Evolution of Pharmacy Practices and Healthcare Supply Chain Management
Explore the historical evolution and expanding roles of pharmacists in healthcare management, patient care, and optimizing the healthcare supply chain for efficient and cost-effective medication delivery. Dive into the responsibilities of key healthcare personnel in hospitals and pharmacies, emphasizing the critical role of pharmacists in ensuring timely access to essential medications and enhancing healthcare outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
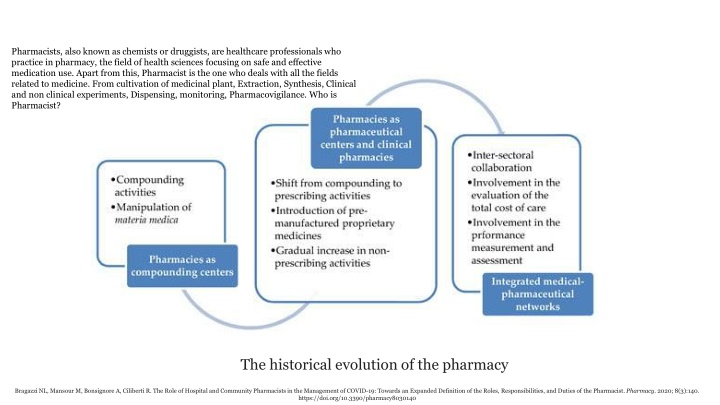
Pharmacists, also known as chemists or druggists, are healthcare professionals who practice in pharmacy, the field of health sciences focusing on safe and effective medication use. Apart from this, Pharmacist is the one who deals with all the fields related to medicine. From cultivation of medicinal plant, Extraction, Synthesis, Clinical and non clinical experiments, Dispensing, monitoring, Pharmacovigilance. Who is Pharmacist? The historical evolution of the pharmacy Bragazzi NL, Mansour M, Bonsignore A, Ciliberti R. The Role of Hospital and Community Pharmacists in the Management of COVID-19: Towards an Expanded Definition of the Roles, Responsibilities, and Duties of the Pharmacist. Pharmacy. 2020; 8(3):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8030140
The historical evolution of the roles, responsibilities and duties of the pharmacist
Hospital Chief Medical Officer (CMO) Nurses Administrator/CEO: Pharmacies Medical Equipment Dealer Pharmacist Figure: Glimpses of key persons at Hospitals, Pharmacies and dealers
Role Responsibilities Hospital Administrator/CEO Overssees overall hospital operations. Sets budget and strategic direction. Ensures compliance with regulations. Chief Medical Officer (CMO) Leads medical staff and oversees patient care quality. Implements quality control measures. Makes treatment decisions in collaborations with physicians. Department Heads Manage specific departments (e.g. Surgery, Nursing, Pharmacy). Oversee inventory levels and resource allocation within their departments. Place timely orders for medications, equipment and supplies. Physicians Diagnose and treat patients. Prescribe medications based on expertise and drug interactions. Nurses Provide bedside care to patients. Administer medications according to prescribed dosages. Monitor patient condition for adverse reactions. Table: Bridge the roles and responsibilities for patient care and improved healthcare conditions
Patient Care: Ensures timely access to essential medications, medical equipment, and supplies. Delays or shortages can directly impact treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes. Cost Optimization: Streamlines processes, potentially reduces overall healthcare costs. Efficient logistics and inventory management can lead to significant cost savings. Improved Efficiency: Enables healthcare providers to focus on patient care rather than logistical challenges. Well-coordinated supply chains ensure smooth operations and better resource utilization. Resilience: Adapts to changing circumstances and unexpected disruptions. A robust supply chain can mitigate the impact of emergencies and shortages. Innovation: Facilitates the timely delivery of new technologies and treatments to patients. Efficient distribution networks support the adoption of advancements in healthcare. Visual Options: Consider using an image depicting a connected network of hospitals, pharmacies, and suppliers. minimizes waste, and Figure: Healthcare supply chain
Figure: An example configuration of healthcare supply chain network Siadati, S., Tarokh, M. J., & Noorossana, R. (2017). Fuzzy Risk Analysis Using Fuzzy Sampling Method: Case Study of Design a Reconfigurable Multi-Agent Supply Chain Network under Risk: Case Study of Design a Reconfigurable Multi-Agent Supply Chain Network under Risk. Industrial Engineering & Management Systems, 16(4), 455-464.
Key Outcomes Understanding the key roles within the healthcare supply chain is vital for ensuring a well-functioning system that ultimately delivers optimal patient care. From hospital administrators setting strategic direction to nurses administering medications, each player contributes significantly. Hospitals rely on department heads to manage resource allocation, physicians to diagnose and prescribe, and pharmacists to dispense medications accurately. Pharmaceutical sales representatives and medical equipment dealers play crucial roles in introducing new technologies and ensuring equipment functionality. Appreciating the interconnectedness of these sectors reveals the intricate dance of communication and collaboration that keeps the supply chain moving. Each role, from hospitals to pharmacies and dealers, forms a vital link in the chain, ensuring the timely flow of medications and supplies that ultimately empowers healthcare professionals to deliver quality care to patients.






















