Enterprise Architecture Application with MS .NET Blazor, Azure, and GreatIdeaz TrellisPark
In this architecture, learn about data-less service components, nano-service architecture, building strategies, and technology stack for efficient development. Explore examples using MS .NET Blazor, Azure, and GreatIdeaz TrellisPark.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
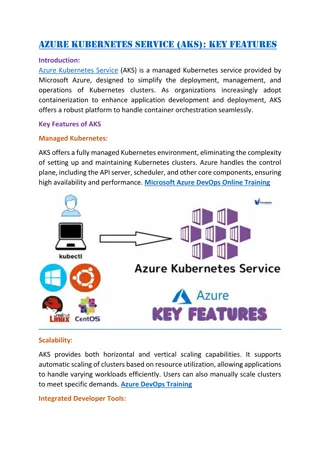
Workflow Components Enterprise Architecture Application Architecture, with examples using MS .NET Blazor, Azure and GreatIdeaz trellispark
Overview What are data-less Service Components? What is nano-service architecture? How do we build them? How do we call them? What are the DevOps advantages? How does this impact sustainability?
What are data-less service components? Are run in the context of a secure user session with appropriate access Are provided with the InstanceGUID of a record upon which to operate Place locks on the record to prevent multiple concurrent updates (if required) Use the latest version of the record from Data at Rest Perform work on the record as required to complete the action Stores the results of the action back to Data at Rest
What is nano-service architecture? Going beyond Micro-service architecture Micro services typically encapsulate the data they operate on They aggregate many distinct operations on the encapsulated data Require use of complex performance patterns: caching , eventual consistency , Use Domain Driven Design principles to create Functionality data models All record data is persisted to the Data at Rest service area (System of Record) No state of any kind is stored by the Data in Action service components All Data in Action service components have direct access to Data at Rest Allows for the efficient development of nano-scale service components Each configurable component can provide a single operation Makes them easily versioned, deployable and scalable
How do we build them? Push the processing as close to the data as possible Keep the service hierarchy as flat as possible Build fine grained services with a common interface plug and play Create generic services that can be configured with data Separate as much logic into re-usable class libraries as possible Easier to build and test Execute within a service boundary minimize inter-service communication
What technology do we use to build them? Can use any technology that can be invoked and connect to Data at Rest Databases: T-SQL Stored Procedures, Triggers Server based APIs: Any programming language that supports RPCs Web APIs: Any programming stack that supports TCP/IP Operating Services: Windows, Linux, Cloud Services: Serverless functions, workflow/orchestration engines,
How do we call them? Triggered by: Users interacting with interfaces Updates the records The arrival of messages or events Scheduled by: Database service agents Operating System Timers Polling background services
What are the DevOps advantages? Compartmentalised Secure Reliable and Robust Easy to test and integrate Horizontally scalable Reusable and Composable Versioned and easy to deploy / upgrade
How does this impact sustainability? Minimise the number of technologies in use Standardise how each technology is used and share best practise Update architecture as better technologies become available Design reusable components that can be easily configured using data Maintain a consistent interface so that services can be easily composed Keep configurable units small to make them easy to version and deploy Use automated tests to maintain quality Use automated CI/CD pipeline tools Uses a smaller infrastructure footprint