Equations and Conversions in Electrical Circuits
"Learn how to convert between different circuit configurations like Y and delta, understand total resistances, and derive conversion equations in electrical circuits. Examples and illustrations included."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
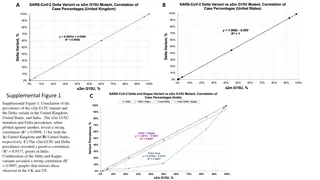
Lect. 10 Lect. 10 - -Y Y- - (T AND AND - -Y (P Y (P- -T) CONVERSIONS T) CONVERSIONS conversion (T- -P) P)
be the same with the configuration inserted in place of the Y configuration (and vice versa).
Developing the equations for converting from to Y, or vice versa Developing the equations for converting from to Y, or vice versa. . If the two circuits are to be equivalent, the total resistance between any two terminals must be the same. Consider terminals a-c in the - Y configurations in Fig. 78.
Converting the (RA, RB, RC) to the Y (R1, R2, R3). Converting the (RA, RB, RC) to the Y (R1, R2, R3).
Continue Continue
Converting from a Y to a , Converting from a Y to a , first divide Eq. (5a) by Eq. (5b):
Special case where all the values of a or Y were the same. If RA =RB = RC
Continue Continue The Y and the often appear as shown in Fig. 79. They are then referred to as a tee (T) and a pi (p) network, respectively. The equations used to convert from one form to the other are exactly the same as those developed for the Y and transformation
EXAMPLE EXAMPLE- - 27 Convert the in Fig. 80 to a 27 Convert the in Fig. 80 to a Y.