interrupted by a short, completed action in the past (usually in the past simple tense). Example: I was studying when the power went out. In this case, was studying is the ongoing action, and went is the action that interrupts it.
- -When + past simple (used to show an interruption) When + past simple (used to show an interruption) Example: I was reading when she called.
Examples of All Forms: 1. Affirmative: They were talking during the meeting. I was studying all night. 2. Negative: She wasn t paying attention in class. We weren t waiting for anyone. 3. Question: Was she listening to music when you arrived? Were they playing football yesterday?
Tips for Using the Past Continuous: 1. Context matters: The past continuous is useful when describing what was happening at a specific time, especially if it was happening in the background or in progress. Example: I was watching TV when she arrived. 2. Don t confuse with past simple: Use the past simple for actions that are finished or completed in the past. The past continuous focuses on actions in progress. Example: I ate dinner (completed action) vs. I was eating dinner when she called (action in progress).
Conclusion: The past continuous tense is essential for describing actions that were happening over time in the past. It s used for ongoing actions, parallel actions, and interruptions. By following the structure and rules above, you can accurately describe various actions in the past!