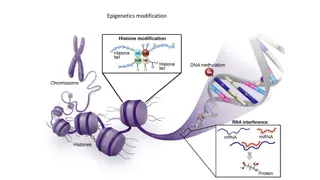
Epigenetics update
Investigating candidate genes and DNA methylation markers for breast cancer detection, two case-control studies were conducted, showing promising results with an AUC of 0.937 in an independent test cohort. Additionally, the association of smoking-related DNA methylation with phenotypic age acceleration and the prognostic value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in brain cancer patients were studied. Furthermore, early life social and ecological factors were found to influence global DNA methylation in wildlife. Air pollution exposure did not yield new genomic loci associated with DNA methylation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Epigenetics update July 15, 2019
Candidate genes for breast cancer detection Downs, Mercado-Rodriguez, Cimino-Mathews, Chen, Yuan, Van Den Berg, Cope, Schmitt, Tse, Ali, Meir-Levi, Sood, Li, Richardson, Mosunjac, Rizzo, Tulac, Kocmond, de Guzman, Lai, Rhees, Bates, Wolff, Gabrielson, Harvey, Umbricht, Visvanathan, Fackler, Sukumar. DNA Methylation Markers for Breast Cancer Detection in the Developing World. Clin. Cancer Res. 31300453 "Two case-control studies were conducted comparing cancer and benign breast tissue identified from clinical repositories in the U.S., China, and South Africa for marker selection/training (N=226) and testing (N=246). Twenty-five methylated markers were assayed ... In the independent test cohort, this panel yielded an AUC of 0.937 (95% CI = 0.900-0.970)"
Phenoage and smoking Yang, Gao, Just, Colicino, Wang, Coull, Hou, Zheng, Vokonas, Schwartz, Baccarelli. Smoking-Related DNA Methylation is Associated with DNA Methylation Phenotypic Age Acceleration: The Veterans Affairs Normative Aging Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 31277270 n=692 Yes, PhenoAge is associated with smoking, unlike Horvath s DNAm age.
Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio and brain cancer Brenner, Friger, Geffen, Kaisman-Elbaz, Lavrenkov. The Prognostic Value of the Pretreatment Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme Brain Tumors: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Patients Treated with Combined Modality Surgery, Radiation Therapy, and Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Oncology. 31288238 n=89 "pretreatment NLR was not prognostic"
Global methylation and social factors Laubach, Faulk, Dolinoy, Montrose, Jones, Ray, Pioon, Holekamp. Early life social and ecological determinants of global DNA methylation in wild spotted hyenas. Mol. Ecol. 31291495 "maternal rank, anthropogenic disturbance, and prey availability early in life are associated with later life global DNA methylation" 2.75% global methylation in offspring of high and low rank mothers
EWAS of pollution Sayols-Baixeras, Fernandez-Sanles, Prats-Uribe, Subirana, Plusquin, Kanzli, Marrugat, Basagana, Elosua. Association between long-term air pollution exposure and DNA methylation: The REGICOR study. Environ. Res. 31260916 N=630 discovery (REGICOR) N=454 validation (EPIC-Italy) "NOX, NO2, PM10, PM2.5, PMcoarse, traffic intensity and traffic load exposure were measured Neither new genomic loci associated with long-term air pollution were identified, nor previously identified loci were replicated."
EWAS in non-peripheral tissues Ho, Winham, Armasu, Blacker, Millischer, Lavebratt, Overholser, Jurjus, Dieter, Mahajan, Rajkowska, Vallender, Stockmeier, Robertson, Frye, Choi, Veldic. Genome- wide DNA methylomic differences between dorsolateral prefrontal and temporal pole cortices of bipolar disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 31279243 20 BD, ten major depression (MDD), and ten control age-and-sex-matched subjects. No associations with BD survived adjustment for multiple tests. Cardenas, Sordillo, Rifas-Shiman, Chung, Liang, Coull, Hivert, Lai, Forno, Celedon, Litonjua, Brennan, DeMeo, Baccarelli, Oken, Gold. The nasal methylome as a biomarker of asthma and airway inflammation in children. Nat Commun. 31300640 "we collect nasal swabs from the anterior nares of 547 children (mean-age 12.9 y) EWAS of current asthma, allergen sensitization, allergic rhinitis, fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and lung function. asthma (285-CpGs), FeNO (8,372-CpGs; 191-DMRs), total IgE (3-CpGs; 3-DMRs), environment IgE (17-CpGs; 4-DMRs), allergic asthma (1,235-CpGs; 7-DMRs) and bronchodilator response (130-CpGs).
Multiple cell types Bradford, Nair, Statham, van Dijk, Peters, Anwar, French, von Martels, Sutcliffe, Maddugoda, Peranec, Varinli, Arnoldy, Buckley, Ross, Zotenko, Song, Stirzaker, Bauer, Qu, Swarbrick, Lutgers, Lord, Samaras, Molloy, Clark. Methylome and transcriptome maps of human visceral and subcutaneous adipocytes reveal key epigenetic differences at developmental genes. Sci Rep. 31266983 "we characterised transcriptomes and methylomes of isolated adipocytes from matched SA and VA tissues of individuals with normal BMI to identify epigenetic differences and their contribution to cell type and depot-specific function. Mendizabal, Berto, Usui, Toriumi, Chatterjee, Douglas, Huh, Jeong, Layman, Tamminga, Preuss, Konopka, Yi. Cell type-specific epigenetic links to schizophrenia risk in the brain. Genome Biol. 31288836 "whole-genome methylomes (N = 95) and transcriptomes (N = 89) from neurons and oligodendrocytes". Identified DNAm differences between schizophrenia and controls at FDR < 0.2: 60 in NeuN+ and 201 in OLIG2+.
EWAS of microRNAs Huan, Mendelson, Joehanes, Yao, Liu, Song, Bhattacharya, Rong, Tanriverdi, Keefe, Murabito, Courchesne, Larson, Freedman, Levy. Epigenome-wide association study of DNA methylation and microRNA expression highlights novel pathways for human complex traits. Epigenetics. 31282290 283 miRNAs and DNAm at 450K CpG sites in whole blood N=3565 individuals 227 CpGs associated with the expression of 40 nearby miRNAs 91 independent CpG sites at r2<0.2 Bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis identified 58 CpG/miRNA pairs where DNAm causes miRNA but not the reverse Data available from dbGaP
EWAS with two-sample MR Wiklund, Karhunen, Richmond, Parmar, Rodriguez, De Silva, Wielscher, Rezwan, Richardson, Veijola, Herzig, Holloway, Relton, Sebert, Jarvelin. DNA methylation links prenatal smoking exposure to later life health outcomes in offspring. Clin Epigenetics. 31262328 prenatal maternal smoking with offspring blood DNA methylation in 2821 individuals (age 16 to 48 years) 5 prospective birth cohorts 69 differentially methylated CpG sites Mendelian randomization found four maternal smoking-related CpG sites increased risk of either inflammatory bowel disease or schizophrenia Richardson, Richmond, North, Hemani, Davey Smith, Sharp, Relton. An integrative approach to detect epigenetic mechanisms that putatively mediate the influence of lifestyle exposures on disease susceptibility. Int J Epidemiol. 31257439 412 CpG sites associated with prenatal smoking 2SMR identified 22 associations with complex traits (from among 412 CpG sites and 634 traits) Exposure -> CpG -> Complex trait 1. Exposure -> CpG: published EWAS 2. CpG -> Complex trait: mQTLdb + published GWAS and UK Biobank
Wiklund et al: 69 CpG sites and 106 diseases (associated with prenatal smoke in peripheral blood at age 16-48) Exposure Gene Disease SE P value FDR P value Unit cg15578140 MIR548F3 Inflammatory bowel disease 0.104 0.018 3.73E 09 2.54E 07 Log odds cg09935388 GFI1 Inflammatory bowel disease 0.152 0.034 7.27E 06 2.18E 04 Log odds cg04598670 Unknown Inflammatory bowel disease 0.410 0.091 7.27E 06 5.24E 04 Log odds cg09935388 GFI1 Crohn s disease 0.162 0.040 4.74E 05 7.12E 04 Log odds cg04598670 Unknown Crohn s disease 0.439 0.108 4.74E 05 1.71E 03 Log odds cg09935388 GFI1 Ulcerative colitis 0.160 0.042 1.47E 04 1.47E 03 Log odds cg04598670 Unknown Ulcerative colitis 0.433 0.114 1.47E 04 3.52E 03 Log odds cg25189904 GNG12 Schizophrenia 0.222 0.053 3.37E 05 1.82E 03 Log odds
Richardson et al: 412 CpG sites and 643 complex traits (associated with prenatal smoke in cord blood) CpG site Gene Complex trait MR Beta (SE) MR P PPAabc 1.84E 05 cg26930078 C17orf53 BMD 0.093 (0.010) 1.50E 20 cg02812767 LOXL1 FVC 0.051 (0.006) 3.78E 20 0.220 cg08685733 C17orf53 BMD 0.108 (0.013) 5.78E 18 0.176 cg25313468 REST Height 0.064 (0.008) 5.37E 17 9.61E 06 cg06105699 ASPSCR1 FEV1 0.053 (0.007) 7.29E 15 1 cg23184042 DLX6AS BMD 0.038 (0.005) 1.26E 14 1.31E 04 cg14150774 QSOX2 FVC 0.038 (0.005) 1.99E 12 5.31E 05 cg18883198 TMEM57 LDL 0.099 (0.016) 2.72E 10 5.22E 06 cg01401641 TSHZ3 SBP 0.040 (0.007) 4.25E 09 0.158 cg01307174 ARPP-21 Worrying 0.025 (0.004) 2.65E 08 0.003 cg25313468 REST FEV1 0.030 (0.006) 4.86E 8 0.955 cg18089426 DLK1 Age at menarche 0.099 (0.019) 9.00E 08 1.09E 04 cg06070002 PRDX1 Waist-to-hip ratio 0.056 (0.011) 1.08E 07 9.62E 05
Methods Liu, Yang, Wang, Lin, Kang, Jia, Ye. MEpurity: estimating tumor purity using DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics. 31297508 a beta mixture model-based algorithm, to estimate the tumor purity based on tumor-only Illumina Infinium 450k methylation microarray data Weber, Saelens, Cannoodt, Soneson, Hapfelmeier, Gardner, Boulesteix, Saeys, Robinson. Essential guidelines for computational method benchmarking. Genome Biol. 31221194 Gomez, Odom, Young, Martin, Liu, Chen, Griswold, Gao, Zhang, Wang. coMethDMR: accurate identification of co-methylated and differentially methylated regions in epigenome-wide association studies with continuous phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 31291459 Instead of testing all CpGs within a genomic region, coMethDMR carries out an additional step that selects co-methylated sub-regions first. Next, coMethDMR tests association between methylation levels within the sub-region and phenotype via a random coefficient mixed effects model that models both variations between CpG sites within the region and differential methylation simultaneously - Compared to comb-p, DMRcate, bumphunter, seqlm.
Reviews Yuan, Xu. Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) in Action: Cross-Talking with Epigenetics. Int J Mol Sci. 31284662 Tert is normally silent in most cell types except "stem cells, activated lymphocytes, and other highly proliferative cells." "TERT induction is widespread in human malignant cells" "TERT/telomerase extends telomere length" But, TERT/telomerase may participate in other processes. We discuss: 1. "How TERT contributes to epigenetic alterations in physiological processes and cancer" 2. "how the aberrant epigenetics in turn facilitate TERT expression and function, eventually promoting cancer either initiation or progression or both." 3. "Finally, we briefly discuss clinical implications of the TERT-related methylation"
Reviews Ehrlich. DNA hypermethylation in disease: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Epigenetics. 31284823 "Disease-linked DNA hypermethylation can help drive oncogenesis partly by - its effects on cancer stem cells and by the CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP); - atherosclerosis by disease-related cell transdifferentiation; - autoimmune and neurological diseases through abnormal perturbations of cell memory; and - diverse age-associated diseases by age-related accumulation of epigenetic alterations." CIMP: Many CpG islands have increasing DNAm levels with age. However, there are additionally, in colorectal cancer, specific CpG islands near tumor supressor genes with increased DNA methylation.