Enhancing Psychomotor Skills in Education
Explore the psychomotor domain focusing on physical movement, coordination, and motor skills development. Understand the importance of practice, precision, and techniques in mastering psychomotor skills, from manual tasks to complex activities like operating machinery or dancing.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE of PSYCHOMOTOR DOMAIN Sumit Kumar Assistant Professor School Of Education
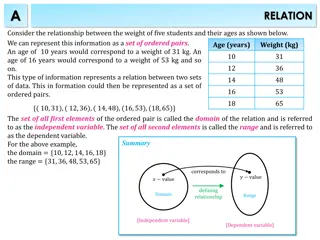
INTRODUCTION The psychomotor domain includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor- skill areas. Development of these skills requires practice and is measured in terms of speed, precision, distance, procedures, or techniques in execution.
INTRODUCTION Thus, psychomotor skills rage from manual tasks, such as digging a ditch or washing a car, to more complex tasks, such as operating a complex piece of machinery or dancing.
Definition The psychomotor domain includes those objectives which deal with manual and motor skill.
Types of Objectives According to type of objective According to domain According to person Cognitive Teacher Institutional Domain Centred Departmental Affective Student Domain centred Specific Psychomotor Domain
Taxonomies of Educational Objective
Complex Overt Behaviour Mechanism Guided Response Set Perception Psycho-motor Domain
Perception (awareness): The ability to use sensory cues to guide motor activity. This ranges from sensory stimulation, through cue selection, to translation. Set: Readiness to act. It includes mental, physical, and emotional sets. These three sets are dispositions that predetermine a person's response to different situations (sometimes called mind-sets).
This category includes performing without hesitation, and automatic performance. For example, players are often utter sounds of satisfaction or expletives as soon as they hit a tennis ball or throw a football, because they can tell by the feel of the act what the result will produce.
Guided Response: The early stages in learning a complex skill that includes imitation and trial and error. Adequacy of performance is achieved by practicing. Mechanism : This is the intermediate stage in learning a complex skill. Learned responses have become habitual and the movements can be performed with some confidence and proficiency.
Complex Overt Response : The skilful performance of motor acts that involve complex movement patterns. Proficiency is indicated by a quick, accurate, and highly coordinated performance, requiring a minimum of energy. This category includes performing without hesitation, and automatic performance. For example, players are often utter sounds of satisfaction or expletives as soon as they hit a tennis ball or throw a football, because they can tell by the feel of the act what the result will produce.
Action Verb for different objectives in Psychomotor Domain Perception Set Guided Response Chooses, Begins, displays, copies, traces, describes, detects, explains, moves, follows, react, differentiates, proceeds, reacts, reproduce, responds distinguishes, shows, states, identifies, isolates, volunteers. relates, selects.
Action Verb for different objectives in Psychomotor Domain Mechanism Complex Overt Response Assembles, calibrates, Manipulates, measures, constructs, dismantles, mends, mixes, organizes, displays, fastens, fixes, grinds, sketches. heats.