Explore Force and Motion Vocabulary for Week 2
Dive into the vocabulary of force and motion for Week 2, covering balanced and unbalanced forces, gravity, inertia, friction, Newton's laws, and more. Understand the impact of forces on objects and how they affect motion.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FORCE AND MOTION Vocabulary Week 2 You will need 11 cards.
S8P3b. Demonstrate the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object in terms of gravity, inertia, and friction.
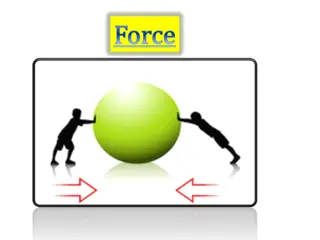
FORCE Using energy to do work. Examples: Pushing or pulling https://www.yout ube.com/watch?v =_LdcxCdB-s8
BALANCED FORCE Equal forces acting on one object in opposite directions are called balanced forces. Each force is balanced by the other. Balanced forces acting on an object do not change the objects motion.
UNBALANCED FORCE Whenever there is a net force acting on an object, the forces are unbalanced. Unbalanced forces can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. Unbalanced forces acting on an object result in a net force and cause a change in the object s motion. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEJOybRxclk
INERTIA This is the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion. An object at rest stays at rest unless a force is enacted upon it. Newton s First law of motion is also called the law of inertia. Inertia depends on Mass. Some objects have more inertia than others. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ncn2LH9yYms
GRAVITY (GRAVITATIONAL FORCE) This is a force that pulls objects toward eachother. Isaac Newton concluded that a force acts to pull objects straight down toward the center of the earth. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ljRlB6TuMOU
NEWTON (UNIT) The strength of force is the unit of measurement named for Isaac Newton. It is equal to the amount of net force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared. Example: You exert approximately 1 Newton of force when you lift a small lemon.
FRICTION The force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other is called friction. Smooth surfaces create less friction than rough surfaces. The strength of the force of friction depends on two factors: how hard the surfaces push together and the types of surface involved.
SLIDING FRICTION Occurs when 2 surfaces slide over each other.
ROLLING FRICTION Occurs when an object rolls across a surface.
FLUID FRICTION Occurs when a solid object moves through a fluid.
STATIC FRICTION Friction between two or more solid objects that are not moving relative to each other. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C7NPD9W0kro
QUIZLET https://quizlet.com/_366zua
ON-LEVEL: TOTD How would you explain an objects movement across a smooth surface versus its movement across a rough surface?
ADVANCED: SCIENCE IS H.O.T. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4yyb_RNJWUM How could you compare/contrast the theories of Newton and Einstein?