Establishing Tudor Monarchical Authority: Methods & Consequences
Explore how the Tudor monarchs established their authority from 1485 to 1603, analyzing key events and decisions of Henry VII, Henry VIII, and other Tudor rulers. Understand the impact of religious changes, foreign policies, and internal dynamics on the monarchy's stability and power.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
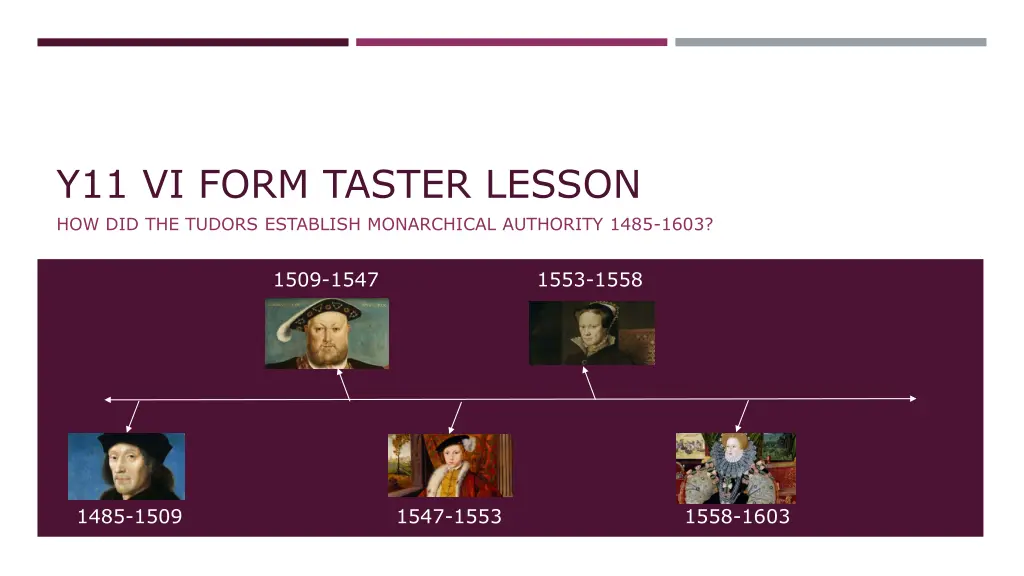
Y11 VI FORM TASTER LESSON HOW DID THE TUDORS ESTABLISH MONARCHICAL AUTHORITY 1485-1603? 1509-1547 1553-1558 1485-1509 1547-1553 1558-1603
HOW MANY POINTS CAN YOU GET? What war happened before Henry VII took the throne? How old was Edward VI when he took the throne? Name one of Henry VIII s wives. Who was the last Tudor monarch? What were the two houses in England before Henry VII took the throne? Why is Mary I known as bloody Mary ? Which country did Elizabeth I defeat in 1588? Name one of Henry VIII s children. 1 point 2 points 3 points 4 points
HOW DID THE TUDORS ESTABLISH MONARCHICAL AUTHORITY 1485-1603? You have a series of statements one for each of the Tudor monarch. Your task is to note down four consequences of the statement or decision.
TUDOR CONSEQUENCES Henry VII He punished those that went against him and rewarded those that were loyal to him. Henry VIII changed the religion in England from Catholic to Protestant making himself the Head of the English Church thus alienating the Pope. Edward VI The boy King who would never rule his throne and be always under the watchful eye of his uncles Lord Somerset and Northumberland. Mary I She was brought up in the Spanish court and when made Queen of England returned the country back to the Catholic faith. Elizabeth I She changed the religion of this country back to Protestantism, supported rebels in the Netherlands against Spain and defeated the Armada.
HOW DID THE TUDORS ESTABLISH MONARCHICAL AUTHORITY 1485-1603? A large theme in the study of the Tudors is whether the monarchs established their authority. In your packs, you ve got some key events/methods of establishing authority for Henry VII and Henry VIII. Your job is to categorise which boxes show how they did establish authority and which boxes show they didn t or they were threatened. Challenge: Which monarch do you think was the strongest?
HOW DID THE TUDORS ESTABLISH MONARCHICAL AUTHORITY 1485-1603? What s the overall opinion of the extract? What s fact and what is opinion? Extract B: From The Reign of Henry VII by B. Thompson (ed.), 1995. The avoidance of war was no solution for a new monarchy, since war was more popular than not, and was therefore backed by money and manpower, especially when successful. Even Henry s foreign policy, though astute, was more problematic than it needs to have been as a result of his own need for dynastic security In his quarter-century of instability and uncertainty, Henry never secured the loyalty of the realm through stable and representative rule, and therefore never escaped from the consequences of being a usurper.






















