Equivalent Resistor Calculation Experiment
Explore how to calculate equivalent resistors in electrical circuits by connecting resistors in series and parallel. Learn the theory behind resistor calculations and compare theoretical values with experimental results. Includes practical steps and discussions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
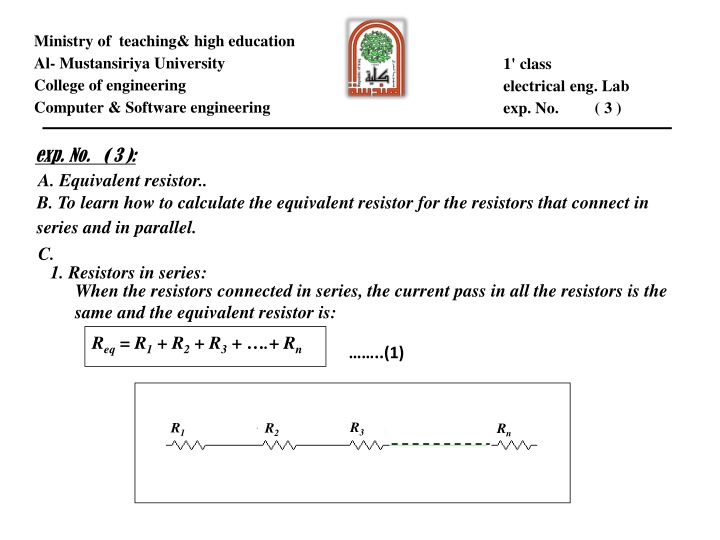
Ministry of teaching& high education Al- Mustansiriya University College of engineering Computer & Software engineering 1' class electrical eng. Lab exp. No. ( 3 ) exp. No. ( 3 ): A. Equivalent resistor.. B. To learn how to calculate the equivalent resistor for the resistors that connect in series and in parallel. C. 1. Resistors in series: When the resistors connected in series, the current pass in all the resistors is the same and the equivalent resistor is: Req= R1+ R2+ R3+ .+ Rn ..(1) R3 R1 R2 Rn
2. Resistors in parallel: When the resistors connected in parallel, the voltage pass in all the resistors is the same and the equivalent resistor is: 1 1 1 1 1 = + + + + ..(2) ??? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? D. Procedure: 1. Connect the circuit shown in fig.1. let the value of R= 100 . Find the value of the current(I) and voltage(V). 2. Change the value of R=200 and repeat step1. Connect the previous two resistors in series and repeat step1.(see fig.2). 3. Connect the previous two resistors in parallel and repeat step1.(see fig.3).
R1 R 10V R2 Fig.1 Fig.2 R1 R2 10V Fig.3
E. Discussion: 1. Calculate the value of resistors from the reading of step 1, step 2 using the relation R = V/I. 2. Calculate the value of equivalent resistor from the reading of step 3, step 4 using the relation R = V/ I. And compare these values with the theoretical values from relation 1, 2.






















