Essential Concepts of Professional Communication
"Explore the fundamentals of communication, the process, features, flow in organizations, importance, and purpose of professional communication. Learn about the differences between general and professional communication, along with common types and barriers. Enhance your understanding of communication for effective business interaction."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fundamentals of Communication
Communication Definition Process Important Features Importance Purpose of Professional Communication Differences between General and Professional Communication Types Flow of Communication in an Organization Informal Network - Grapevine Communication Barriers - Types and Measures 2
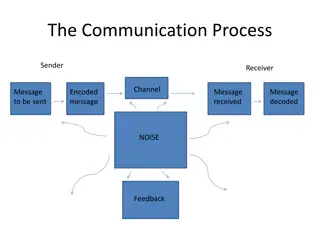
Definition Communication essentially meansthe transfer of ideas, feelings, plans, messages, or information from one person to another. It is effective only when it gets the desired action or response. Communication is a network of interaction where the sender and receiver keep changing their roles. Communication is a dynamic process, the main components of which are sender, message, channel, receiver, and response. 3
Process 4
Features Two-way Creative Functional Sender and receiver keep changing their roles Continuous 5
Communication Flow Means, Kinds, Manners, Forms Types (Parties involved) Linguistic Paralinguist ic Vocal Cues Non- verbal Verb al Intrapersonal Mass Spiral Extralinguist ic Diagon al Horizont al Vertical Interperson al Extraperson al Kinesics Proxemics Chronemics Haptics (Touch) Artefacts Oral Writte n Speech Reports Seminar Letter Memo Minutes GD Meetings Intervie w Professional Presentation 6
Importance of Communication Business has grown in size Business activity has become complex Business has become competitive Workers are organized through trade union Promotes a spirit of understanding and cooperation 7
Purpose of Professional Communication Advising Counseling Giving Orders Providing Instructions Marketing Persuasion Giving Warnings Raising Morale Staffing Projecting Image Preparing Advertisements Making Decisions Getting Feedback 8
Differences between General and Professional Communication General Communication Professional Communication Content:Contains general message Nature: Informal in style and approach Structure: No set pattern of communication Method: Mostly oral Audience: Not always for a specific audience Language: Does not normally involve the use of technical vocabulary or graphics, etc. Content: Contains a formal and professional message Nature: Mostly formal and objective Structure: Follows a set pattern such as sequence of elements in a report Method: Both oral and written Audience: Always for a specific audience, e.g., customers, banks, etc. Language: Frequently involves jargon, graphics, etc. for achieving professional purposes 9
How much time do you spend on the following? Informal note Memos Letters Circulars and notices Press releases Reports Handbooks Manuals Unplanned exchanges Meetings Brainstorming Telephone Interviews Formal presentations Discussion groups Seminars 10
Different Types of Communication Flow Horizontal Vertical o Upward o Downward Crosswise Spiral 11
Flow of Communication in an Organization 12
Barriers to Communication Definition: When you convey your message to someone or a group of people and the message is not received clearly and unambiguously, it is known as barrier to communication. Thus, the message received is not as the message sent. Barriers to effective communication could cause roadblocks in your professional and personal life and it could be one of the major hurdles in achieving your professional goals. 13
Further Discussed Measures to rectify communication failure Types of communication barriers Tips for Effective Communication 14
Steps to Rectify Communication Failure 1. Identify the problem 2. Find out its cause 3. Select and apply the best alternative 4. Follow up religiously 15
Types of Communication Barriers Based on the Nature of Barriers Barriers of psychological nature Barriers arising due to emotional reactions, negative attitudes, and wrong timing of messages Barriers originating from the communication networks established by organizations 16
Verbal Barriers Lack of proper planning Selection of a wrong variety of language Badly encoded or wrongly decoded messages Semantic gap Differences in perceptions Variation in language Wrong inferences Categorical thinking 17
Non-verbal Barriers Raising eyebrows Keeping your hands or thumbs constantly in the pockets of your trousers Awkward gestures Flashing eyes Rolling eyes Quick movements Very slow movement Avoiding eye contact 18
Listening Barriers Making the speaker feel as though he/she is wasting the listener s time Being distracted by something that is not part of the ongoing communication Getting ahead of the speaker and completing his/her thoughts Topping the speaker s story with one s own set of examples Forgetting what is being discussed Asking too many questions for the sake of probing Note: These barriers are elaborately discussed in the chapter entitled Developing Effective Listening Skills . 19
Miscellaneous Barriers Premature evaluation of message Information overload Distrust, threat, and fear Less time for orientation and for adjustment to change Emotional reaction Rigidity in attitudes 20
Some Remedies Send the data only to the people who require them Emphasize the major ideas Delete unwanted ideas Maintain transparency in policy matters Ensure clarity in message and look for a genuine feedback Understand others emotions Understand other cultures and language variations and use the appropriate variety in the given context 21
Some Remedies Make sure that information overload does not affect the communication environment adversely. Maintain openness and acknowledge that people have different perceptions and views regarding one thing. Encourage innovative ideas and views so that people should not unnecessarily live in fears. Listen attentively to others Speak with clarity and conviction 22