Evolution of Cryptography: From Ancient Techniques to Modern Security Systems
"Explore the fascinating world of cryptography, from its historical roots to its crucial role in modern network security. Learn about different types of cryptography, its everyday applications, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as the future outlook of this essential field."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
www.studymafia.org Seminar On Cryptography And Network Security Submitted To: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Submitted By:
CONTENT Abstract Introduction Cryptography Evolution of Cryptography Types of Cryptography Cryptography in Everyday Life Advantages and Disadvantages Future Conclusion
INTRODUCTION Network security deals with the problems of legitimate messages being captured and replayed. Network security is the effort to create a secure computing platform. The action in question can be reduced to operations of access, modification and deletion. Many people pay great amounts of lip service to security but do not want to be bothered with it when it gets in their way.
CRYPTOGRAPHY Cryptography Cryptography is the science of using mathematics to encrypt and decrypt data. Cryptography enables you to store sensitive information or transmit it across insecure networks (like the internet). So that it cannot be read by anyone expect the intended recipient. While cryptography is the science of securing data, cryptanalysts are also called attackers. Cryptology embraces both cryptography and cryptanalysis.
EVOLUTIONOF CRYPTOGRAPHY Improved coding techniques such as Vigenere Coding came into existence in the 15th century, which offered moving letters in the message with a number of variable places instead of moving them the same number of places. Only after the 19th century, cryptography evolved from the ad hoc approaches to encryption to the more sophisticated art and science of information security. In the early 20th century, the invention of mechanical and electromechanical machines, such as the Enigma rotor machine, provided more advanced and efficient means of coding the information. During the period of World War II, both cryptography and cryptanalysis became excessively mathematical.
TYPES OF CRYPTOGRAPHY: 1. Symmetric Key Cryptography It is an encryption system where the sender and receiver of message use a single common key to encrypt and decrypt messages. Symmetric Key Systems are faster and simpler but the problem is that sender and receiver have to somehow exchange key in a secure manner. The most popular symmetric key cryptography system is Data Encryption System(DES).
TYPES OF CRYPTOGRAPHY 2. Hash Functions There is no usage of any key in this algorithm. A hash value with fixed length is calculated as per the plain text which makes it impossible for contents of plain text to be recovered. Many operating systems use hash functions to encrypt passwords.
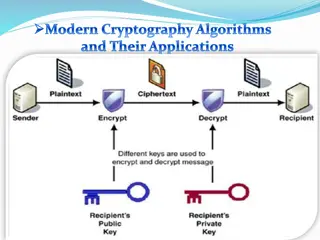
TYPES OF CRYPTOGRAPHY 3. Asymmetric Key Cryptography Under this system a pair of keys is used to encrypt and decrypt information. A public key is used for encryption and a private key is used for decryption. Public key and Private Key are different. Even if the public key is known by everyone the intended receiver can only decode it because he alone knows the private key.
DIFFERENCEBETWEEN CYBERSECURITY AND CRYPTOGRAPHY Cyber Security Cryptography It is a process of keeping networks, devices, programs, data secret and safe from damage or unauthorized access. It is all about managing cyber risks in all aspects such as people, process, technology, etc. Its main objective is to prevent or mitigate harm or destruction of computer networks, applications, devices, and data. It is generally used for the protection of internet-connected systems like software, hardware, and data, risk management, disaster planning, access control, policies. It is a process of keeping information secret and safe simply by converting it into unintelligible information and vice-versa. It is all about math functions and can be applied in technical solutions for increasing cybersecurity. Its main objective is to keep plain text secret from eaves or droppers who are trying to have access to some information about the plain text. It is generally used for integrity, entity authentication, data origin authentication, non-repudiation, etc.
DIFFERENCEBETWEEN STEGANOGRAPHYAND CRYPTOGRAPHY Steganography Steganography means covered writing. Cryptography Cryptography means secret writing. While cryptography is more popular than Steganography. Steganography is less popular than Cryptography. Attack s name in Steganography is Steganalysis. While in cryptography, Attack s name is Cryptanalysis. In steganography, structure of data is not usually altered. While in cryptography, structure of data is altered. Steganography supports Confidentiality and Authentication security principles. While cryptography supports Confidentiality and Authentication security principles as well as Data integrity and Non-repudiation. In steganography, the fact that a secret communication is taking place is hidden. While in cryptography only secret message is hidden.
CRYPTOGRAPHYIN EVERYDAY LIFE Authentication/Digital Signatures Time Stamping Electronic Money Encryption/Decryption in email Encryption in WhatsApp Encryption in Instagram Sim card Authentication
CRYPTOGRAPHY BENEFITS Confidentiality Encryption technique can guard the information and communication from unauthorized revelation and access of information. Authentication The cryptographic techniques such as MAC and digital signatures can protect information against spoofing and forgeries. Data Integrity The cryptographic hash functions are playing vital role in assuring the users about the data integrity. Non-repudiation The digital signature provides the non-repudiation service to guard against the dispute that may arise due to denial of passing message by the sender.
CRYPTOGRAPHY DRAWBACKS A strongly encrypted, authentic, and digitally signed information can be difficult to access even for a legitimate user at a crucial time of decision-making. The network or the computer system can be attacked and rendered non-functional by an intruder. High availability, one of the fundamental aspects of information security, cannot be ensured through the use of cryptography. Other methods are needed to guard against the threats such as denial of service or complete breakdown of information system. Another fundamental need of information security of selective access control also cannot be realized through the use of cryptography. Administrative controls and procedures are required to be exercised for the same.
FUTUREOF CRYPTOGRAPHY Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) has already been invented but its advantages and disadvantages are not yet fully understood. ECC allows to perform encryption and decryption in a drastically lesser time, thus allowing a higher amount of data to be passed with equal security. However, as other methods of encryption, ECC must also be tested and proven secure before it is accepted for governmental, commercial, and private use. Quantum computation is the new phenomenon. While modern computers store data using a binary format called a "bit" in which a "1" or a "0" can be stored; a quantum computer stores data using a quantum superposition of multiple states. These multiple valued states are stored in "quantum bits" or "qubits". This allows the computation of numbers to be several orders of magnitude faster than traditional transistor processors.
CONCLUSION: Network security is a very difficult topic. Every one has a different idea of what security is, and what levels of risks are acceptable. The key for building a secure network is to define what security means to your organization.
REFERENCE www.google.com www.wikipedia.com www.studymafia.org www.projectsreports.org