Essential Macromolecules in Living Organisms
Biological macromolecules, also known as polymers, are large molecules made of small subunits critical for all living organisms. They are created and broken down through condensation and hydrolysis reactions, respectively. Condensation joins monomers to form polymers by removing water, while hydrolysis breaks down polymers into smaller components using water. Explore the processes through clear examples and images.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
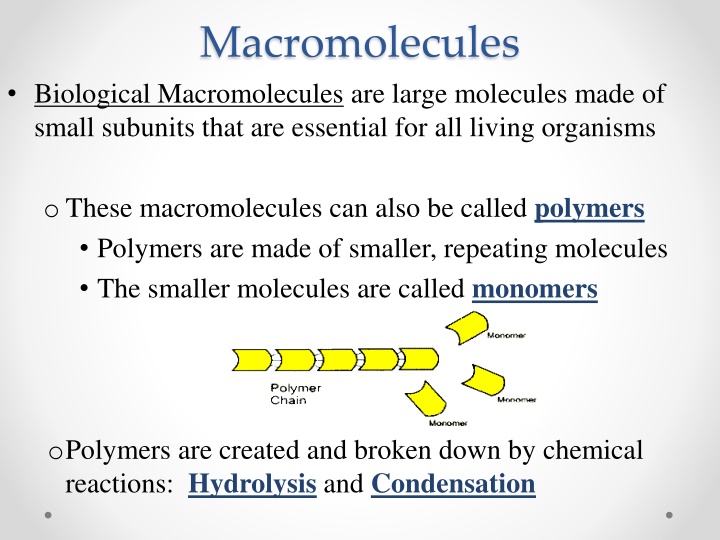
Macromolecules Biological Macromolecules are large molecules made of small subunits that are essential for all living organisms o These macromolecules can also be called polymers Polymers are made of smaller, repeating molecules The smaller molecules are called monomers oPolymers are created and broken down by chemical reactions: Hydrolysis and Condensation
1. Condensation Reaction (aka: Dehydration Synthesis) Joins monomers together to create a polymer by removing a water molecule from the monomers o Water is produced This is the process by which larger molecules are created or built Example : o Parts of water (OH & H) are removed from each monomer o The remaining pieces of the monomer join together to make a polymer o OH & H come together to form water (H2O)
2. Hydrolysis Hydro = Water ; lysis = to cut/split Hydrolysis reactions use water to cut or break down polymers into smaller pieces This is how large molecules are broken into smaller parts o Digestion of food Example: o Water splits the polymer in half o The parts of water are added to each monomer where the bond was broken o 2 separate monomers are formed
If hydrolysis, a reaction will start with a polymer and water and end with 2 monomers: If condensation, a reaction will start with 2 monomers and end with a polymer and water:
Identify the reaction Hydrolysis
Identify the reaction Condensation
Identify the reaction Condensation
Identify the reaction Hydrolysis