Evolution of English Arts and Inventions Through the Centuries
Explore the rich cultural heritage of England from the 9th to the 21st century, covering key landmarks such as the founding of Oxford and Cambridge, the works of Geoffrey Chaucer, and the impact of the Printing Press. Discover the geographical divisions of England and its contributions to arts and inventions over 2000 years.
Download Presentation

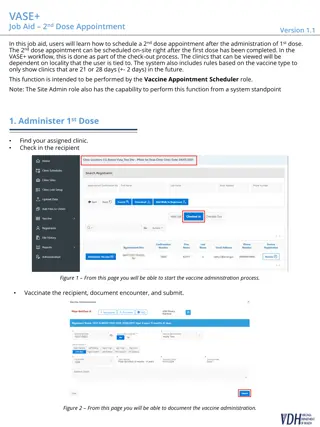
Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geographical Location Of England Arts & Inventions in the English Culture 9thc. 21stc.
The United Kingdom consists of four political regions: England- Scotland Wales North Ireland England is geographically divided into two main zones: 1- Lowlands: midlands- Anglia-Pennines- Lake district in north 2- Uplands: Dartmoor- Exmoor in southwest
2000 years of Art and Invention 9thc. - Beowulf / Schools for English nobles File:Beowulf.firstpage.jpeg
- 11thc. _ Doomsday book File:Domesday-book-1804x972.jpg
12thc. _ Oxford founded Four kings, 46 Nobel Prize winners (and counting), several great poets, the inventor of DNA "fingerprinting", and three saints have studied or taught at Oxford University.
13thc. _ Cambridge founded Scientists of stellar intellect Newton, Maxwell, Rutherford, Watson, and Crick have studied or taught at Cambridge along with one queen, several martyrs, and more Nobel Prize winners than any other institution in the world.
14 c _ Geoffrey Chaucer Geoffrey Chaucer, known as the Father of English literature, is widely considered the greatest English poet of the Middle Ages and was the first poet to have been buried in Poet's Corner of Westminster Abbey. File:Geoffrey Chaucer (17th century).jpg
15thc. Setting of the Printing press. Le Morte d'Arthur is a compilation by Sir Thomas Malory of Romance tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, and the Knights of the Round Table. Le Morte d'Arthur is perhaps the best- known work of English-language Arthurian literature today. Many modern Arthurian writers have used Malory as their principal source. File:Boys King Arthur - N. C. Wyeth - title page.jpg
16th c. _ 1stEnglish translation of Bible / Shakespeare The first English translation of the whole Bible. William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon".
17 c _ Circulation of blood William Harvey was an English physician. He was the first to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the body by the heart, though earlier writers had provided precursors of the theory. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/42/William_Harvey_2.jpg/260px-William_Harvey_2.jpg
17th c. George Chapman : translates he Greek epic Homer into English John Milton: considered the 2nd most imp English literary writer after Shakespeare- Wrote his famous epic poem paradise lost about the story of Adam & Eve in 12 books
17th c. Isaac Newton Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP was an English physicist and mathematician who is widely regarded as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. Portrait of man in black with shoulder-length, wavy brown hair, a large sharp nose, and a distracted gaze
18 c. 1st steam engine/ cricket/ 1st English dictionary/Oxygen/Rights of women Mary Wollstonecraft was an eighteenth- century British writer, philosopher, and advocate of women's rights. Left-looking half-length portrait of a possibly pregnant woman in a white dress
18th c. Samuel Johnson, often referred to as Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. He compiled the first useful English Dictionary. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/20/Samuel_Johnson_by_Joshua_Reynolds.jpg/220px-Samuel_Johnson_by_Joshua_Reynolds.jpg
19th c. _ 1st steam locomotive/ 1st passenger railway/ 1st thesaurus/Rugby football/1st synthetic dye/1st traffic light/ 1st tube train/ 1st brain tumor surgery
20th c. Vitamins/ 1st motion picture/ 1st TV studio/ 1st jet engine aircraft/ 1st computer at Manchester univ/DNA/ The Beatles/ High Speed trains/ genetic fingerprinting/ World Wide Web Francis Harry Compton Crick, OM, FRS was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist, and most noted for being a co-discoverer of the structure of the DNA molecule in 1953 together with James D. Watson. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d2/Francis_Crick.png/250px-Francis_Crick.png
20th c. Sir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, OM, KBE, FRS, FREng, FRSA, also known as "TimBL," is a British computer scientist, best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3a/Tim_Berners-Lee_closeup.jpg/220px-Tim_Berners-Lee_closeup.jpg
21th c. _Cosmology (discover the lightest particle in the universe) Nanotechnology Nanotechnology (sometimes shortened to "nanotech") is the manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular scale. With a variety of potential applications, nanotechnology is a key technology for the future and governments have invested billions of dollars in its research. Nanotechnology could be used to eradicate disease, improve agriculture, and create easily available sources of energy for cars and low-cost materials for everything from computers and electronic devices to wound dressings. Semiconductor development at the University of Sheffield represents some of the most industrially advanced areas of nanotechnology. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/C60a.png/175px-C60a.png
21th c. Sir Jonathan Paul "Jony" Ive, KBE is an English designer and the Senior Vice President of Industrial Design at Apple Inc. He revolutionized computer designs, including imacs, ipads, ipods and iphones. He also provides leadership and direction for Human Interface software teams across the company. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Jonathan_Ive_%28OTRS%29.jpg/220px-Jonathan_Ive_%28OTRS%29.jpg